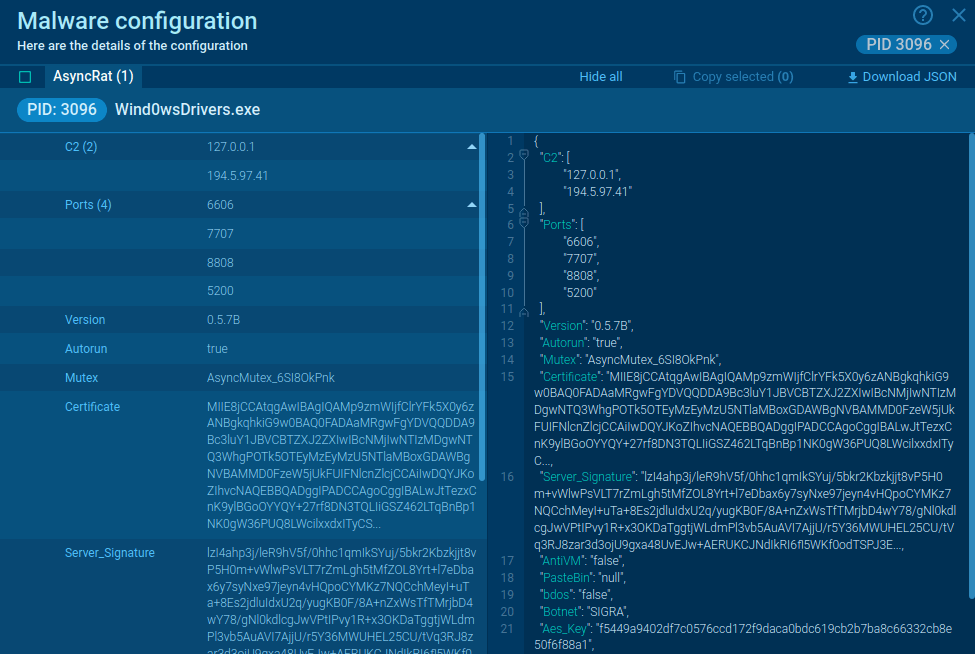
What is XWorm malware?
XWorm is a remote access trojan (RAT) that gives cybercriminals unauthorized access to a victim's computer. It is a modular malware, meaning that it can be customized to perform a variety of malicious tasks, such as stealing sensitive data and cryptocurrency, launching DDoS attacks, and deploying ransomware. It first came into the spotlight in July 2022 and is believed to have originated in the ex-USSR.
XWorm is sold as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS), which makes it extremely dangerous. It lowers the barrier to entry and opens hacking opportunities to more people. Since its first appearance in the global threat landscape in July 2022, XWorm has gone through several iterations. As of August 2023, the 4.2 version and the 5.0 version were the latest ones available for purchase.
Criminals use multi-stage attacks to deploy XWorm on victims’ computers. For example, an attack might start with a phishing email that contains a malicious Word document attachment. When the document is opened, it will load an .rtf file from an external link. This file will contain an Excel spreadsheet with macros that will execute a PowerShell script, which will then download XWorm onto the computer.
Technical details of the XWorm malicious software
XWorm is developed with the .NET Framework, which makes it a significant threat to Windows systems. The malware is also configurable, offering a wide range of tools for manipulating the infected machine.
Here are some of XWorm’s key capabilities:
- Encrypted connection: XWorm is capable of maintaining a secure connection with its C&C server, even during poor network conditions.
- Information gathering: The malware can collect a wide range of information from the infected computer, including credit card numbers, browsing history, bookmarks, downloads, as well as Firefox and Chromium passwords and cookies.
- Account hijacking: XWorm can hack Discord, Telegram, and MetaMask accounts, as well as get hold of WiFi keys and product keys.
- User activity tracking: The malware enables attackers to monitor the victim’s activities on their computer by logging their keystrokes, automatically saving webcam images, listening to their microphone, scanning their network connections, and viewing opened windows.
- Clipboard access: XWorm can retrieve the information that has been copied to the clipboard and replace victims’ crypto wallet credentials with those of the attacker.
- File management: It can gain control of a computer’s file system to transfer sensitive documents and content to its C2 or download additional malware and run it.
In order to bypass User Account Control (UAC), XWorm attempts to get administrator permissions on the infected computer. This allows it to make changes to the system without requiring user consent. To ensure persistence, the malware adds itself to the list of programs that run automatically when the computer starts up by editing the registry.
It is also polymorphic, meaning that the malware’s code regularly transforms itself to throw detection software off course. Although XWorm has a built-in functionality to terminate its execution once it senses that it is launched in a virtualized environment, the ANY.RUN sandbox has no problem identifying the malware.
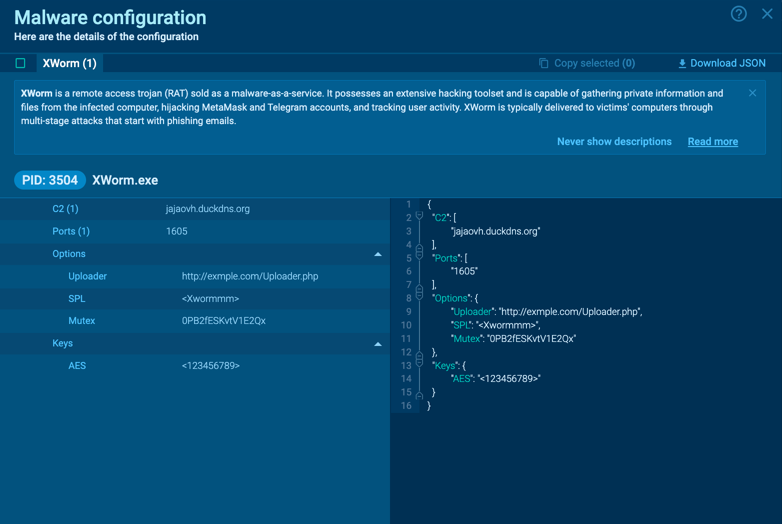
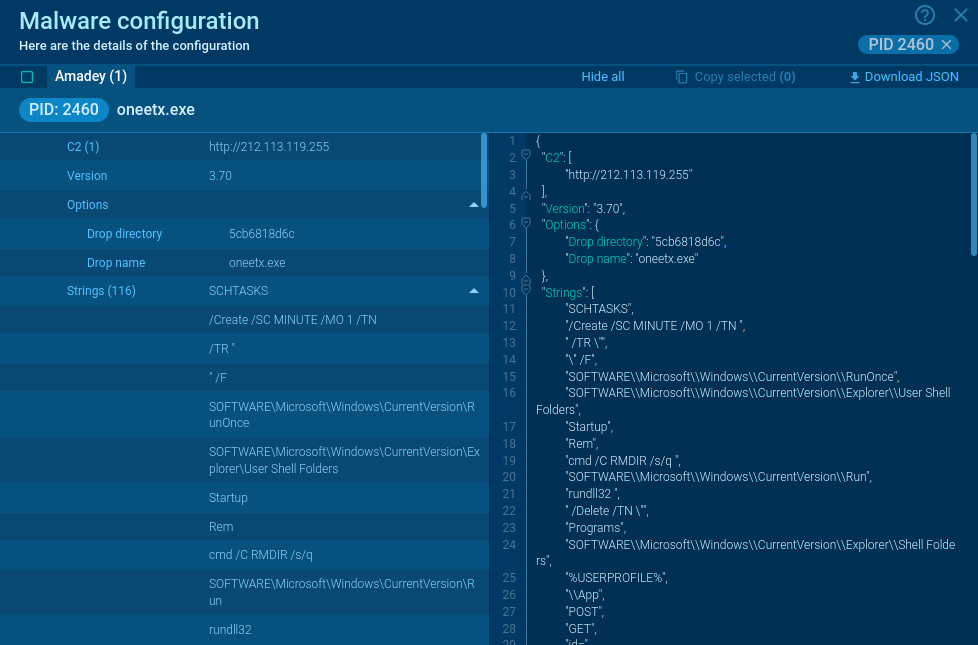
XWorm’s configuration
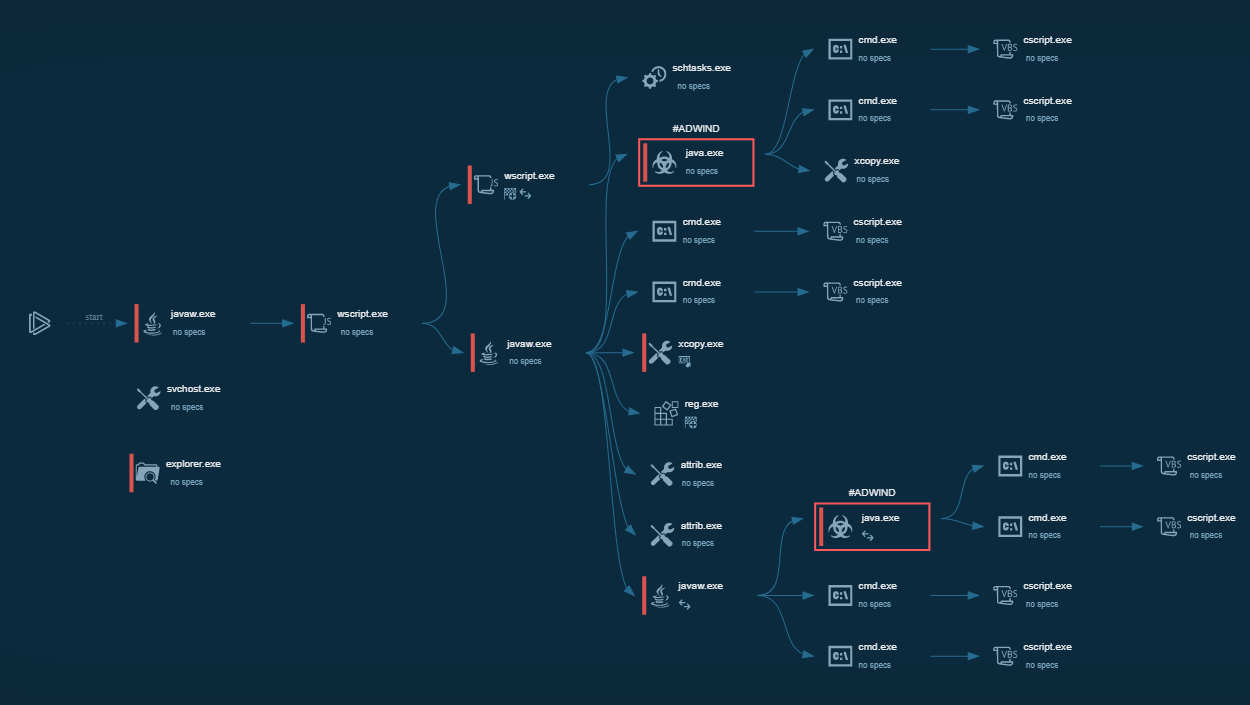
Execution process of XWorm
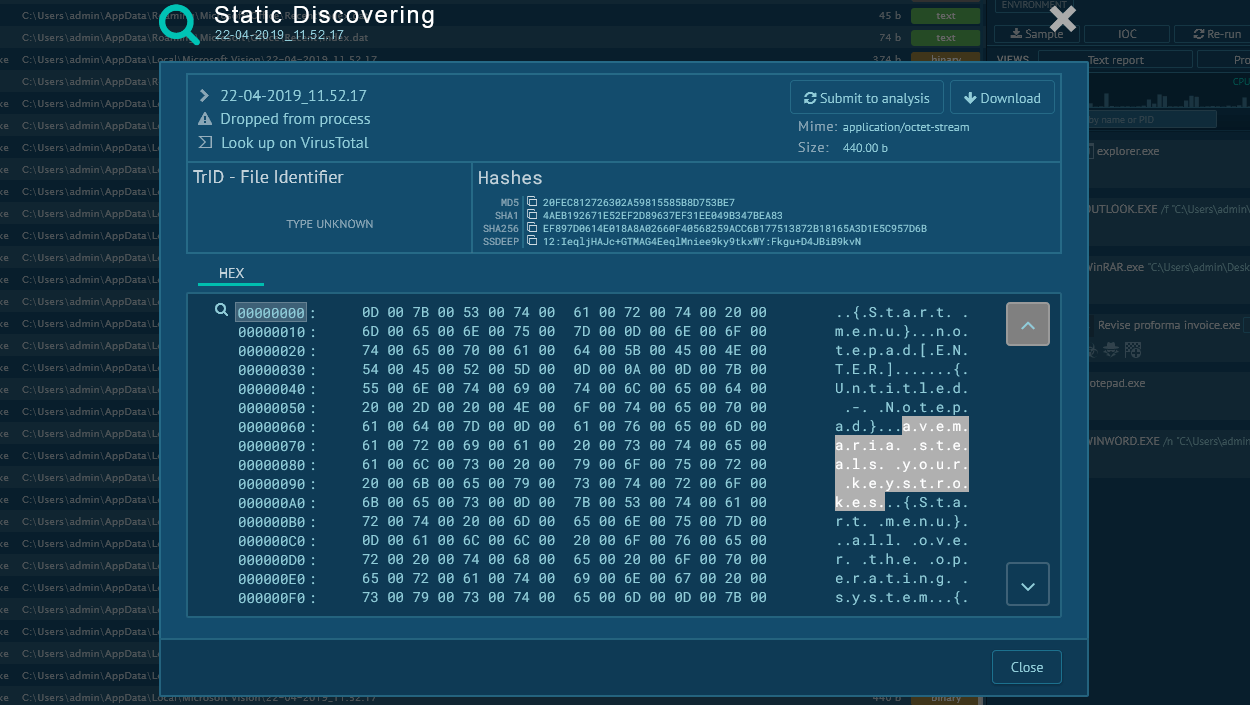
The malicious behavior of XWorm can be easily uncovered by uploading it to the ANY.RUN sandbox. Here is a sample of this malware on the platform.
Immediately upon execution, XWorm drops an executable file into the Startup directory (“C:\Users\admin/AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup\XWorm.exe”) and into the Roaming directory (“C:\Users\admin/AppData\Roaming\XWorm.exe”).
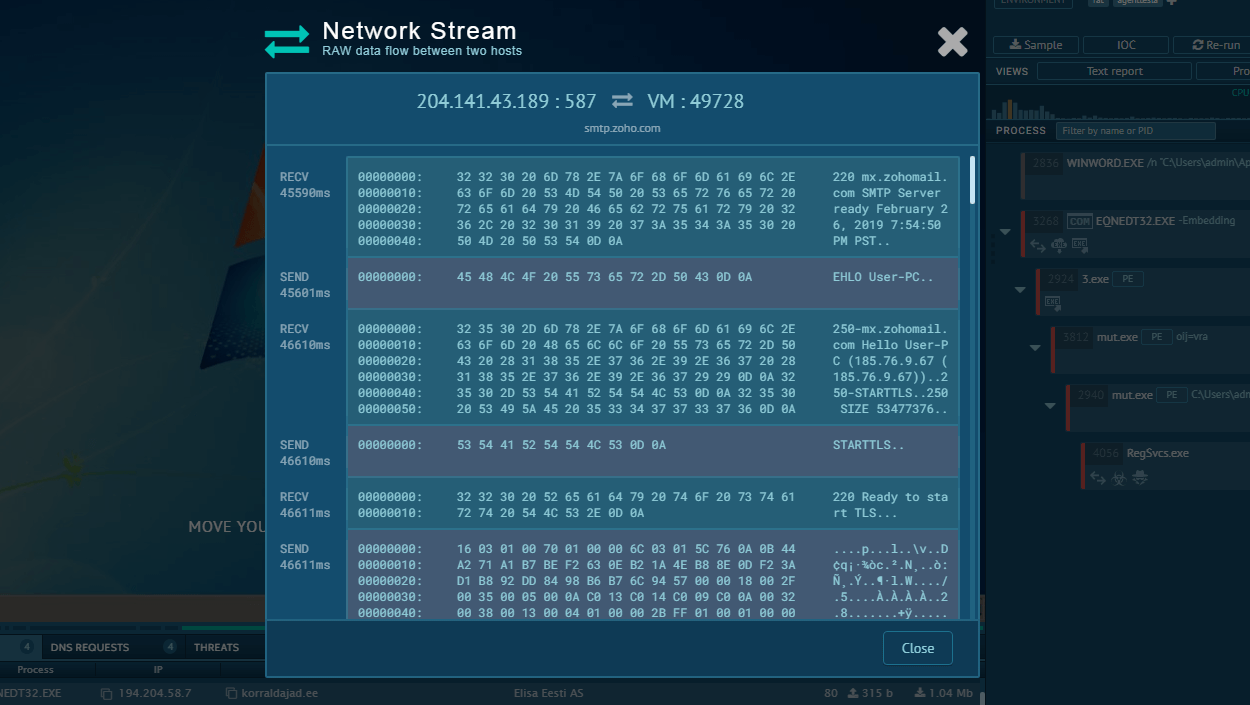
For the latter directory, a persistent service is created using the Task Scheduler. Malware checks for an external IP, which we can bypass with ANY.RUN’s Residential Proxy feature. After this, XWorm starts sending beacons to the C&C server, waiting for commands to execute.
Read a detailed analysis of XWorm in our blog.

XWorm’s process graph
Distribution methods of the XWorm malware
As with most malware families, email phishing campaigns serve as XWorm’s main gateway to victims’ computers. The attack begins with an email containing an attachment. By exploiting different social engineering techniques, threat actors can persuade a user to download the attached file and open it.
Analysts have observed several file formats used by attackers, including .rtf, .lnk, and .pdf. In most cases, the email attachment itself does not contain any macros and is used primarily to kick off a chain reaction that involves downloading several other files, executing PowerShell scripts, and finally delivering the payload.
Such attacks can be facilitated by specialized tools, such as Freeze[.]rs and SYK Crypter, which are equipped with advanced capabilities for circumventing defense systems to drop a variety of malware families including Remcos RAT, njRAT, and RedLine Stealer.
One of the most recent XWorm attacks targeted businesses in Germany. It involved sending a .docx document to victims with a name that suggested it contained hotel reservation information. Instead of using macros, the file exploited the Follina vulnerability (CVE-2022-30190) to run external malicious files and a PowerShell script, which eventually dropped XWorm.
Conclusion
XWorm retains considerable staying power due to the consistent updates and wide availability, making it a top concern for organizations around the world. To protect your system from this threat, you need to have a stricter approach towards handling any links or files arriving in your inbox from unknown senders.
Instead of downloading documents and opening URLs, you can first analyze them in the ANY.RUN sandbox to quickly understand whether the file is malicious or not. ANY.RUN also provides you with a detailed report about the malware, such as its IOCs and TTPs. This information can be used to protect your organization from future attacks.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!




 0
0