A recent update by CrowdStrike on July 18, 2024, resulted in a worldwide outage, causing significant disruption for users who were left with blue screens of death (BSODs) on their devices.
Cybercriminals seized the opportunity to target affected users with phishing scams and malware.
The ANY.RUN team has been closely monitoring the situation after the outage and has identified two primary sources of threats — domains and malware disguised as updates or bug fixes.
Fake CrowdStrike Domains
One of the earliest consequences of the outage was the creation of websites with domain names that mimicked CrowdStrike’s official domain. Although some of them were created with no malicious intent, others were used as part of phishing attempts.
These websites included newly registered ones and those that were still under construction.
Some examples:
- Crowdstriketoken[.]com: https://app.any.run/tasks/f58a7af0-e5ad-4d1c-8c18-f2093cddc28c/
- Crowdstrikebluescreen[.]com: https://app.any.run/tasks/789aa98b-fe9d-4758-a023-72a0b67530f8/
- crowdstrikedown[.]site: https://app.any.run/tasks/577a9a3c-148d-419f-9eb2-89adbbabeef4/
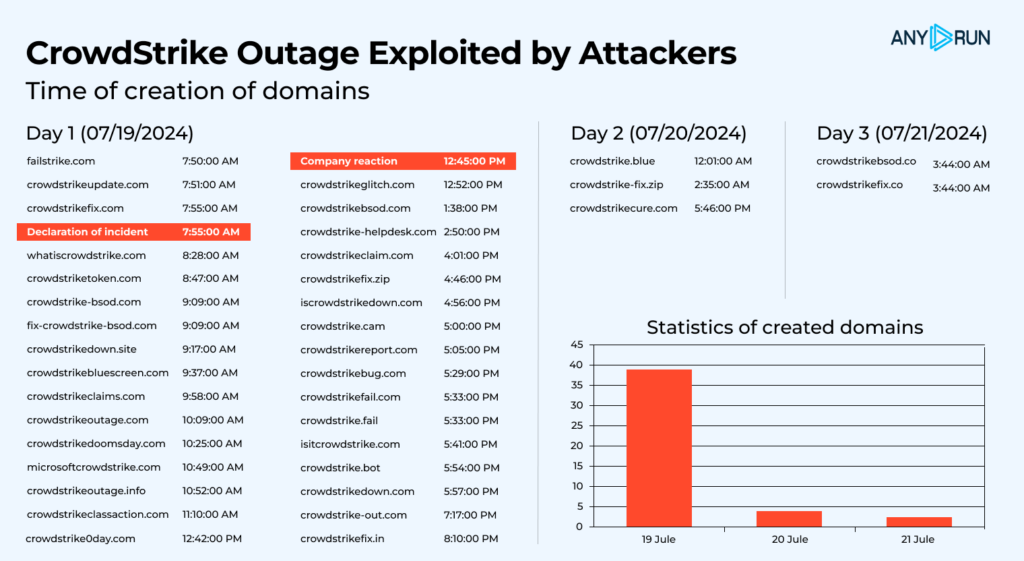
Looking at the data, the first day after the outage saw the highest volume of newly-generated fake domains. Threat actors were quick to respond, potentially tricking numerous users into visiting fake websites while they were trying to fix the problem on their own.
Here is a list of domains collected by ANY.RUN so far:
| crowdstrike-bsod[.]co | crowdstrike-bsod[.]com | crowdstrike-fix[.]zip | crowdstrike-helpdesk[.]com | crowdstrike-out[.]com |
| crowdstrike[.]blue | crowdstrike[.]bot | crowdstrike[.]cam | crowdstrike[.]ee | crowdstrike[.]es |
| crowdstrike[.]fail | crowdstrike0day[.]com | crowdstrikebluescreen[.]com | crowdstrikebsod[.]co | crowdstrikebsod[.]com |
| crowdstrikebug[.]com | crowdstrikeclaim[.]com | crowdstrikeclaims[.]com | crowdstrikeclassaction[.]com | crowdstrikecure[.]com |
| crowdstrikedoomsday[.]com | crowdstrikedown[.]com | crowdstrikedown[.]site | crowdstrikefail[.]com | crowdstrikefix[.]co |
| crowdstrikefix[.]com | crowdstrikefix[.]in | crowdstrikefix[.]zip | crowdstrikeglitch[.]com | crowdstrikehelp[.]com |
| crowdstrikelawsuit[.]com | crowdstrikemedaddy[.]com | crowdstrikeold[.]com | crowdstrikeoops[.]com | crowdstrikeoopsie[.]com |
| crowdstrikeoopsies[.]com | crowdstrikeout[.]com | crowdstrikeoutage[.]com | crowdstrikeoutage[.]info | crowdstrikepatch[.]com |
| crowdstrikeplatform[.]com | crowdstrikeplatform[.]info | crowdstrikerecovery[.]com | crowdstrikereport[.]com | crowdstrikesettlement[.]com |
| crowdstrikesuporte[.]com | crowdstrikesupport[.]info | crowdstriketoken[.]com | crowdstrikeupdate[.]com | crowdstrikeyou[.]xyz |
| crowdstrikezeroday[.]com | fix-crowdstrike-apocalypse[.]com | fix-crowdstrike-bsod[.]com | fix-crowdstrike[.]com | fixcrowdstrike[.]com |
| fixmycrowdstrike[.]com | fuckcrowdstrike[.]com | howtofixcrowdstrikeissue[.]com | iscrowdstrikedown[.]com | iscrowdstrikefixed[.]com |
| iscrowdstrikestilldown[.]com | isitcrowdstrike[.]com | microsoftcrowdstrike[.]com | microsoftoutagescrowdstrike[.]com | secure-crowdstrike[.]com |
| suportecrowdstrike[.]com | whatiscrowdstrike[.]com |
To stay informed about the latest suspicious domains, use TI Lookup. Our service lets you search our continuously updated threat database using 40 parameters, including domain names.
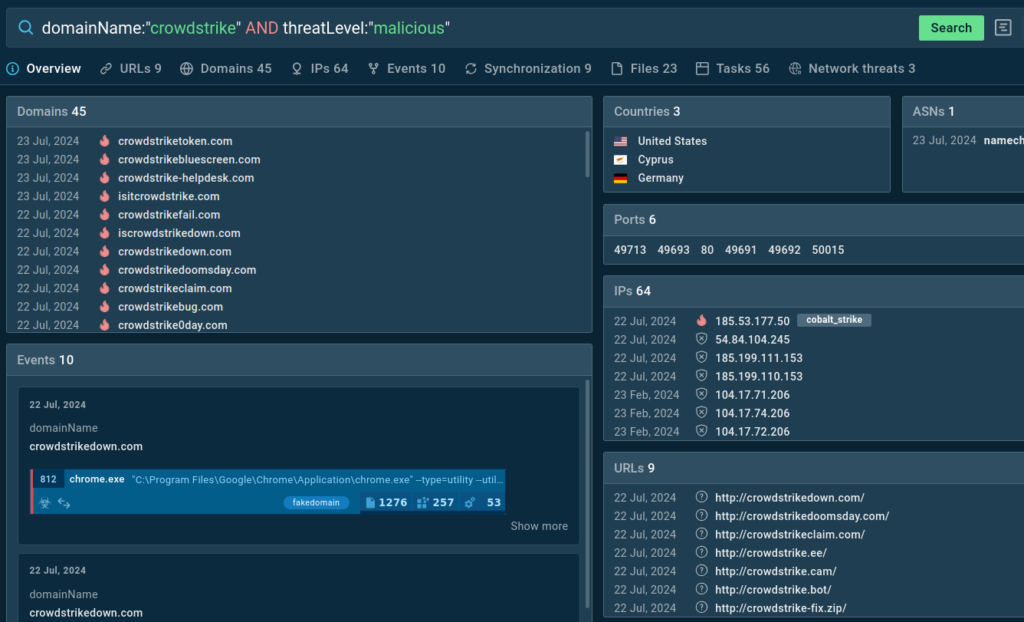
Use queries like the ones below to look for more examples of websites impersonating CrowdStrike:
|
domainName:”crowdstrike" AND threatLevel:"malicious"
domainName:”crowdstrike" AND threatLevel:"malicious" |
Our analysts have created a Suricata rule to identify domains that may contain phishing or malicious software.
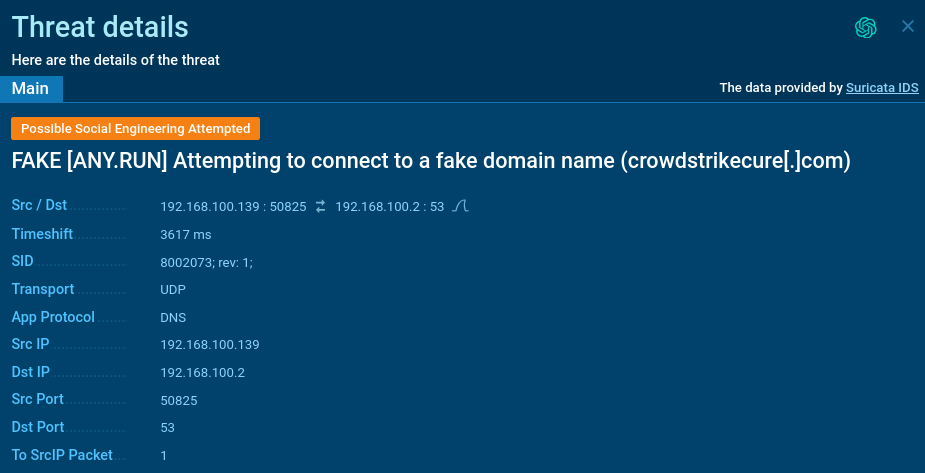
Such domains are now tagged with “fakedomain” to warn users of potential dangers. Use this tag in Public Submissions to locate additional samples:
Malicious Archive with Remcos
After the incident, there has been a rise in campaigns spreading malware as updates or bug fixes.
One of the first instances of malware observed by ANY.RUN, disguised as a CrowdStrike hotfix, was an archive containing Hijackloader.
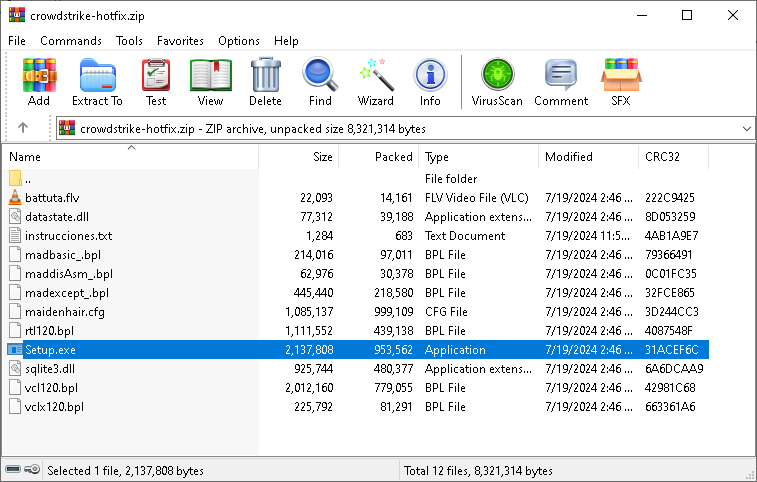
The malicious file, named “crowdstrike-hotfix”, was distributed from hxxps://portalintranetgrupobbva[.]com. After execution, it delivered Remcos to the infected system.
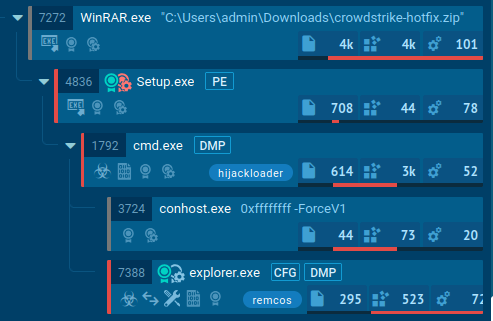
To identify more suspicious files disguised as CrowdStrike updates, use TI Lookup with queries like:
IOCs:
| crowdstrike-hotfix.zip | c44506fe6e1ede5a104008755abf5b6ace51f1a84ad656a2dccc7f2c39c0eca2 |
| Setup.exe | 5ae3838d77c2102766538f783d0a4b4205e7d2cdba4e0ad2ab332dc8ab32fea9 |
| maddisAsm_.bpl | 52019f47f96ca868fa4e747c3b99cba1b7aa57317bf8ebf9fcbf09aa576fe006 |
| battuta.flv | be074196291ccf74b3c4c8bd292f92da99ec37a25dc8af651bd0ba3f0d020349 |
| sqlite3.dll | 02f37a8e3d1790ac90c04bc50de73cd1a93e27caf833a1e1211b9cc6294ecee5 |
| vclx120.bpl | 2bdf023c439010ce0a786ec75d943a80a8f01363712bbf69afc29d3e2b5306ed |
| rtl120.bpl | b1fcb0339b9ef4860bb1ed1e5ba0e148321be64696af64f3b1643d1311028cb3 |
| maidenhair.cfg | 931308cfe733376e19d6cd2401e27f8b2945cec0b9c696aebe7029ea76d45bf6 |
| datastate.dll | 6010e2147a0f51a7bfa2f942a5a9eaad9a294f463f717963b486ed3f53d305c2 |
| madexcept_.bpl | 835f1141ece59c36b18e76927572d229136aeb12eff44cb4ba98d7808257c299 |
| vcl120.bpl | b6f321a48812dc922b26953020c9a60949ec429a921033cfaf1e9f7d088ee628 |
| madbasic_.bpl | d6d5ff8e9dc6d2b195a6715280c2f1ba471048a7ce68d256040672b801fda0ea |
| instrucciones.txt | 4f450abaa4daf72d974a830b16f91deed77ba62412804dca41a6d42a7d8b6fd0 |
| Domain: | hxxps://portalintranetgrupobbva[.]com/ |
| C2 | 213.5.130.58:443 |
| URLs: | mail.zoomfilms-cz[.]com discussiowardder[.]website wxt82[.]xyz |
Phishing Email with a Data Wiper
One of the most sophisticated attacks involved the distribution of a data wiper.

It began with the CrowdStrike-themed phishing email and PDF attachment, which, in turn, included a link to downloading a ZIP file.
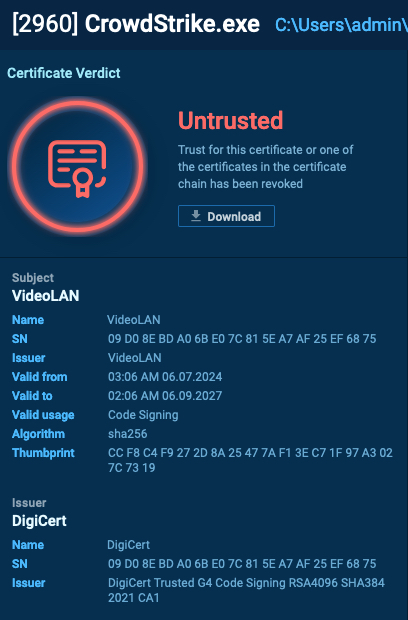
The archive contained an executable that, once launched, asked the user if they wanted to install the update.
Upon launching, the wiper devastated the system by overwriting files with zero bytes and then reported it over Telegram.
See analysis session in ANY.RUN
IOCs
| update2.pdf | 1bbb795ce19f4dcc4ac9f8e8c12f3452f1f07c68a53ef631c76e392e1d06ea43 |
| update.zip | 96dec6e07229201a02f538310815c695cf6147c548ff1c6a0def2fe38f3dcbc8 |
| CrowdStrike.exe | 4491901eff338ab52c85a77a3fbd3ce80fda738046ee3b7da7be468da5b331a3 |
| URL | hxxps://link.storjshare[.]io/s/jwyite7mez2ilyvm2esxw2jq3apq/crowdstrikeisrael/update.zip?download=1 |
Malicious Document with a Stealer
Attackers also used other ways to trick unsuspecting victims into running malware.
The picture below shows a harmful document that claims to provide instructions on how to resolve the issue.
Yet, when opened, it uses a bad VBS (Visual Basic Script) to start a series of tools on the infected computer.
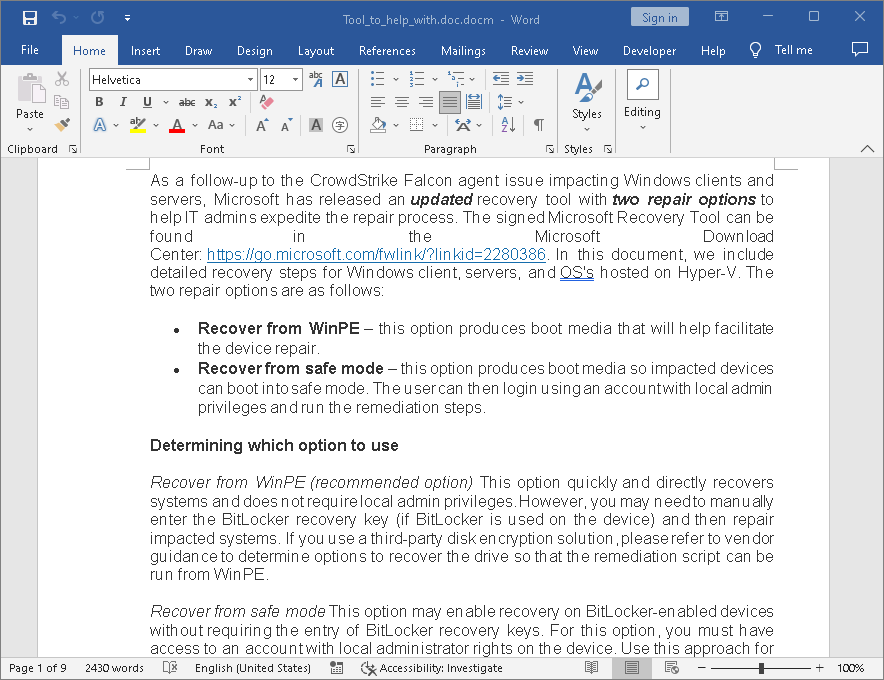
After execution, it downloads and launches a stealer malware using curl.
IOCs
Malicious document
| Name | New_Recovery_Tool_to_help_with_CrowdStrike_issue_impacting_Windows.docm |
| Hash sum | 803727ccdf441e49096f3fd48107a5fe55c56c080f46773cd649c9e55ec1be61 |
| URL | hxxp[://]172.104.160[.]126:8099/payload2[.]txt |
Stealer
| Hash sum | 4ad9845e691dd415420e0c253ba452772495c0b971f48294b54631e79a22644a |
| URL | 172.104.160.126:5000 |
Recommendations
Users and organizations are advised to remain vigilant and thoroughly verify any updates or hotfixes before installation.
For any information concerning the course of action for affected users, it is important to follow CrowdStrike’s official statements and guidance.
About ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN helps more than 400,000 cybersecurity professionals worldwide. Our interactive sandbox simplifies malware analysis of threats that target both Windows and Linux systems. Our threat intelligence products, TI Lookup, Yara Search and Feeds, help you find IOCs or files to learn more about the threats and respond to incidents faster.






0 comments