Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Ficker Stealer is a malware that steals passwords, files, credit card details, and other types of sensitive information on Windows systems. It is most often distributed via phishing emails and can perform keylogging, process injection, and browser tracking.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
10 August, 2020
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
10 August, 2020
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 434
434
 0
0

 2292
2292
 0
0

 4444
4444
 0
0
Ficker Stealer is a type of malicious software written in the Rust programming language, which is openly sold on the internet via the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model. Its primary function is to extract confidential data from computers running Windows operating systems. Due to its modular design, the malware can be easily configured to steal specific forms of data. For instance, some of the common types of information targeted by it include passwords, Windows Credential Manager data, crypto wallets, credit card details, and email and chat content.
The malware has been active since 2020 and continues to receive full support from its developers to this day. In fact, it possesses the capability of self-updating, allowing it to automatically get fresh updates from the C2 server. Although the original creators of Ficker Stealer remain unidentified, it is likely that they hail from one of the ex-USSR countries.
Ficker Stealer sets itself apart from other stealers such as RedLine or Arkei by utilizing Rust, a programming language that offers improved performance and safety features compared to its predecessors such as C++. Rust's efficiency helps criminals develop more complex malicious programs, while its built-in safety mechanisms prevent various vulnerabilities within the code. As a result, identifying and combating Rust-based malware can be a tall order for researchers.
Ficker Stealer is engineered to illicitly extract confidential data from a victim's computing system. Once executed, it deploys an array of sophisticated techniques to collect sensitive information, including:
Additionally, to safeguard the data transferred to its C2 from being intercepted, Ficker Stealer utilizes encryption. What’s more, it reports back to the attackers following each successful operation, leaving no records or logs on the target computer. Subsequently, tracking Ficker's activities can be an intricate task. It also operates without the need for any extra DLLs to be downloaded or loaded at runtime, which enhances its stealth and efficiency.
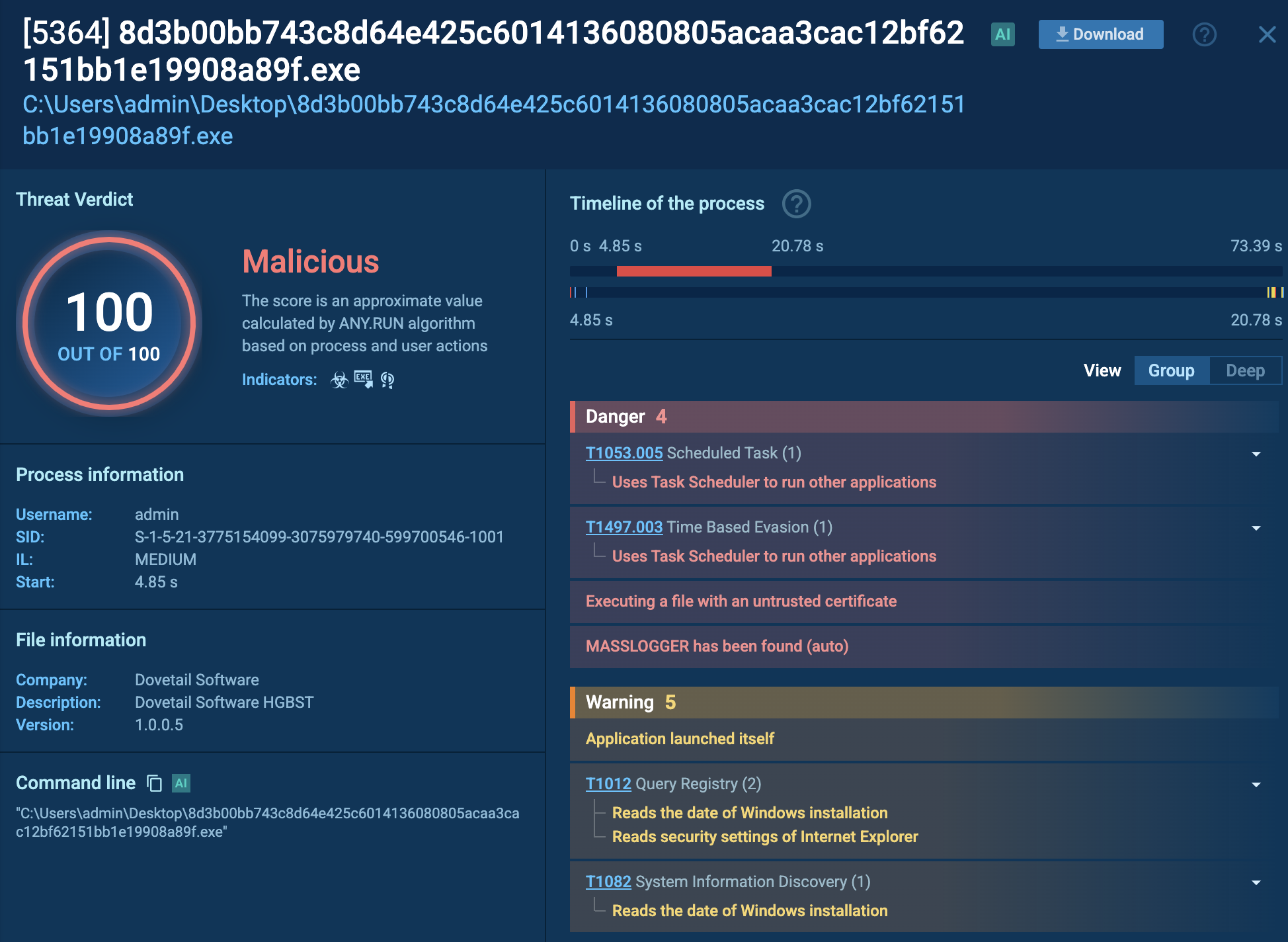
The malicious behavior of Ficker Stealer can be easily uncovered by uploading it to the ANY.RUN sandbox. Here is a sample of this malware on the platform.
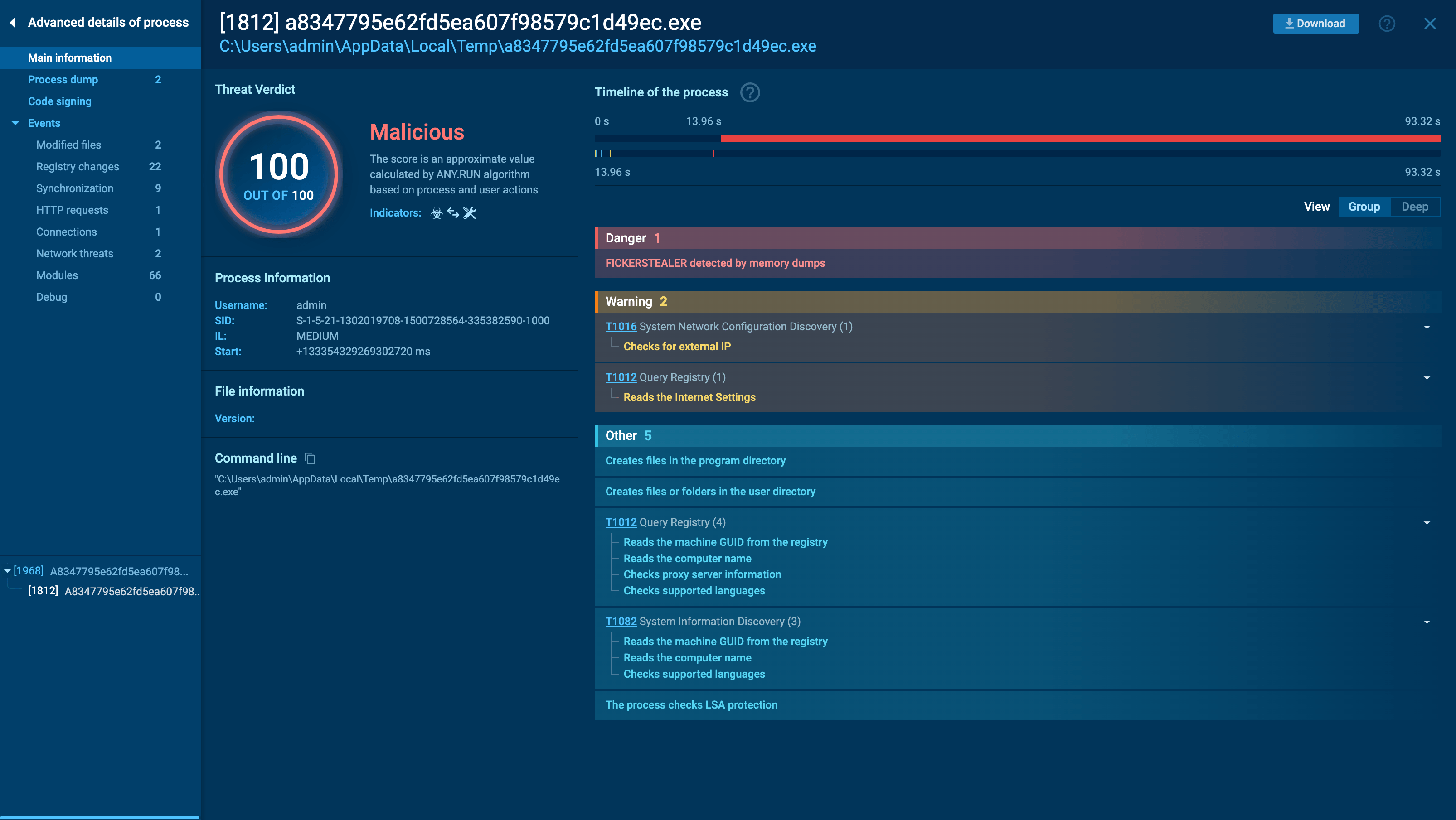 Ficker Stelaler in ANY.RUN
Ficker Stelaler in ANY.RUN
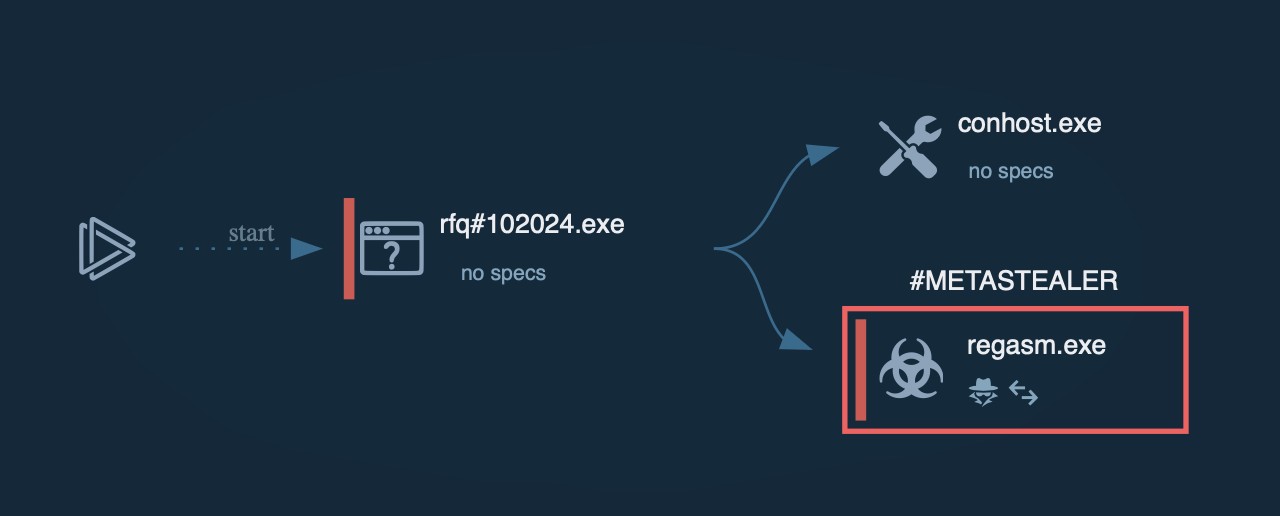
Ficker is a typical representative of the stealer malware family. It creates as little noise as possible in the infected system. The main idea: make its way into the system, start execution, steal information and credentials and try to stay invisible without alerting security solutions about the threat for as long as possible.
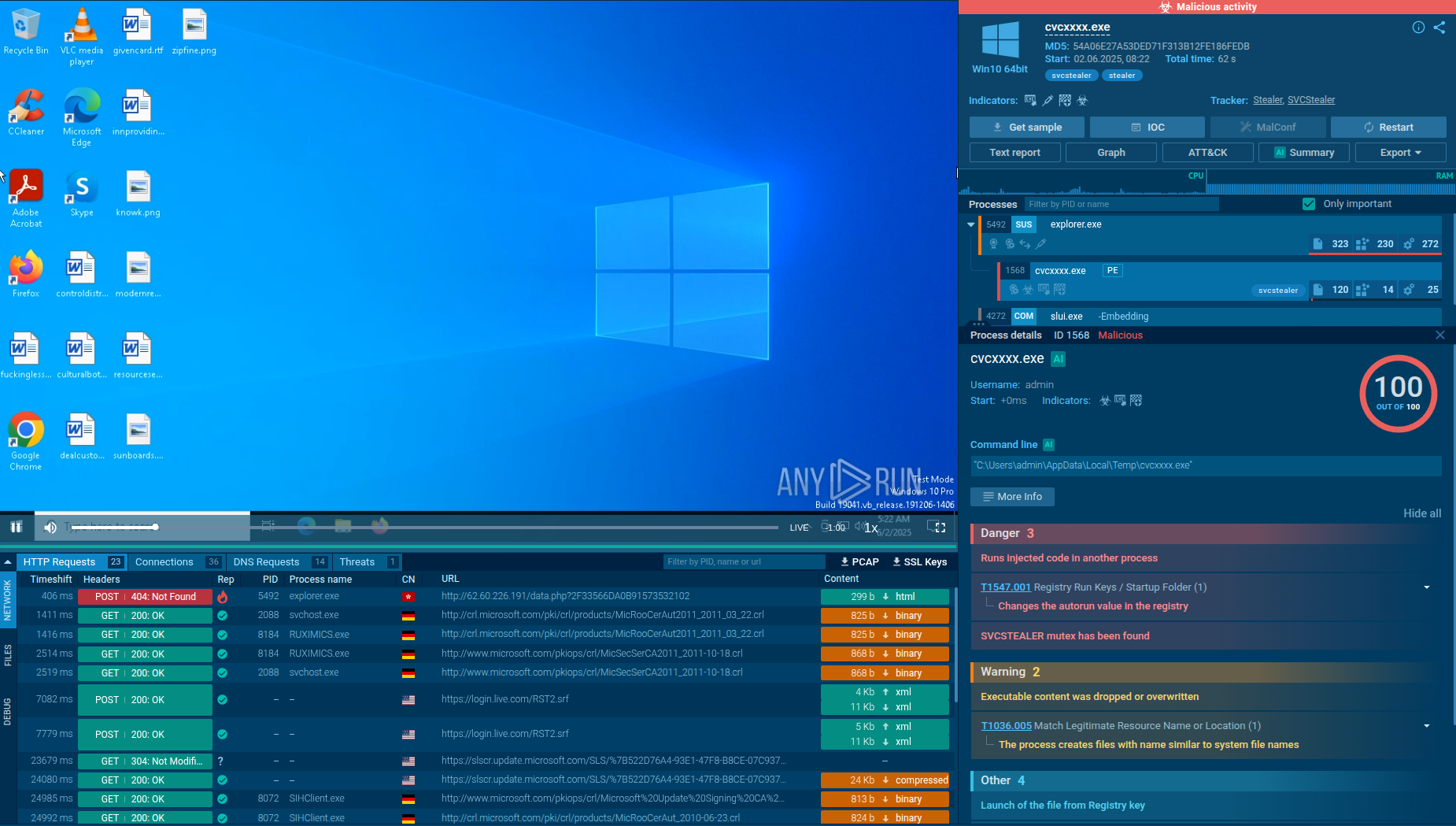
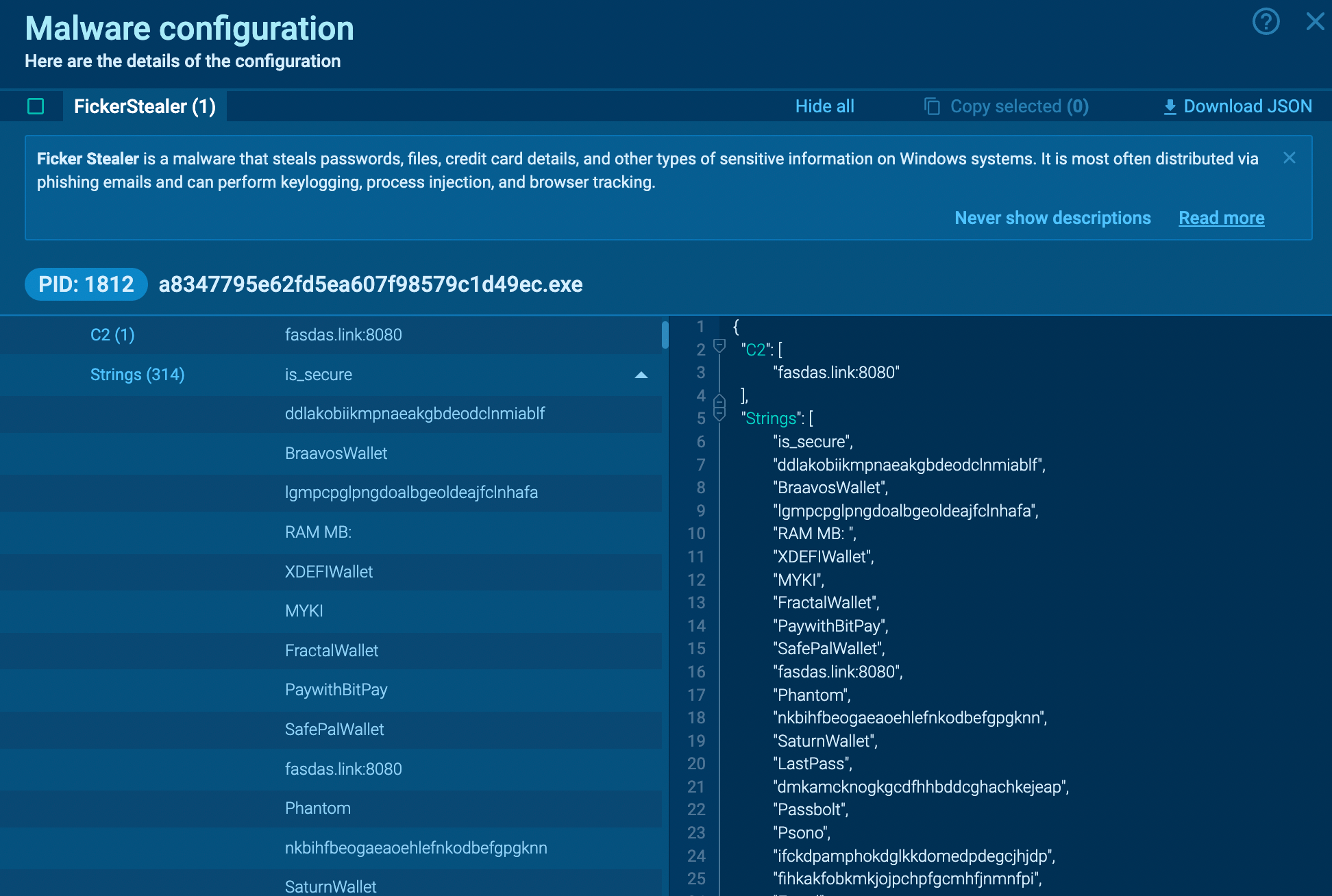 Ficker Stelaler configuration extracted in ANY.RUN
Ficker Stelaler configuration extracted in ANY.RUN
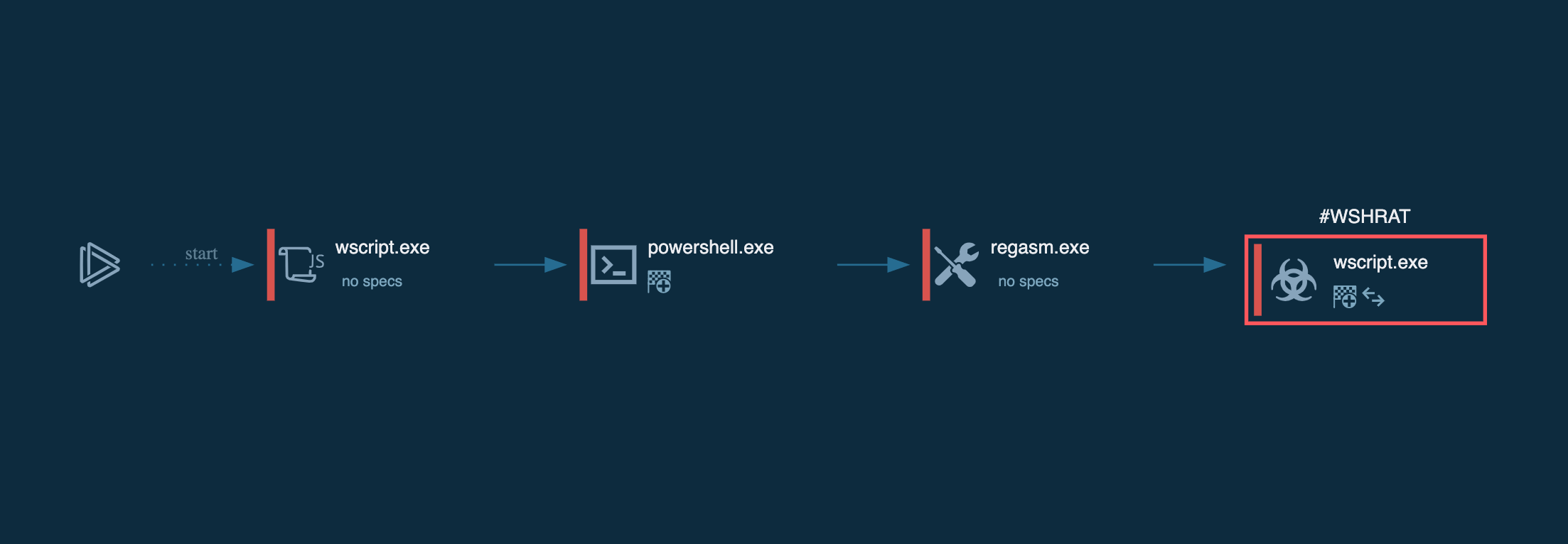
Like other malware families, this particular family may alter execution flows, but it will do so in a way that remains plain and simple. Stealers usually attempt to be less visible, so you may notice reduced activity during the execution of the Ficker, compared to what you might typically expect. After all the information is stolen, the malware may halt its execution and delete itself from the infected system. However, this behavior can vary across different versions and settings.
Ficker Stealer can end up on a victim’s PC in several ways:
Ficker Stealer is a serious threat to MS Windows users. To protect your system from this malware, you must exercise caution when accessing your email inbox. If you come across an email from an unfamiliar sender or if its contents appear suspicious, it is in your best interest to refrain from opening it or clicking on any links.
Instead, you can analyze these samples in the ANY.RUN malware analysis sandbox to promptly discover whether your file or URL is malicious or not. The platform lets you interact with malware in a safe VM environment in real time. Thanks to ANY.RUN, you can get an exhaustive overview of any threat’s behavior and gain insight into its IOCs, TTPs, and other crucial details.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!