Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


DarkVision RAT is a low-cost, modular Remote Access Trojan that gives attackers remote control of infected Windows hosts. Initially observed around 2020 and sold in underground marketplaces, DarkVision has become notable for its full feature set (keylogging, screen capture, file theft, remote command execution and plugin support) and for being distributed via multi-stage loaders in recent campaigns.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 1059
1059
 0
0

 623
623
 0
0

 3021
3021
 0
0
DarkVision RAT is a highly customizable Remote Access Trojan that emerged in 2020, gaining notoriety for its affordability and extensive feature set. Priced as low as $60 on platforms like Hack Forums, it has become a popular tool among cybercriminals, including those with minimal technical skills. Written in C/C++ and assembly, DarkVision RAT poses a significant threat to individuals and organizations worldwide due to its stealthy capabilities and sophisticated attack chain.
Its modular design makes it easy to adapt for credential theft, surveillance, lateral maneuvers, and persistence. Recent technical analyses show it is often delivered via multi-stage loaders (Donut shellcode / PureCrypter and implements a bespoke network protocol to communicate with command-and-control (C2) servers. The RAT also uses a variety of evasion and privilege-escalation techniques (DLL hijacking, process injection, autorun/backdoor patterns).
The malware targets primarily Windows endpoints: home users, SMEs and enterprise workstations.
Its distribution profile — opportunistic criminal operators (ransomware / data theft actors, commodity cybercriminals) and less skilled attackers who buy prebuilt RAT kits.
Sectors observed in campaigns: general business environments where user workstations have internet access and credentials that can unlock broader access (finance, professional services, manufacturing have all been impacted in commodity RAT campaigns). The availability and low price point of DarkVision make it attractive to a wide array of attackers.
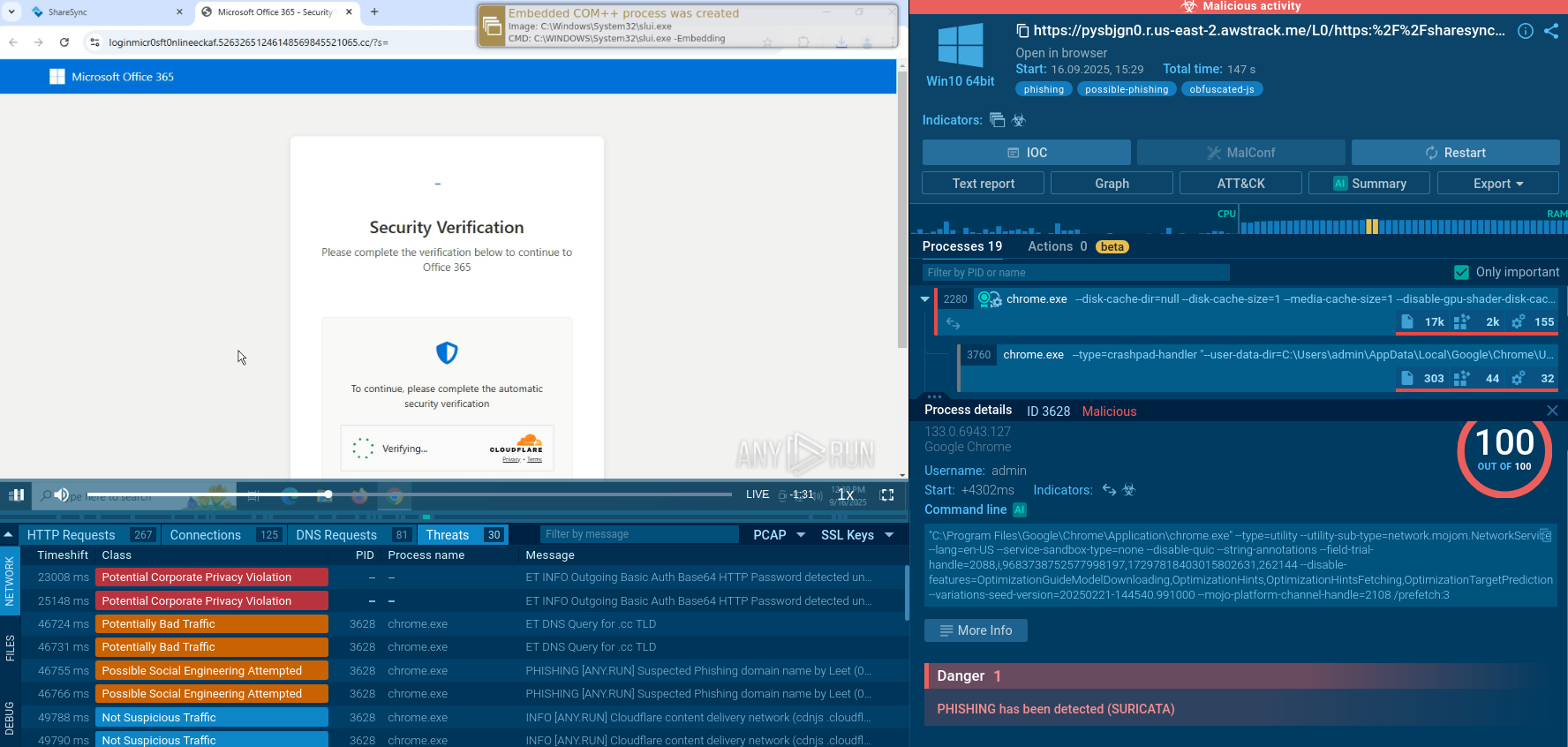
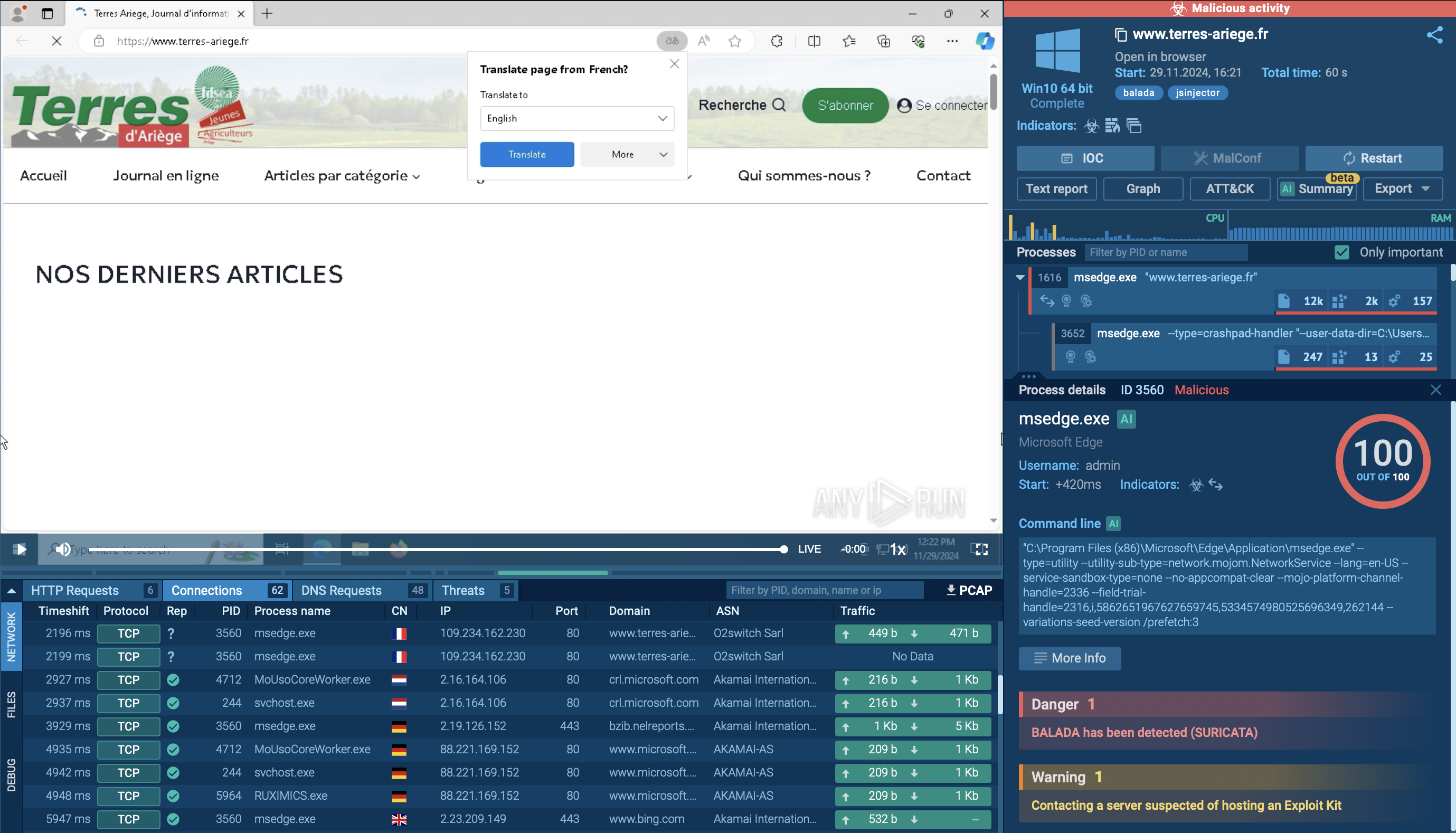
ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox provides fresh samples of DarkVision recently detonated and thoroughly studied by our half-a-million community of threat analysts.
Let’s explore a sample to see the main stages of an attack chain on a live example.
 DarkVision sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
DarkVision sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
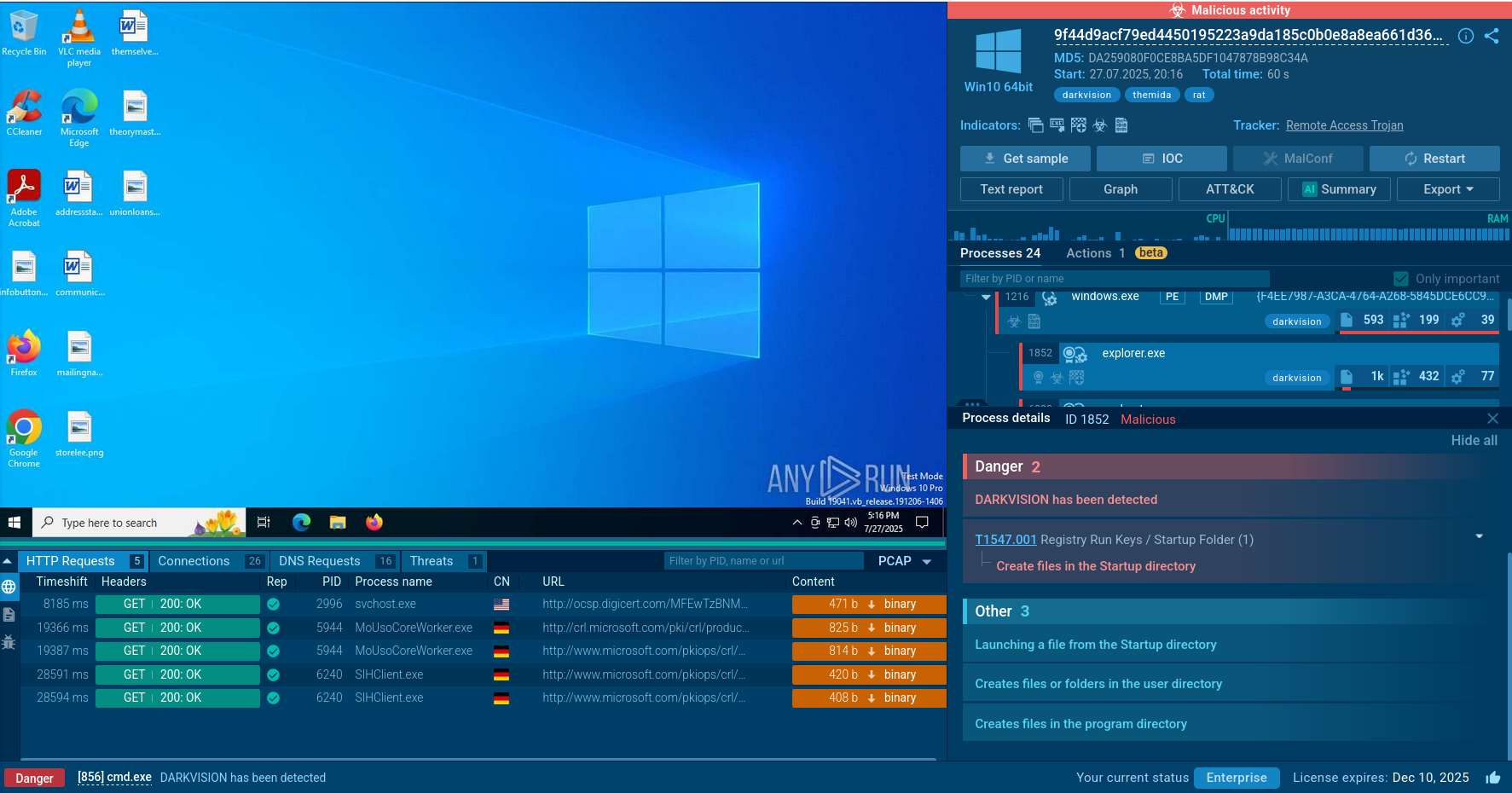
 DarkVision establishes itself in a system directory
DarkVision establishes itself in a system directory
This location and filename are deliberately chosen to mimic a legitimate Windows executable, making it harder for the user or antivirus software to recognize it as malicious.
It then adds three entries, each identified by a hardcoded GUID (Globally Unique Identifier). These values store Current System Time in a FILETIME structure.
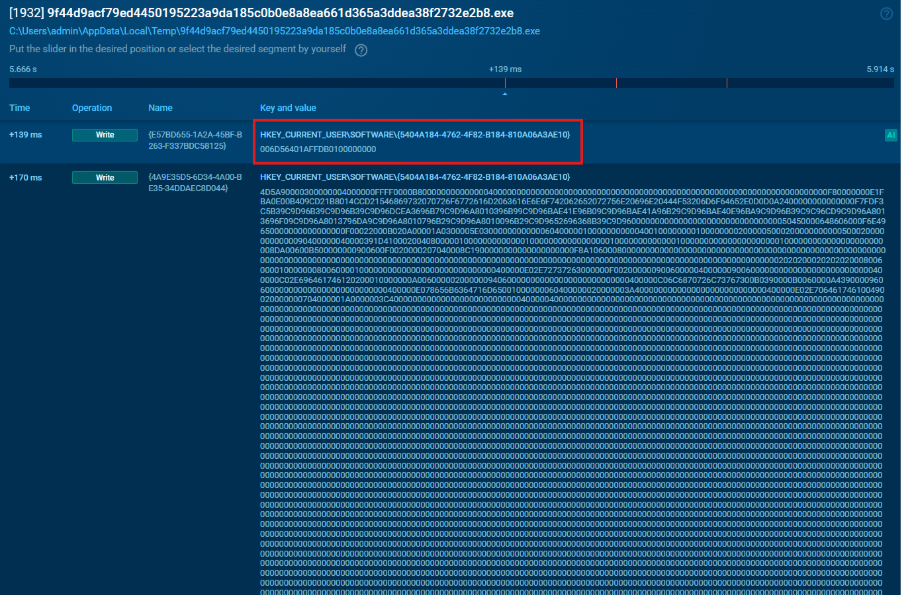 DarkVision registry activity
DarkVision registry activity
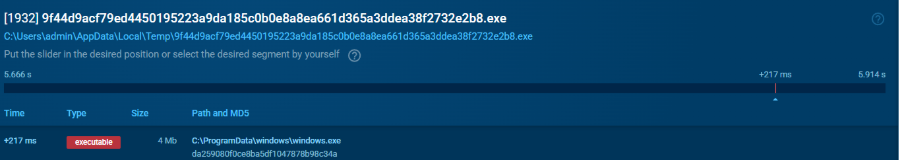
RAT File Content – a large block of hexadecimal data representing the malicious binary’s content.
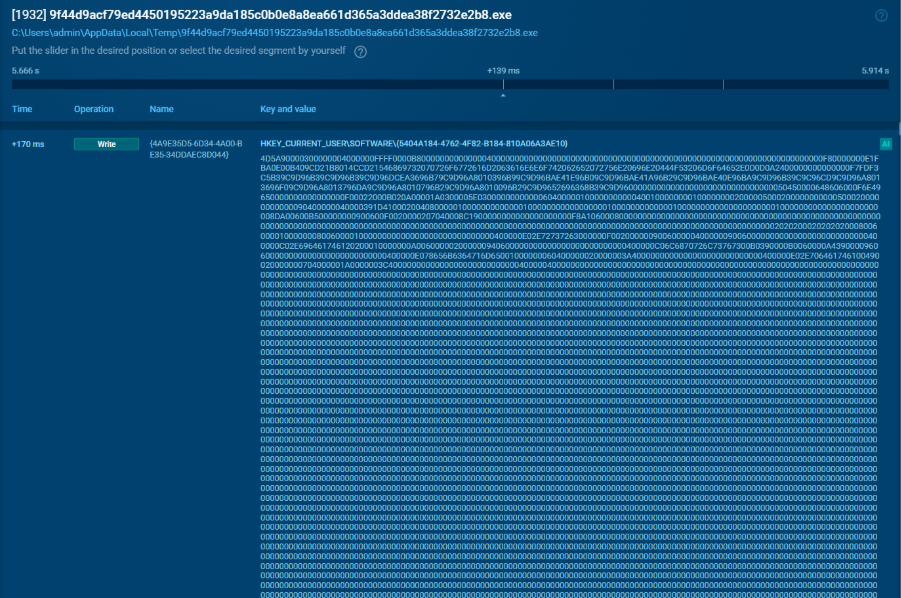 Binary file viewable in ANY.RUN Sandbox
Binary file viewable in ANY.RUN Sandbox
RAT File Path – the full filesystem path to the RAT executable.
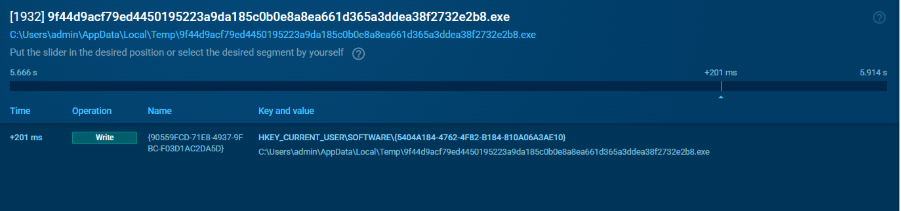 Another DarkVision registry modification for establishing in the system
Another DarkVision registry modification for establishing in the system
These registry entries allow the malware to preserve important execution details and can be used for reloading the payload or tracking the system’s infection state.
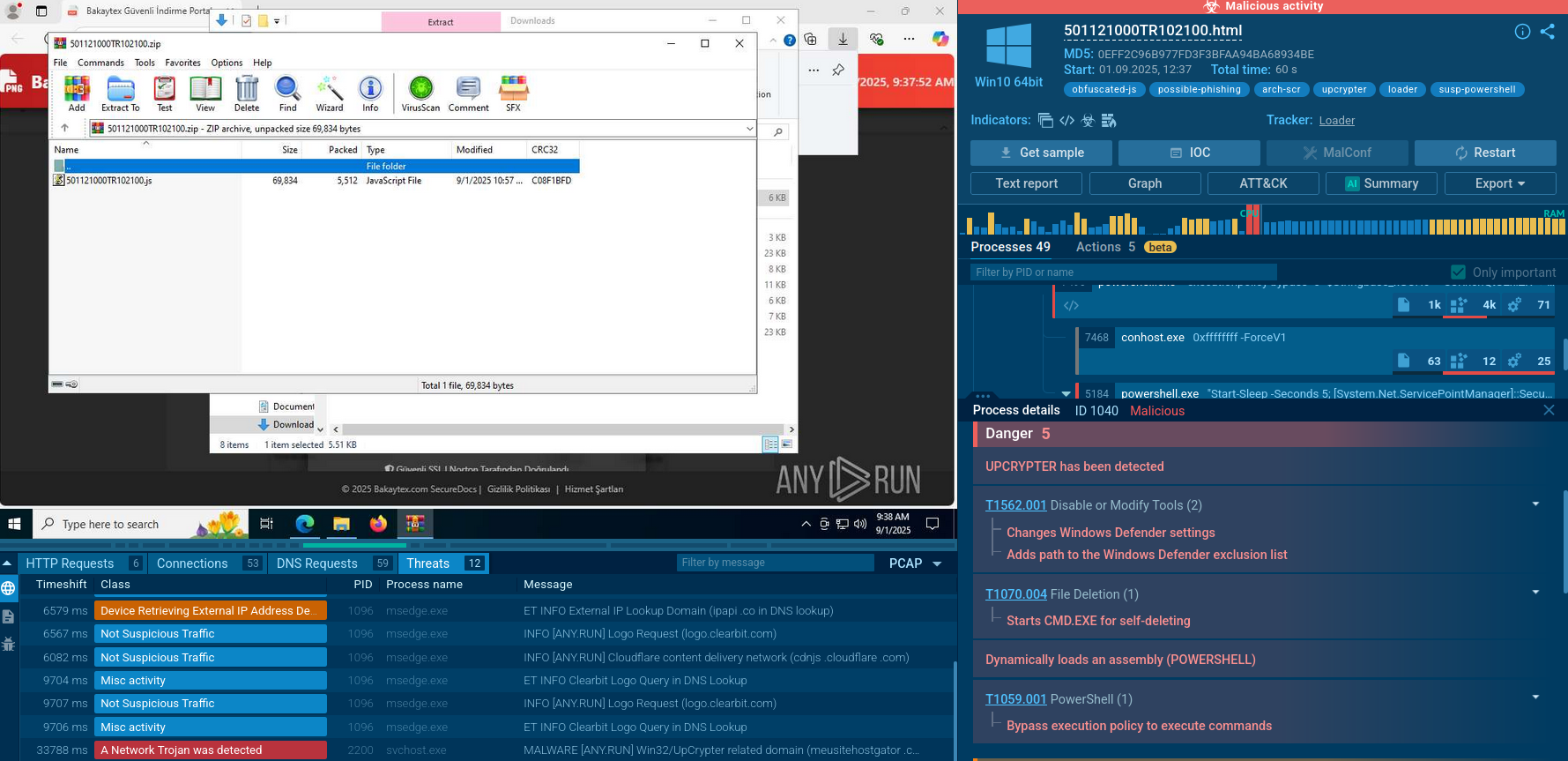
To ensure it runs automatically after the system restarts, DarkVision RAT drops a batch script (.bat) file.
Script content example:
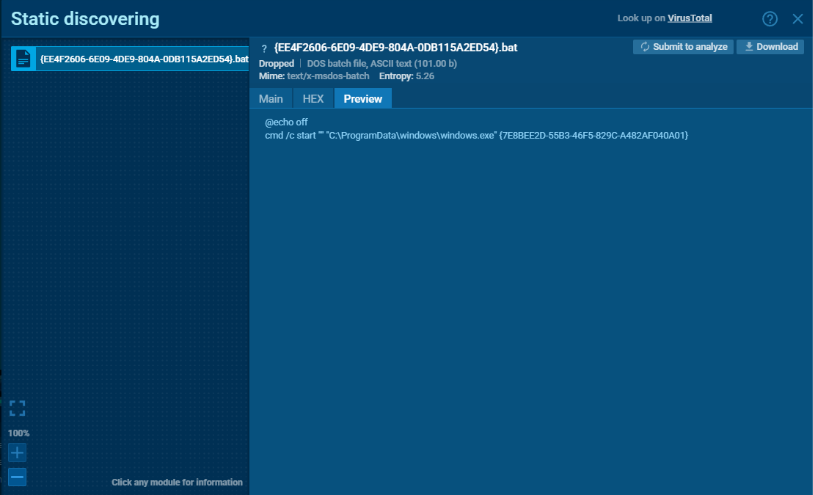 Bat file static analysis in ANY.RUN Sandbox
Bat file static analysis in ANY.RUN Sandbox
The script is then linked via a .lnk shortcut placed in the user’s startup folder
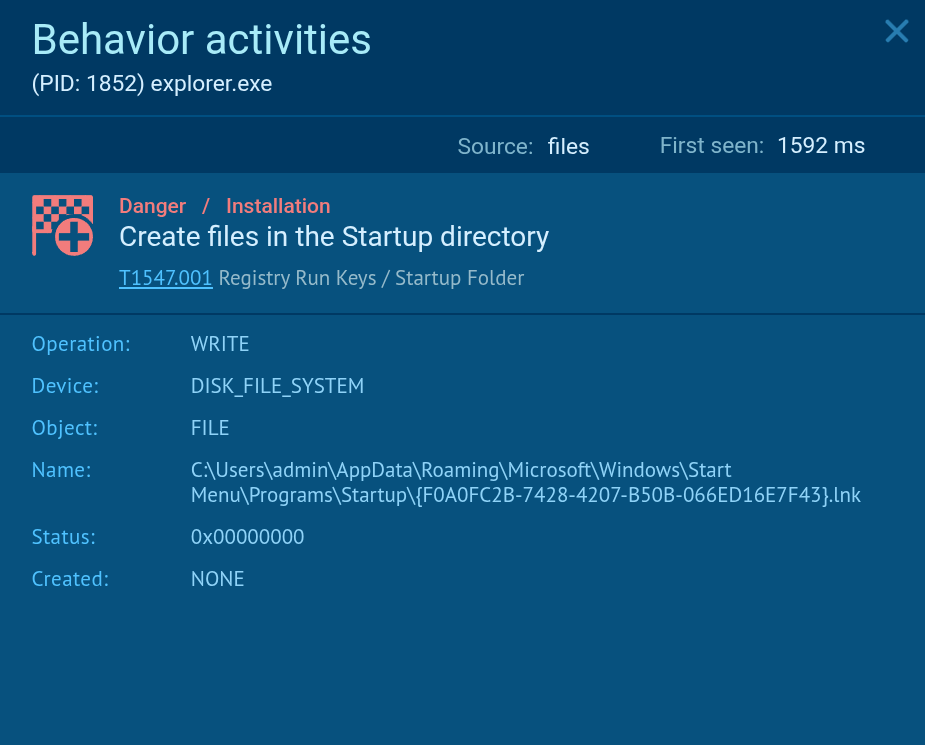 DarkVision persistence mechanism
DarkVision persistence mechanism
This guarantees execution every time the system boots.
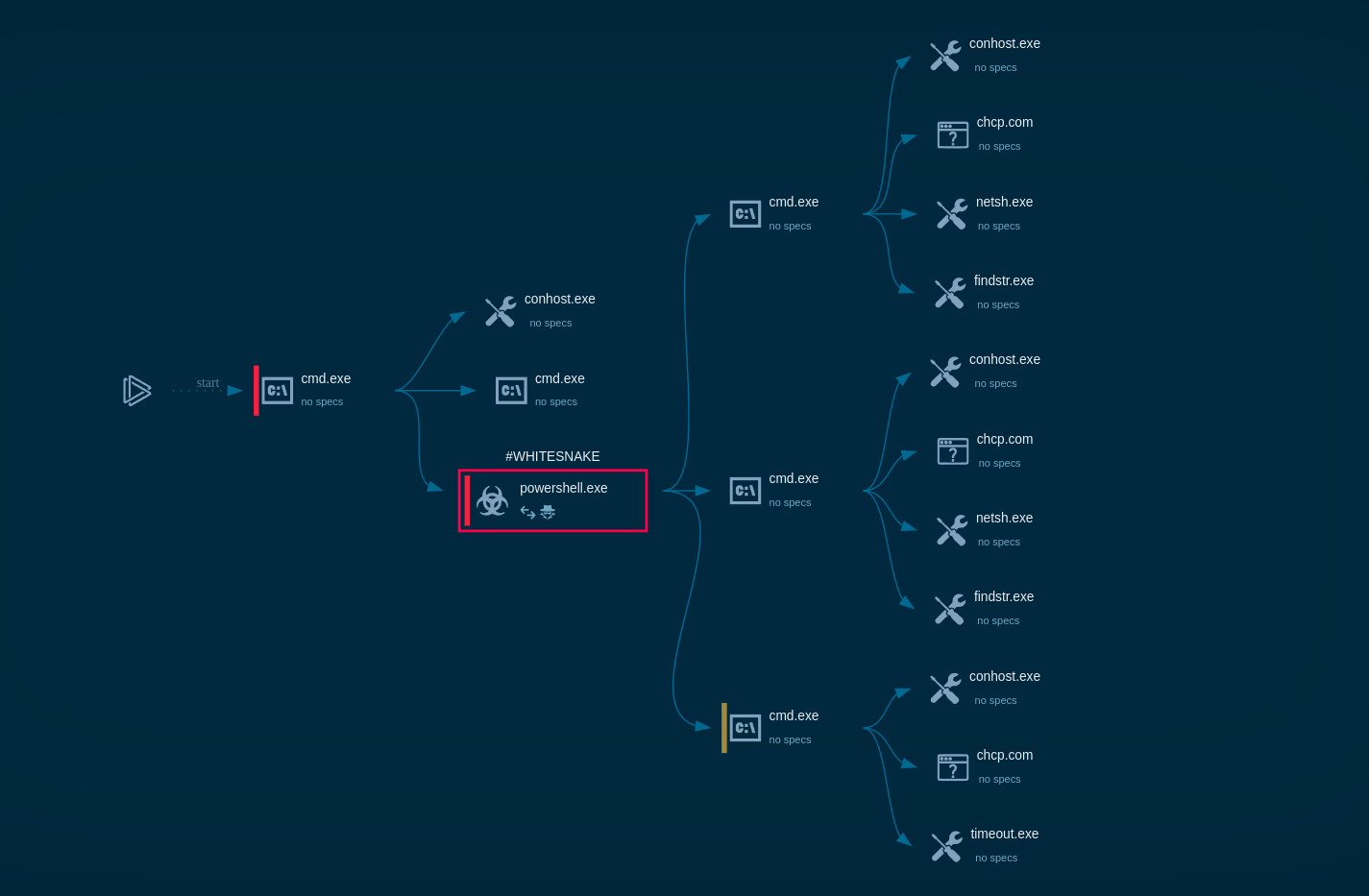
The malware injects its code into multiple legitimate Windows processes to avoid detection and run with elevated privileges. In this observed case, the target processes included explorer.exe, svchost.exe, сmd.exe
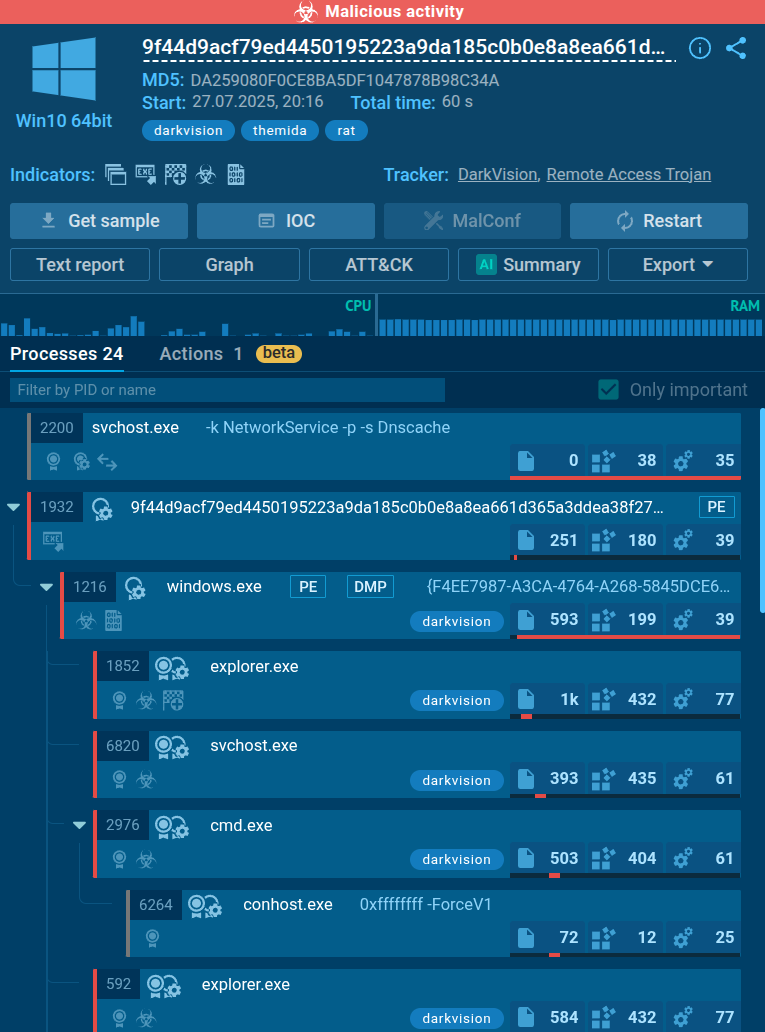 DarkVision injecting system Windows processes
DarkVision injecting system Windows processes
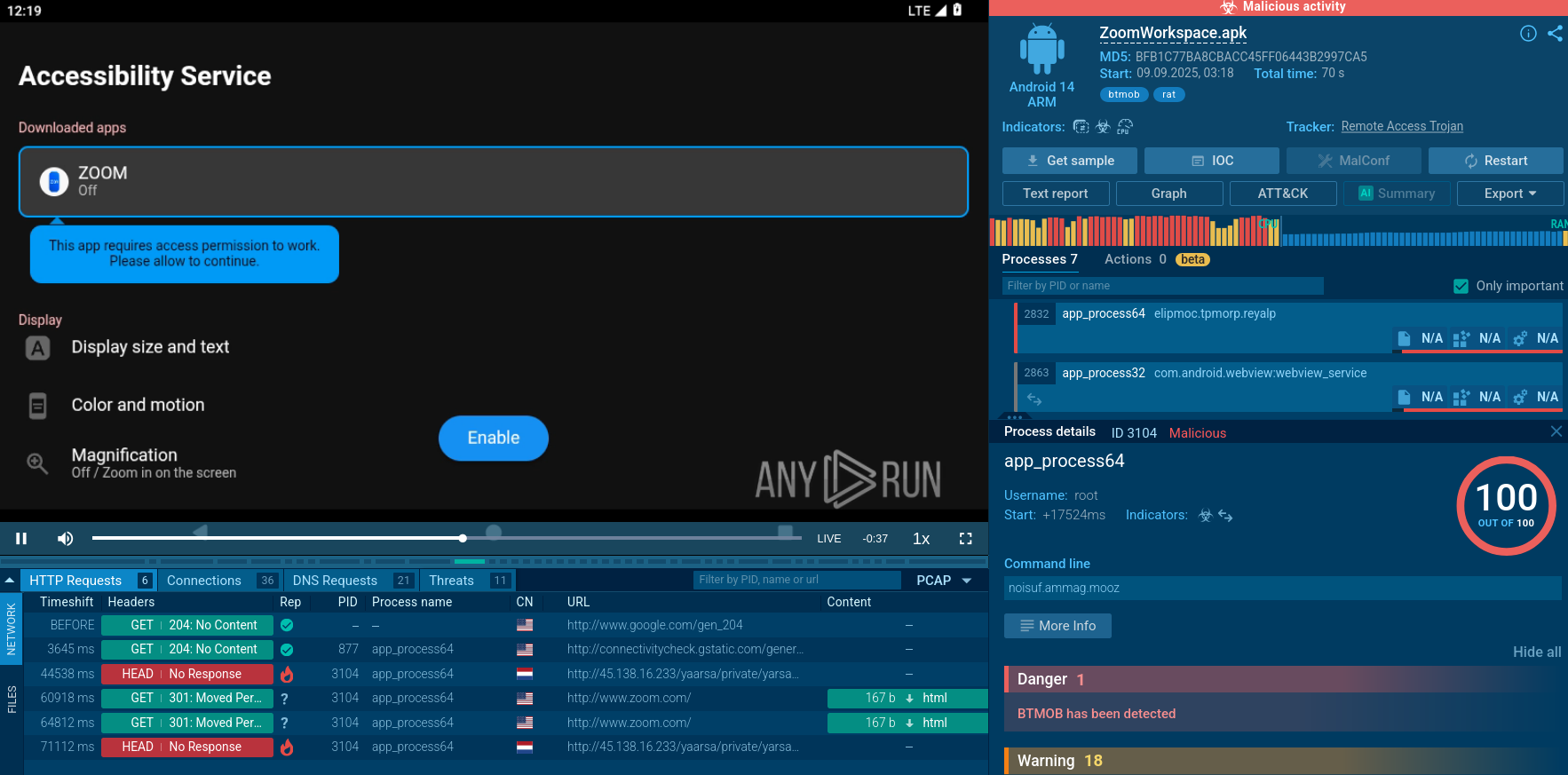
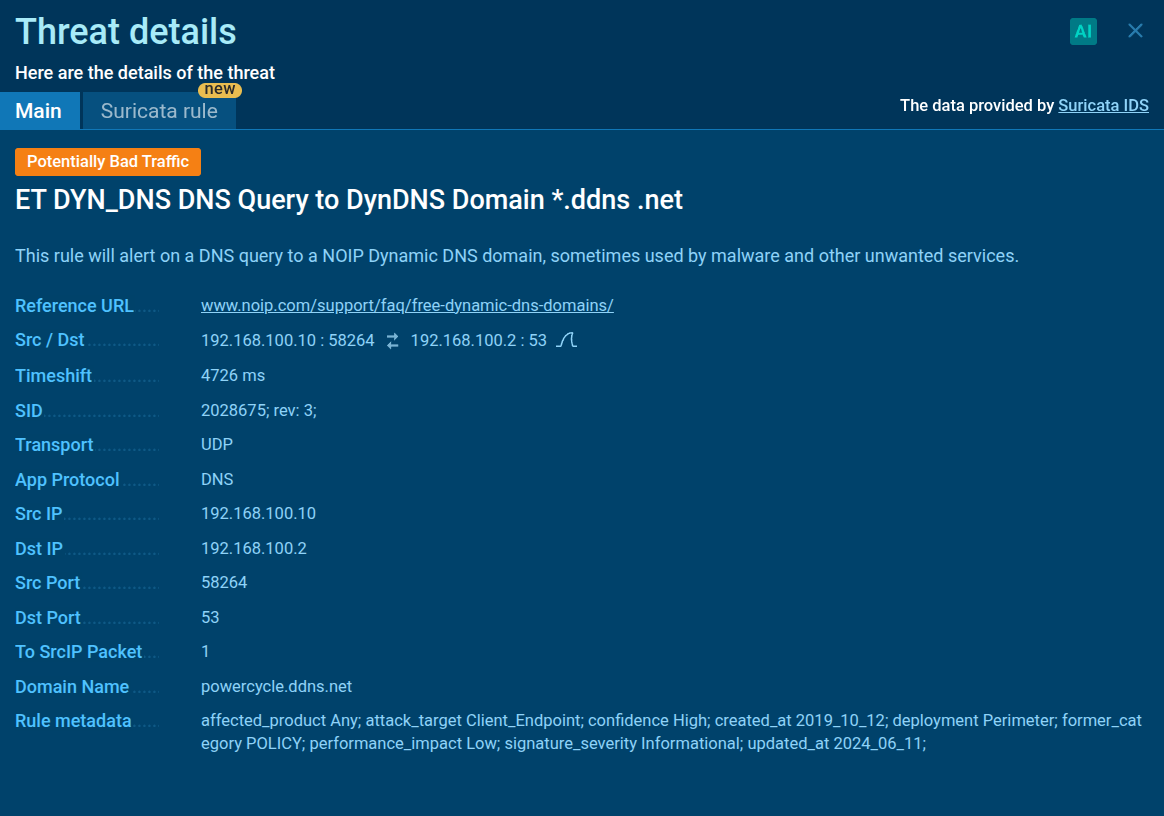 Network activity signaling malicious activity
Network activity signaling malicious activity
This connection is used to receive the C2 IP server and port, as well as later instructions from the threat actor, and to send back collected information about the infected machine. The screenshots confirm DNS queries to the *.ddns.net domain, flagged by Suricata IDS as potentially malicious traffic.
Once communication is established, the RAT stays idle, waiting for the attacker’s commands. Potential capabilities include file exfiltration, system manipulation, additional payload downloads, and real-time surveillance.
DarkVision RAT typically spreads through a multi-stage infection chain, often initiated via phishing campaigns or malicious downloads:
DarkVision RAT operates through a multi-stage attack chain, leveraging sophisticated techniques to infiltrate and persist on systems:
DarkVision RAT is equipped with an extensive array of malicious capabilities that can severely compromise endpoint devices:
Threat intelligence (TI) gives security teams:
Start with a malware name search request to ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup and dive deep into contextual data on DarkVision. View public analyses of the malware’s fresh samples, extract the behavioral patterns, gather IOCs from each session.
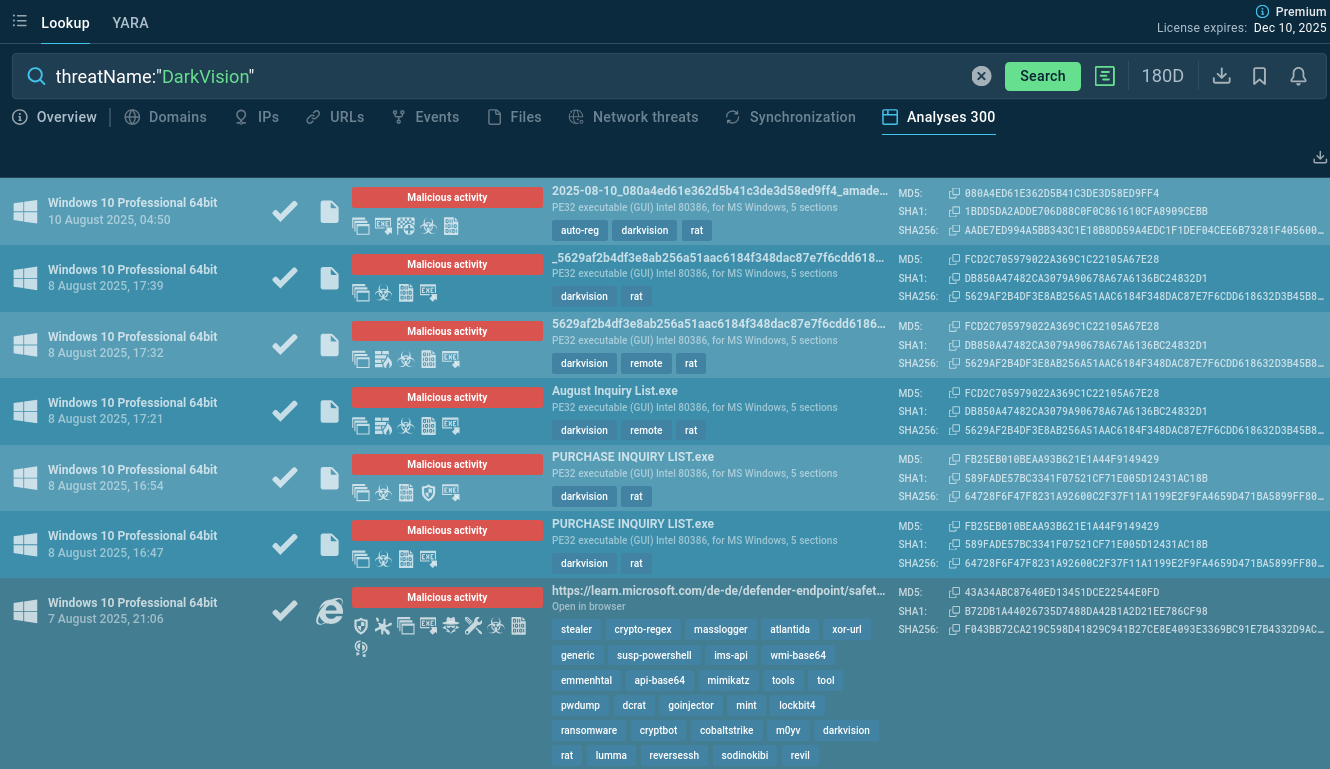 DarkVision sample analyses found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
DarkVision sample analyses found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
DarkVision RAT remains a formidable threat due to its affordability, versatility, and sophisticated evasion techniques. Its ability to compromise endpoint devices, steal sensitive data, and maintain persistence poses significant risks to businesses and individuals alike. By understanding its attack chain, implementing robust detection and prevention measures, and leveraging threat intelligence, organizations can mitigate the risks posed by this malware.
Proactive cybersecurity practices, including user education, endpoint protection, and real-time monitoring, are essential to defend against DarkVision RAT and similar threats in the evolving cyber landscape.
Gather fresh actionable threat intelligence for quick detection and response via ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup: start with 50 trial requests.