Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


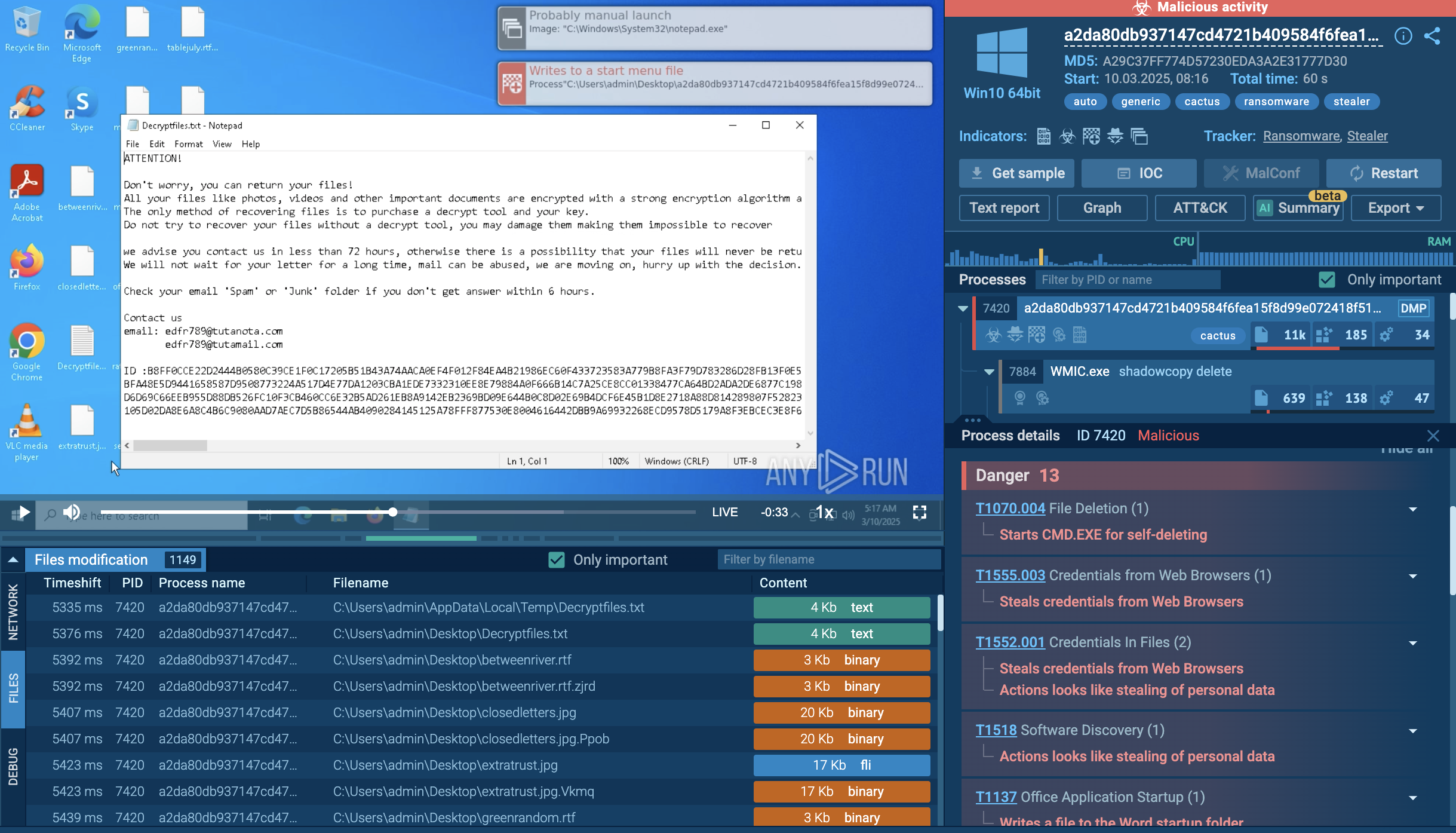
DoubleTrouble is a new-generation Android malware designed to quietly infiltrate mobile devices, harvest sensitive data, hijack financial operations, and maintain long-term persistence. Unlike commodity Android trojans, it blends advanced evasion, dual-stage infection, and dynamic payload updates, making it a rising mobile threat for both consumers and organizations.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2025
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2025
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
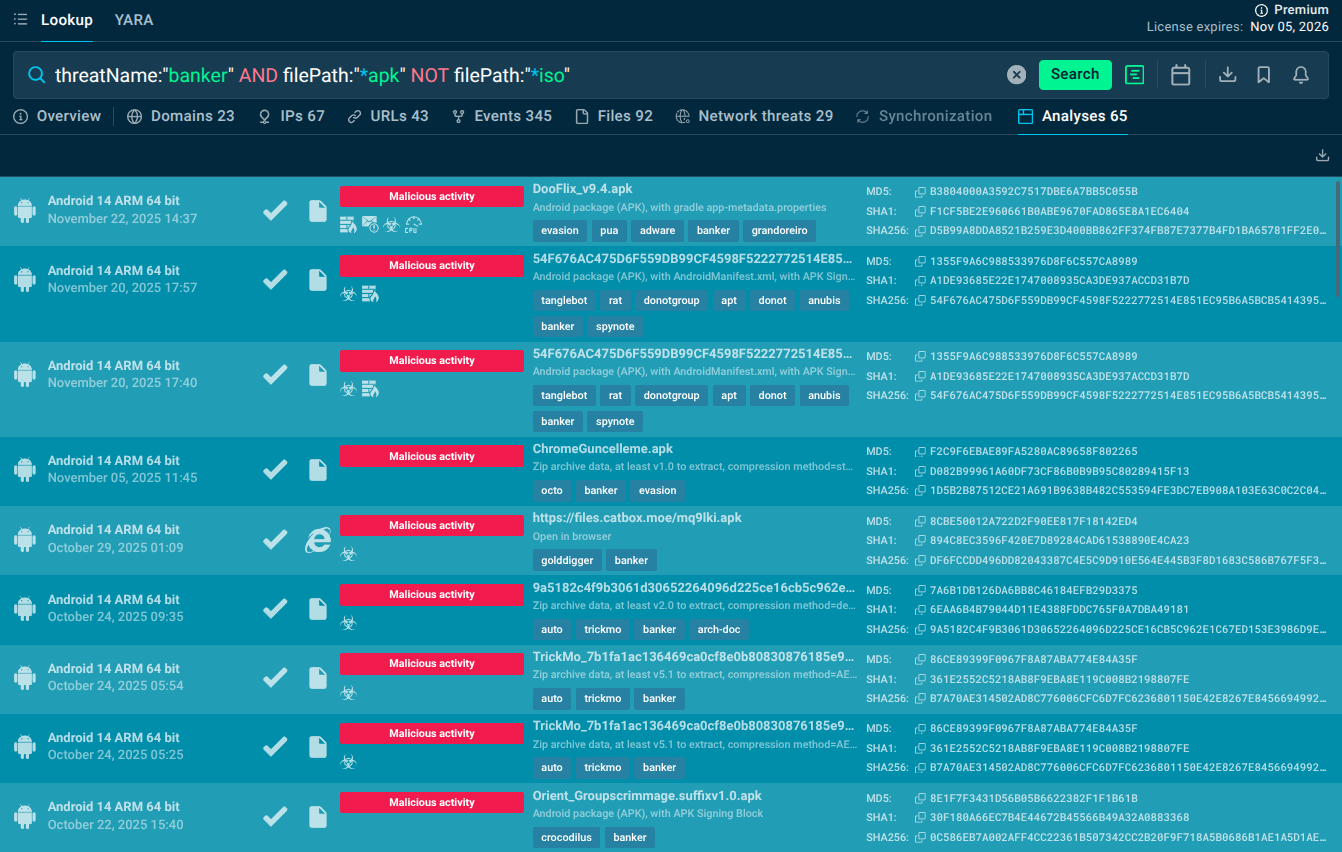 Mobile banker sample analyses found via TI Lookup
Mobile banker sample analyses found via TI Lookup
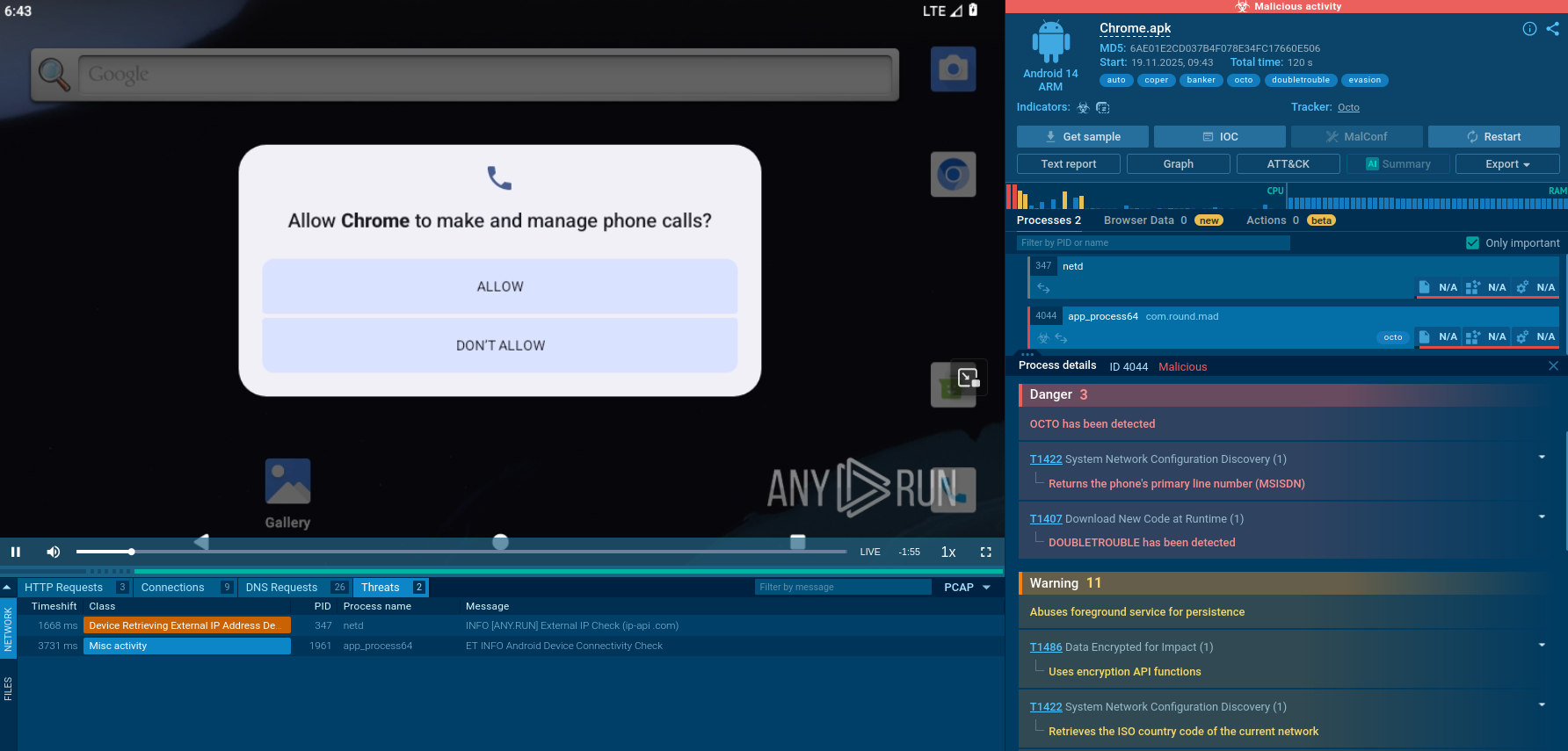 DoubleTrouble live sample detonated in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox
DoubleTrouble live sample detonated in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox
DoubleTrouble is an evolving Android malware family built around modular components. It typically arrives disguised as a legitimate app, uses multiple layers of obfuscation, and deploys two coordinated modules (“double trouble”) that work together to:
Its architecture allows operators to update capabilities in real time. Some variants behave like banking trojans; others serve as full-fledged spyware; more advanced strains use remote access tooling to turn a smartphone into a controllable endpoint.
What started as a phishing-driven menace impersonating European banks has morphed into a Discord-fueled nightmare, hosting malicious APKs that blend seamlessly into gaming and community chats. At its core, DoubleTrouble hijacks Android's Accessibility Services, granting it god-like control over the device without raising immediate alarms. This permission, often requested innocently for "app enhancements," lets the malware spy, steal, and sabotage in real-time.
Its sophisticated command-and-control architecture is what makes DoubleTrouble particularly dangerous. The malware can receive and execute dozens of commands from its C2 server, including simulating touch gestures, managing screen captures, injecting HTML overlays, blocking specific applications, and manipulating system settings. The malware also employs advanced anti-analysis techniques, uses dynamic overlays, and implements real-time visual capture to evade detection and maximize data exfiltration.
The malware is commonly distributed via rogue app stores, phishing campaigns, and malicious SMS messages. In 2025, several campaigns showed DoubleTrouble integrating MFA interception, credential theft, and automated transaction manipulation — expanding its role from pure data theft to active financial fraud.
DoubleTrouble primarily targets Android users throughout Europe, with campaigns specifically focusing on customers of major European banking institutions. The victimology extends beyond individual consumers to include:
The malware's shift to Discord-based distribution broadens its potential victim pool to include younger, tech-savvy users who frequent social media platforms and gaming communities.
The banker works through a multi-stage infection and operation process.
Initial Installation: The malware arrives disguised as a legitimate application, using the Google Play icon to establish trust. During installation, the actual malicious payload remains hidden within the app's Resources/raw directory, employing a session-based installation method to bypass permission restrictions.
Permission Acquisition: Upon first launch, the application prompts users to enable Android Accessibility Services: a powerful permission that grants extensive control over device functions. The request appears legitimate due to the convincing interface and trusted icon, leading many users to grant access without suspicion.
C2 Communication Establishment: Once activated, DoubleTrouble establishes communication with its command-and-control server. The malware receives instructions through a number of commands that enable remote operators to control infected devices.
Data Collection Infrastructure: The trojan implements multiple data collection mechanisms operating simultaneously:
Adaptive Evasion: DoubleTrouble employs sophisticated obfuscation techniques, using random two-word method names to hinder reverse engineering. The malware includes anti-analysis capabilities (start_anti and stop_anti commands) that scan UI elements for threats and can detect sandbox environments.
Exfiltration Process: Captured data is packaged into JSON payloads and transmitted to the C2 server. Screen captures are base64-encoded within these payloads, while keystroke logs and application lists are stored in XML files before exfiltration. This systematic approach ensures comprehensive data theft while maintaining stealth.
Persistent Operation: The malware maintains persistence through its accessibility service permissions, which are difficult for users to revoke once granted. It can block security applications that might detect and remove it, creating a self-protecting ecosystem that ensures continued operation.
ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox provides isolated, instrumented environments where security researchers and analysts can safely execute suspicious files without risking production systems.
View a DoubleTrouble sample analysis
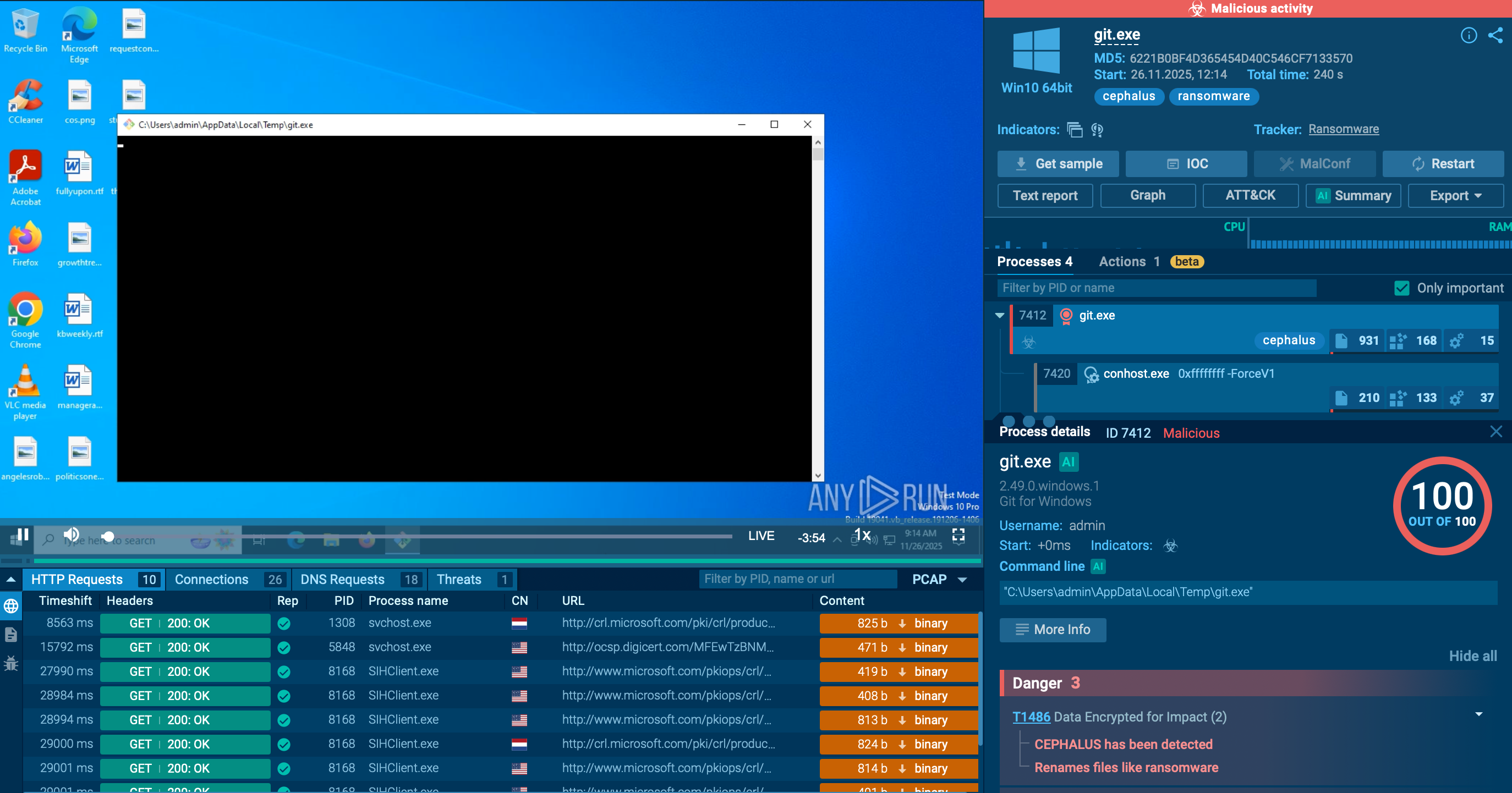
 DoubleTrouble Android banker detonated in the Interactive Sandbox
DoubleTrouble Android banker detonated in the Interactive Sandbox
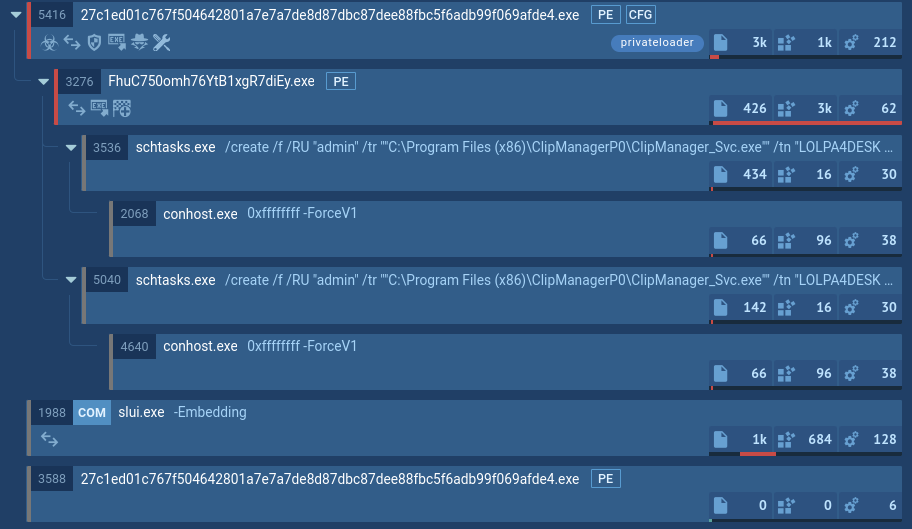
In the analyzed sample, the initial reconnaissance and preparation phase is clearly visible, including telemetry collection and establishing persistence on the device. Let’s view the process tree revealed during the sandbox analysis:
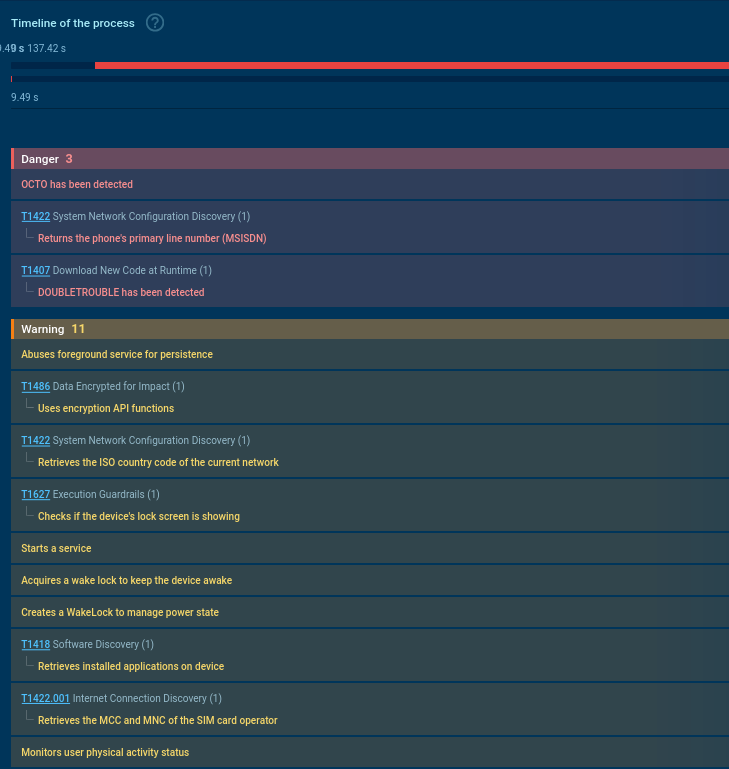 DoubleTrouble's processes
DoubleTrouble's processes
Immediately after launch, the application creates a service and moves it into what is known as foreground mode. This is a special type of background service in Android: the system treats it as “visible” to the user (it must display a persistent notification), so it assigns the service maximum priority and almost never terminates it, even under memory pressure. Power-saving restrictions also barely apply to such services. As a result, the malware achieves a very stable presence on the device.
At the same time, the application acquires a wake lock — a mechanism that prevents the phone from going into sleep mode. This allows the device to remain active for hours even when the screen is off.
Next, the telemetry collection begins. The malware extracts the phone number, the ISO code of the current network’s country, and the SIM card operator’s MCC and MNC. It then performs an HTTP GET request to the public ip-api service — a way to determine the victim’s geolocation based on their external IP.
The application checks whether the lock screen is currently displayed, monitors the user’s physical activity via sensors, tracks battery level and charging status, and subscribes to airplane mode change events. All of this helps the malware determine whether the device is actively in use at the moment and whether heavy operations can be executed without being noticed.
DoubleTrouble enumerates all installed applications, reads from and writes to SharedPreferences, and accesses protected system settings. It also dynamically registers a broadcast receiver and uses reflection. Calls to standard Android cryptographic APIs are visible as well.
The malware patiently establishes persistence, gathers context about the victim and the environment, bypasses system restrictions, and only then decides whether to activate its payload. Such cautious, multi-stage logic is typical of the new generation of mobile threats.
Once installed, DoubleTrouble is capable of:
For organizations, DoubleTrouble poses risks far beyond individual device compromise:
Mobile malware is increasingly becoming a preferred entry point for attackers because corporate mobile security is still underfunded and under-monitored compared to workstation security.
Threat intelligence platforms enable teams to: -Track DoubleTrouble campaigns -Map IOCs to regions, industries, and TTPs -Block malicious IPs, hashes, and domains -Enrich SIEM/SOAR alerts with mobile-specific context
Sandbox analysis + threat intelligence gives defenders both behavioral and contextual visibility.
Use Threat Intelligence Lookup to check suspicious artifacts and view recent analysis sessions run by a community of 15,000 SOC teams.
SHA256:"657a08262d88b16624e99ddf95289537f264eb38e79de387643abc9b63ab124a".
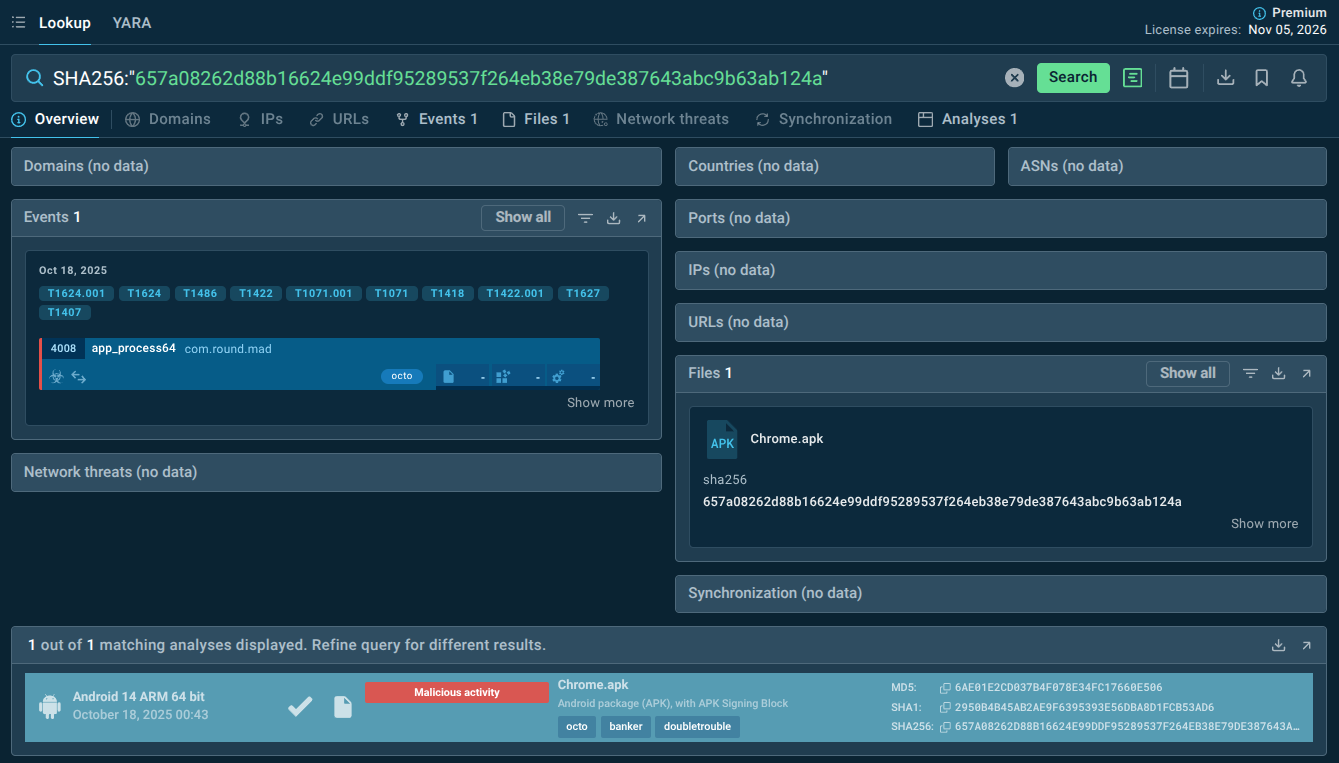 File hash detected as DoubleTrouble indicator via TI Lookup
File hash detected as DoubleTrouble indicator via TI Lookup
DoubleTrouble is a fast-evolving Android threat that weaponizes accessibility abuse, overlay attacks, and modular payloads to steal credentials, bypass MFA, and enable financial fraud. For businesses relying on BYOD and remote work, it introduces significant risks — from account takeover to full corporate compromise.
To stay ahead, organizations need a combination of user education, MDM controls, mobile threat intelligence, and dynamic malware analysis. The earlier you identify malicious APKs in your environment, the faster you can break an attack chain and prevent financial or reputational damage.
Trial TI Lookup to start gathering actionable threat intelligence on mobile malware: just sign up to ANY.RUN.