Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


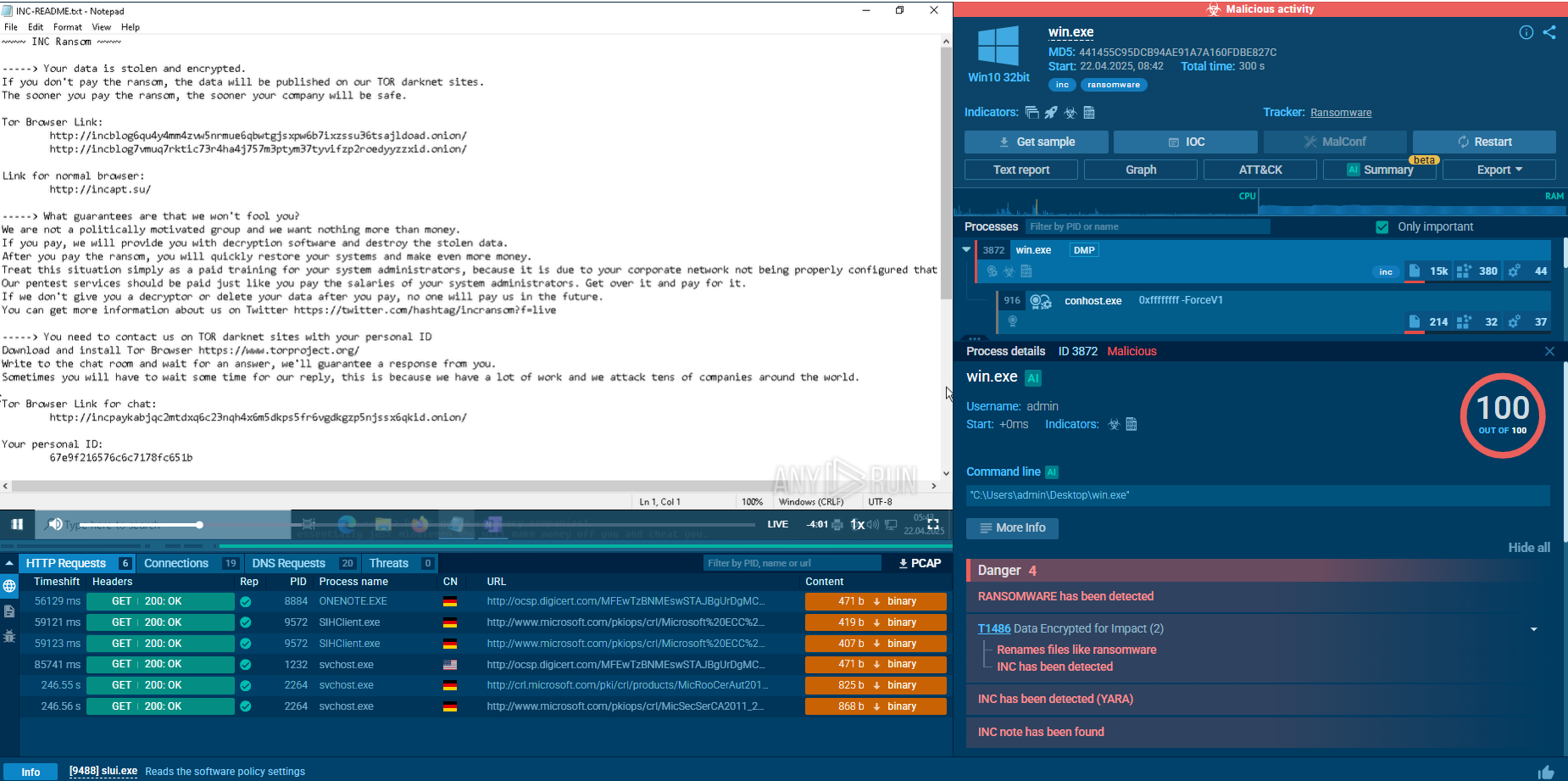
Cephalus is a targeted ransomware threat discovered in 2025. It’s known for infiltrating organizations that deal with sensitive data through compromised RDP access. It leverages DLL sideloading with a legitimate SentinelOne executable. Cephalus is able to exfiltrate data and destroy backup options. Its payload is also tailored to each victim, which makes identification and mitigation more complex.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 November, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 November, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
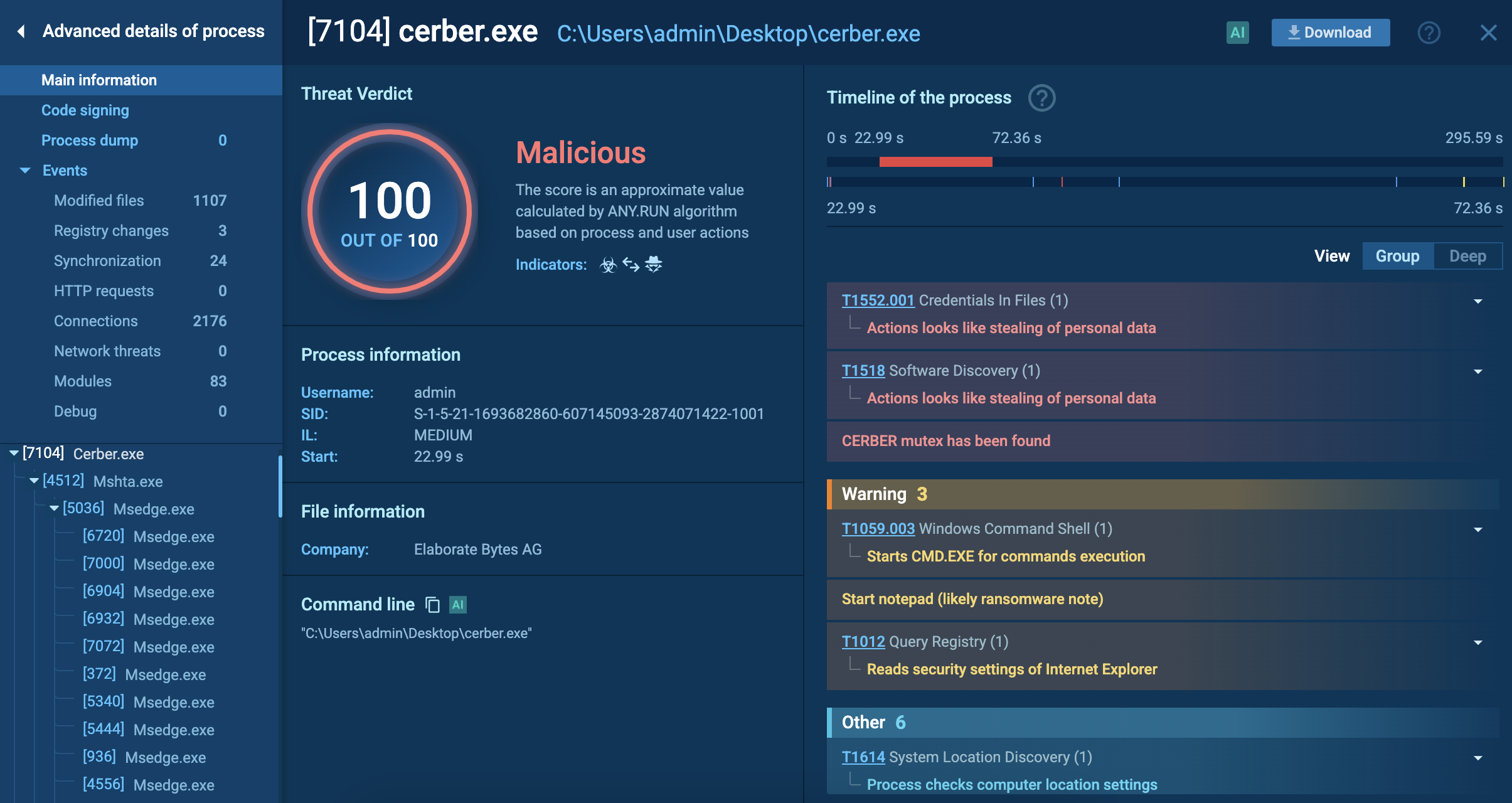
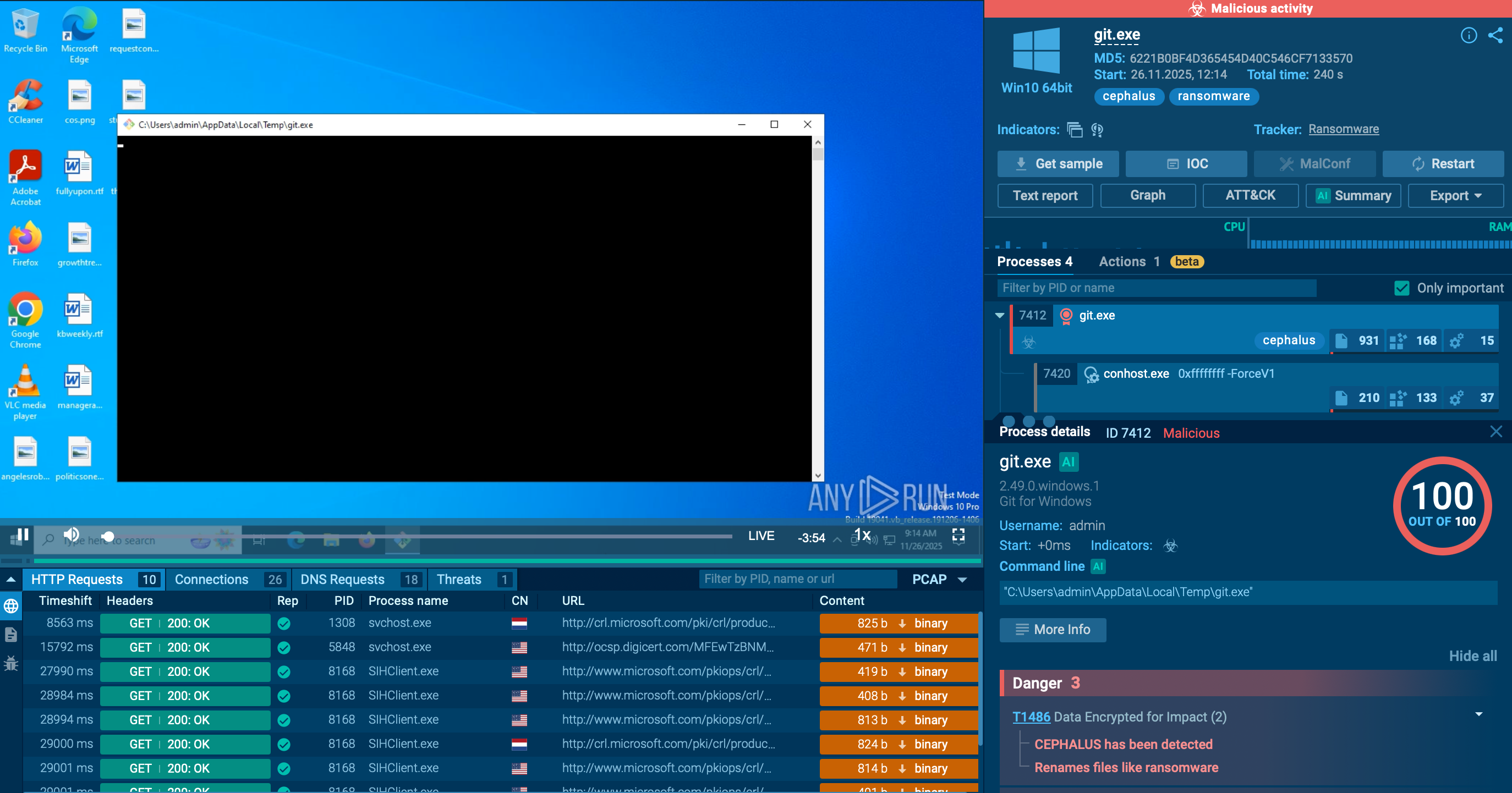 Cephalus threat analyzed in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Cephalus threat analyzed in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
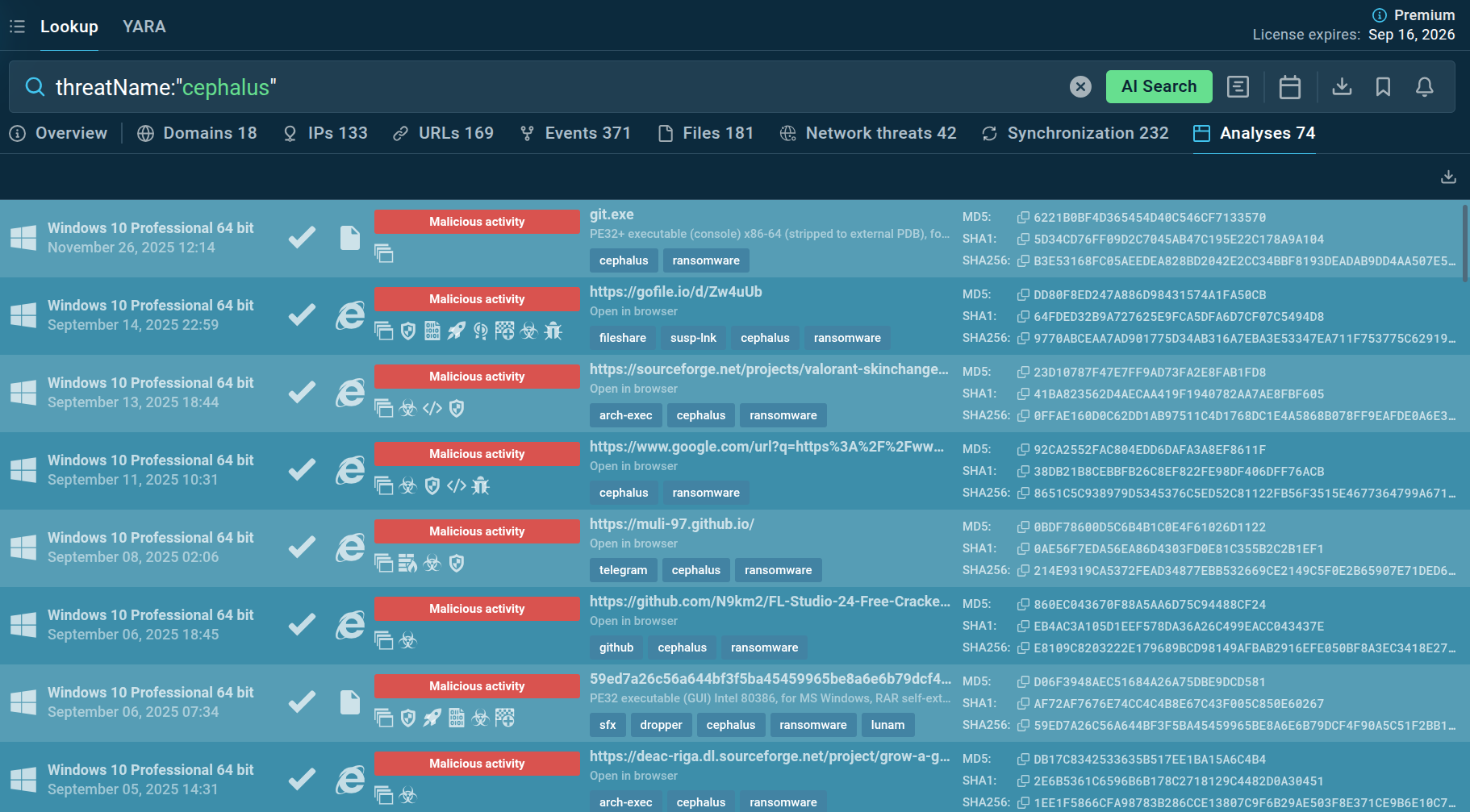 Latest reports on Cephalus shown by ANY.RUN's TI Lookup
Latest reports on Cephalus shown by ANY.RUN's TI Lookup
Cephalus is a recently observed ransomware threat abusing RDP by stealing credentials, often in systems that lack multi-factor authentication (MFA). That’s how it gains initial access. Once inside, it uses DLL sideloading technique to slip past defenses. As it infiltrates the system, Cephalus encrypts data and prevents its recovery, demonstrating a ransom demand.
The threat's name comes from Greek mythology, referencing a character of the same name with a precise, unerring spear. This suggests an accurate and targeted approach to victims — a fitting analogy, as observed attacks involve tailored malware.
Two notable campaigns took place in August 2025. In both cases, legitimate SentinelOne instances were abused to load a malicious DLL and embed ransomware code.
It’s not entirely known at the moment whether it’s a ransomware-as-a-service or an independent group. Geographic and industrial scopes remain diverse. Among the prevalent targeted sectors are healthcare and finance businesses from the US.
The breakdown of how Cephalus typically infiltrates systems:
– Credential theft. Cephalus specifically targets infrastructures where RDP isn’t efficiently protected; this includes the lack of MFA. That’s how threat actors gain initial access.
– Data exfiltration via MEGA cloud storage platform. Before the payload is deployed, threat actors use legitimate RDP accounts to exfiltrate information. Since credentials are legit, this activity doesn’t look suspicious.
– Payload delivery via DLL sideloading. The threat actors abuse legitimate SentinelOne executable, load malicious DLL, and embed malicious code:
– Evasion and anti-forensics. The ransomware is written in Go (Golang) and uses memory obfuscations.
– Security disabling. Commands like vssadmin destroy shadow copies, registry changes disable Windows Defender, and backup services like Microsoft SQL Server are terminated.
– Exfiltration and encryption. Data is uploaded to MEGA cloud storage and files are encrypted with .sss extension.
– Ransom note. Once the defenses and backup solutions are eliminated, the attackers deploy ransomware by sharing a .txt ransom note in numerous locations.
The note urges the user to begin the negotiation ASAP. In the opposite case, threat actors threaten to leak all data and contact the victim’s clients about their sensitive data being compromised.
Tactics like deletion of shadow copies and registry manipulations to disable security tools make recovery increasingly more complex. The result is stolen data and disrupted operations.
Most notable feature is the unique way to launch the ransomware: through legitimate SentinelOne executable file.
The scope of victims and their geography is wide. Cephalus targets a number of sectors — IT, healthcare, finance, law firms, etc. What attracts the threat actors is companies that handle sensitive data or intellectual properties, not a particular industry.
Not only large enterprises, but also mid-sized firms are on the list. This might indicate that Cephalus prioritizes smaller companies with weaker security defenses.
Geographically, most attacks are US-based, but there are victims outside the US too.
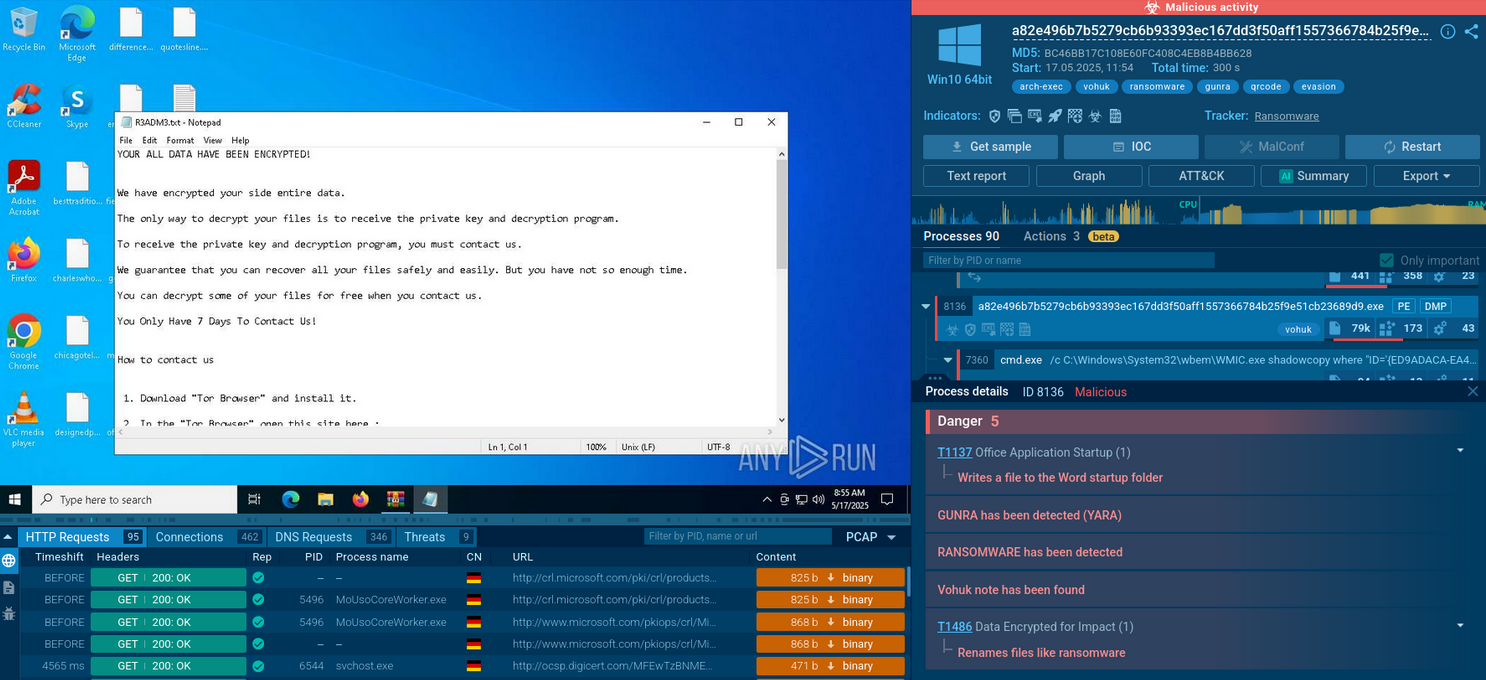
Let's see how Cephalus operates in the ANY.RUN sandbox. Follow this link to see the entire analysis:
View analysis session with Cephalus ransomware
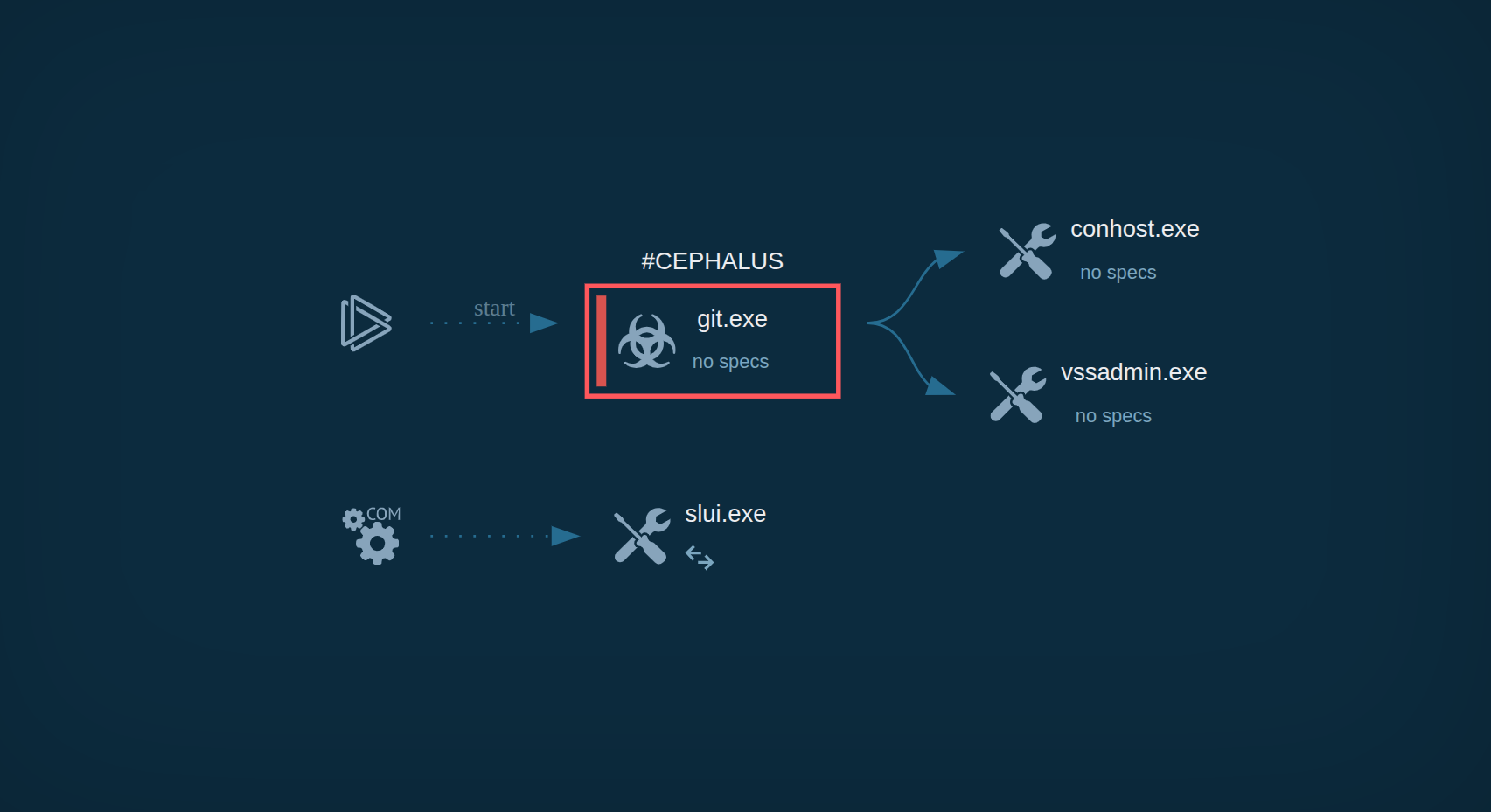 Analysis of Cephalus inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
Analysis of Cephalus inside ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
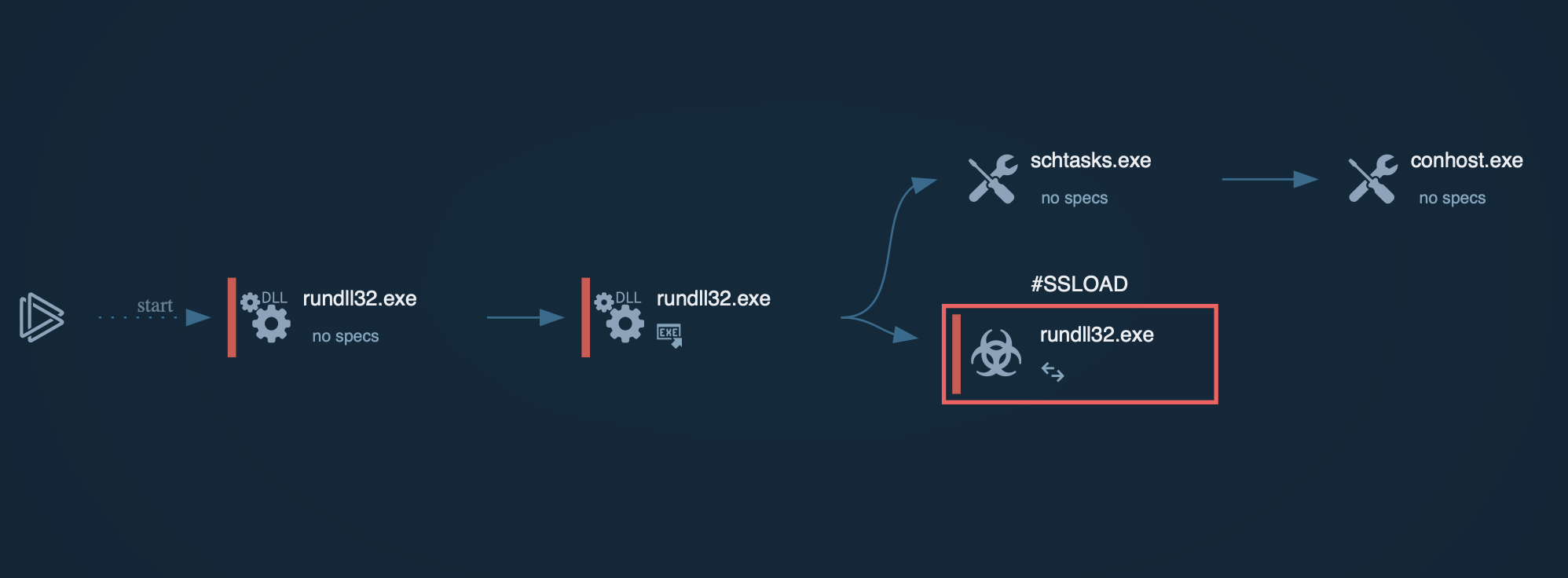
As we can see, upon execution, treat actors collect general info about the victim’s environment. This includes:
– Computer’s name
– Supported languages
– Registry requests
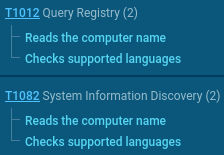 TTPs used by Cephalus to get info on the victim’s system as seen in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
TTPs used by Cephalus to get info on the victim’s system as seen in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
After that, it begins to encrypt user’s files and does so topically. Such an approach accelerates the process as compared to recursive launch across all user catalogs.
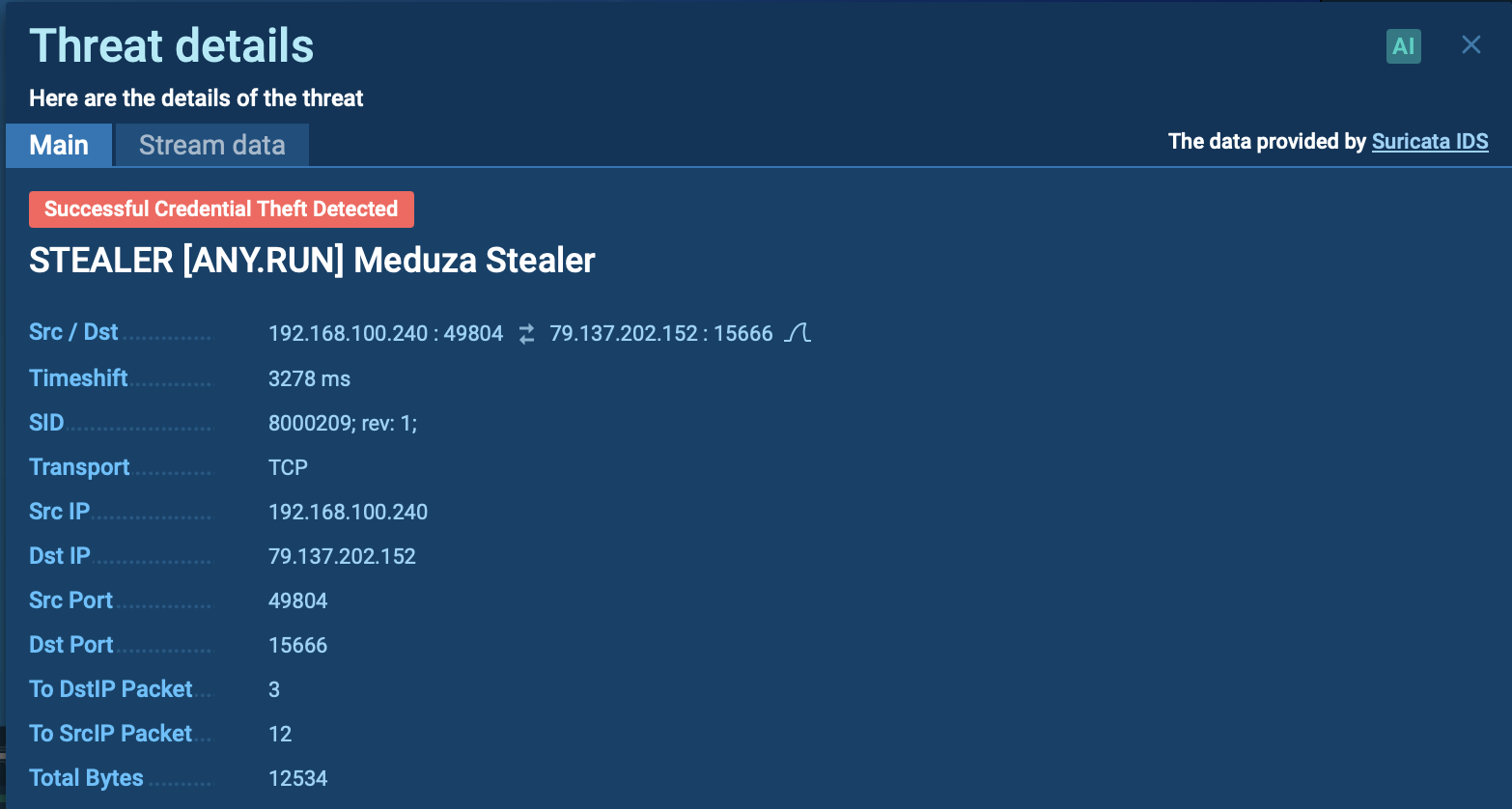
The victim is then shown a ransom note in their infiltrated system. You can see its fragment below:
 Cephalus ransom note fragment shown in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Cephalus ransom note fragment shown in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
The note highlights the urgency of the incident and offers proof of data stealth. It says that confidential data will be leaked, and the victim’s clients will be contacted via calls or emails to inform them about their data being stolen. All this motivates the victim to start the negotiation urgently.
Cephalus also deletes shadow copies using the vssadmin command. This prevents the recovery of the system through VSS. As a result, the chances that the victim will be able to recover data on their own are minimized, once again highlighting the complexity of the situation.
According to research, Cephalus seems to be mostly distributed through stolen and compromised RDP credentials. They hit infrastructures with exposed RDP, for example, in cases where there is no multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Threat Intelligence Lookup enables security teams to quickly search for information about suspicious files, URLs, domains, and IP addresses potentially associated with Cephalus.
By querying file hashes or URLs encountered in environments, analysts can immediately determine if they match known Cephalus samples, view detailed behavioral analysis, and understand the specific capabilities and infrastructure of particular variants.
This rapid intelligence access accelerates incident response and enables proactive blocking of threats before they impact systems.
Start exploring any threat by looking it up by the name, for instance:
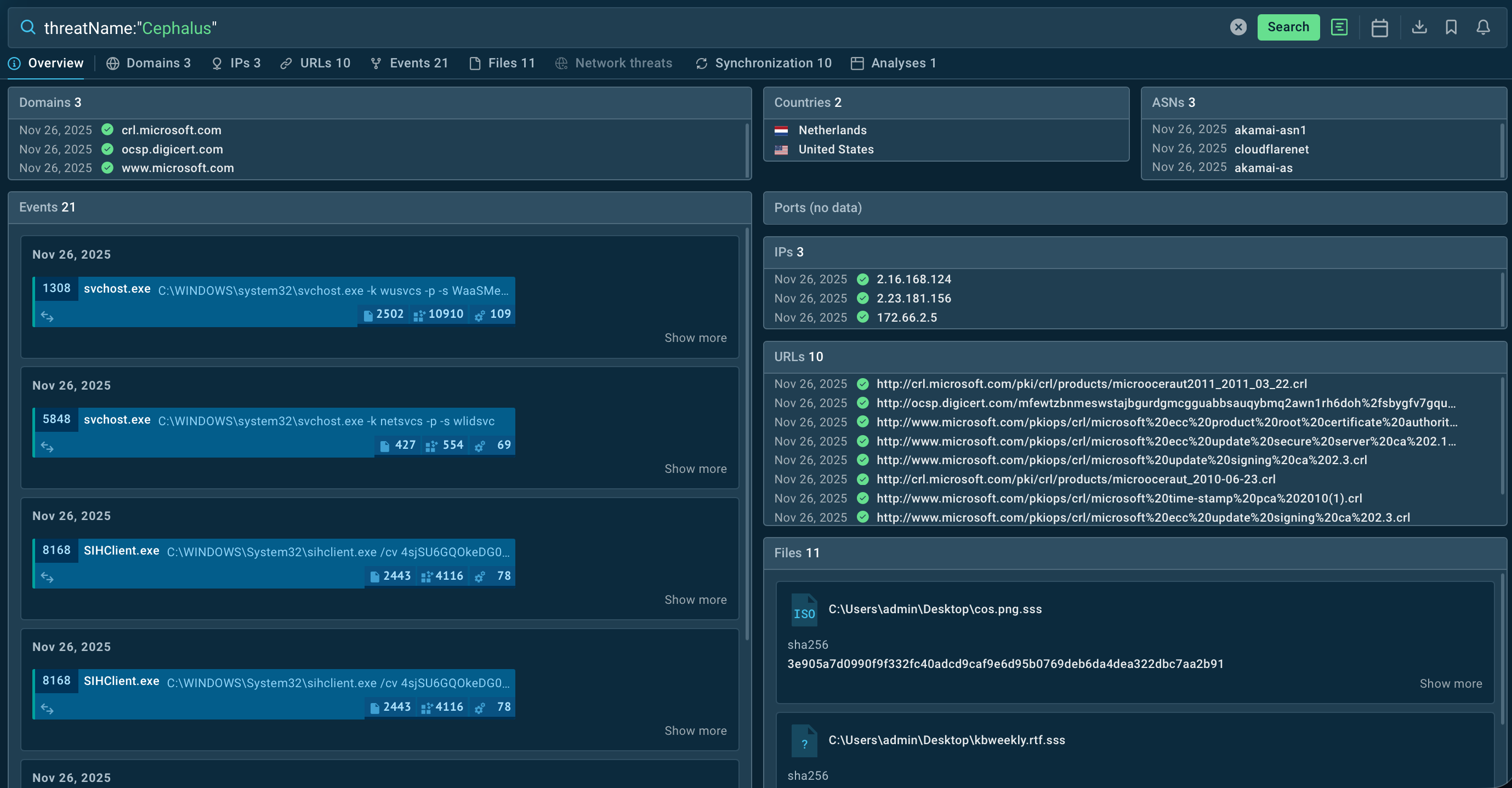 TI Lookup results for Cephalus threats
TI Lookup results for Cephalus threats
Cephalus is a high-impact ransomware threat that abuses legitimate executables to bypass defenses. It terminates backups and copies, making recovery extremely different. The malware targets organizations with sensitive data and weak defenses.
To avoid compromise and start monitoring Cephalus, its new strains, and other threats, apply a proactive approach to security. Analyze suspicious files in sandboxing services like ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
To track emerging threats and enrich your indicators, try Threat Intelligence Lookup, a browsable collection of IOCs and IOBs gathered from live investigations done by 15,000+ SOC teams.
Sign up to start gathering actionable intel in TI Lookup. Get 50 trial requests