Advanced persistent threats (APTs) stand out as one of the most formidable challenges for businesses in the cybersecurity landscape. These threats can cause irreparable damage, leading to financial losses, data breaches, and reputational harm.
APTs are defined as sophisticated targeted attacks typically conducted by highly funded adversaries: national agencies, state-sponsored groups, organized crime groups, corporate espionage actors.
What Are APTs
The name speaks for itself, APTs are:
- Advanced: Having at hackers’ disposal the full (and ever-growing) arsenal of techniques and tools to get and maintain access to the target.
- Persistent: The aim is to keep long-term access to the targeted system or network. This involves constant improving and updating of the tools to evade detection.
- Threats: Such campaigns are intentionally malicious and inevitably harmful. They are backed by coordinated actions of skilled, motivated, organized, and well-resourced professionals.
Why Are APTs a Significant Threat to Businesses
APTs prefer to target large corporations, government entities, and critical infrastructure. Finance, manufacturing, healthcare, and energy are prime targets for APTs due to the high value of their assets, data and infrastructure. The consequences of a successful APT attack extend beyond financial loss and corporate damage — they can impact national security, cause market instability, disrupt economies, and put lives at risk.
But no business, however modest-scale and unrelated to strategic industries, can consider itself safe:
- Small and medium companies still possess valuable assets, handle sensitive customer information, financial data, or intellectual property
- They are part of supply chains that can be disrupted by attacks
- A successful infiltration into their communications grants access to larger partners or clients.
- Along with all this, they have weaker security posture, invest less in cyber threat prevention.
Detect Early, Defend Better: The Power of Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence is a pivotal element of an APT-resistant cybersecurity strategy. By gathering, analyzing, and applying intelligence on cyber threats, organizations can proactively detect and neutralize them before they escalate.
TI provides:
- Early Detection: Identifying indicators of compromise (IOCs) before damage occurs.
- Behavioral Analysis: Understanding attacker tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to anticipate movements.
- Threat Hunting: Actively searching for hidden threats within the network.
- Stronger Security Posture: Defenses based on real-world threat insights.
- Incident Response Efficiency: Rapidly responding to and mitigating APT incidents.
How Threat Intelligence Lookup Facilitates APT Reconnaissance
ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup is a solution fit for all these tasks: a state-of-the-art search engine for threat researchers and cybersecurity teams. It provides detailed insights into indicators of compromise (IOCs), malware behavior, and attack patterns.
It supports over 40 search parameters to query a constantly updated database of threat data, collected from millions of public malware and phishing samples and manually analyzed by a team of threat analysts.
For a business, it’s a source of actionable information for preventing, detecting and mitigating all sorts of cyberattacks up to APTs, thus avoiding operational disruptions, financial and reputational damages.
How TI Lookup helps track APTs
Wicked Panda APT: Closer Look at an Abused Registry Key
A notorious Chinese APT group, APT41 aka Wicked Panda, employs a PowerShell-backdoor for compromising systems.
To maintain persistence, it adds its payload in Windows registry entry HKCU\Environment\UserInitMprLogonScript which allows it to run malicious code automatically at each user login into the system. Besides, the hackers abuse a legitimate Microsoft’s forfiles.exe utility.
This data is enough to combine a query for TI Lookup:
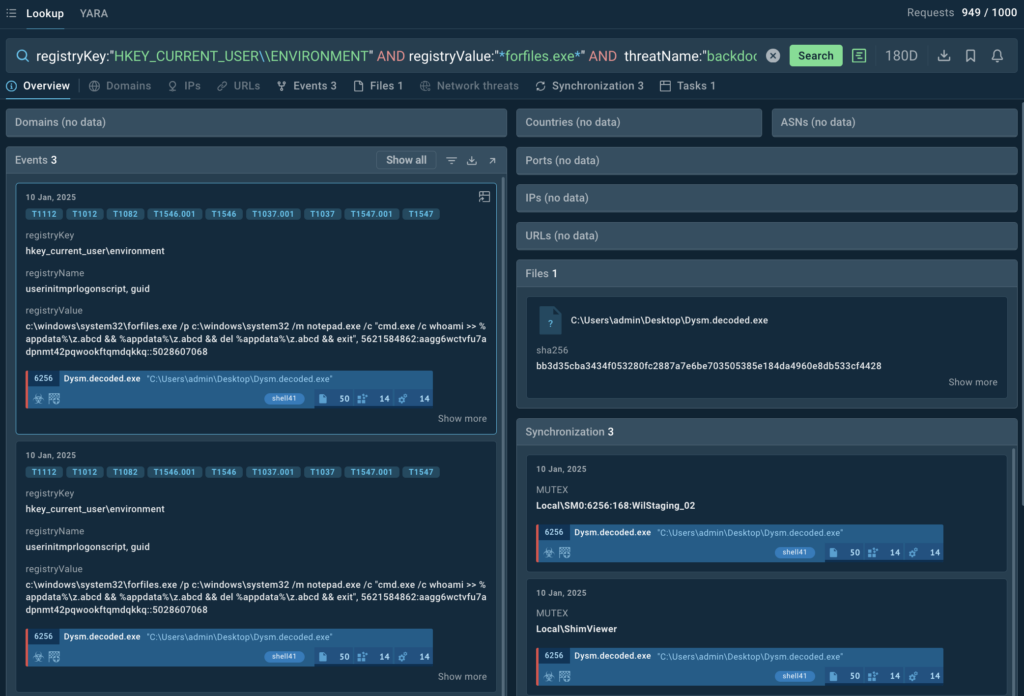
From the search results, we can extract additional IOCs associated with such campaigns, like file hashes or mutexes, and use them for setting up threat detection and alerts.
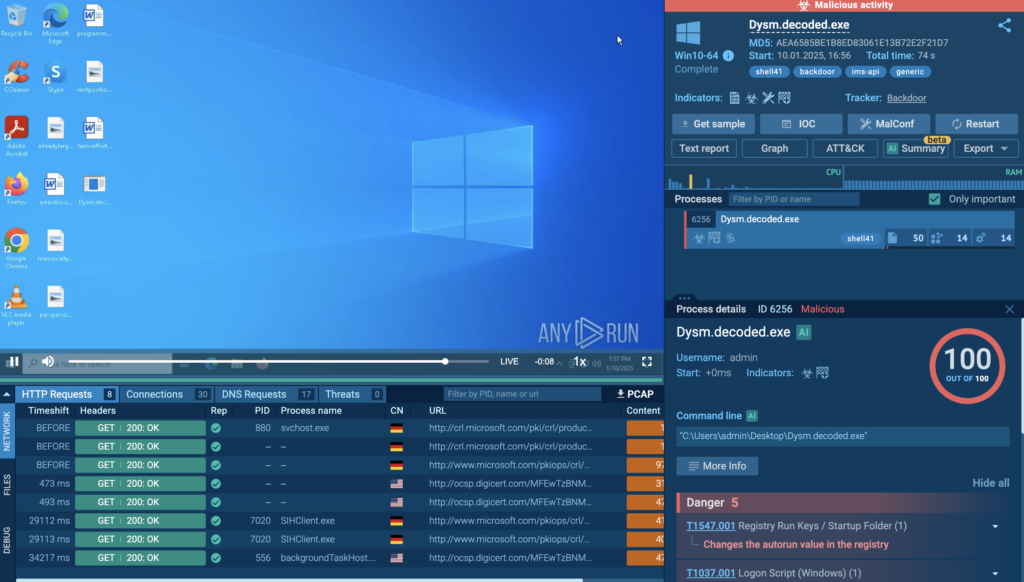
The Tasks tab shows recent sandbox sessions with analysis of the attack. The sessions can be viewed in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to study TTPs and other components of the attack.
MuddyWater APT: Identifying a Backdoor via Mutexes
Another example: MuddyWater APT group from Iran is known for using PackageManager and DocumentUpdater mutexes in their malware campaigns. The mutexes are generated by their BugSleep backdoor.
The attack starts through a phishing email, BugSleep gets deployed, creates a mutex and decrypts its configuration, including the addresses of command-and-control servers. This behavior has been observed in MuddyWater campaigns targeting organizations in Israel and other countries.
We can accommodate both mutexes into a TI Lookup search request:
(syncObjectName:”PackageManager” or syncObjectName:”DocumentUpdater”) and syncObjectOperation:”Create” and threatName:”muddywater”
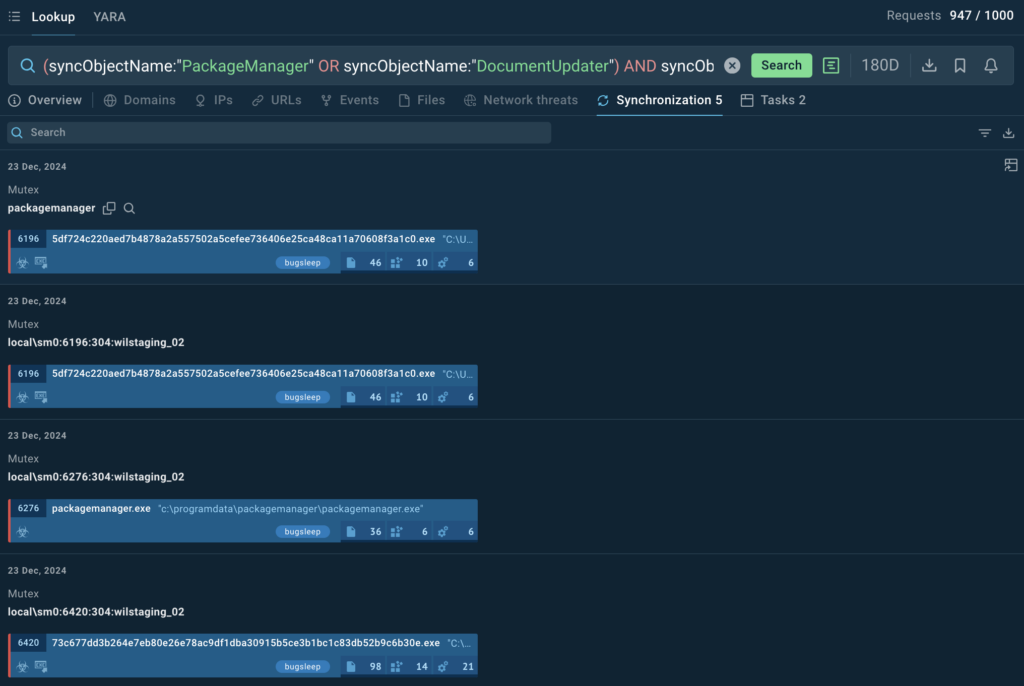
Diving deeper in the search results, we can identify the actual samples that use this mutex.
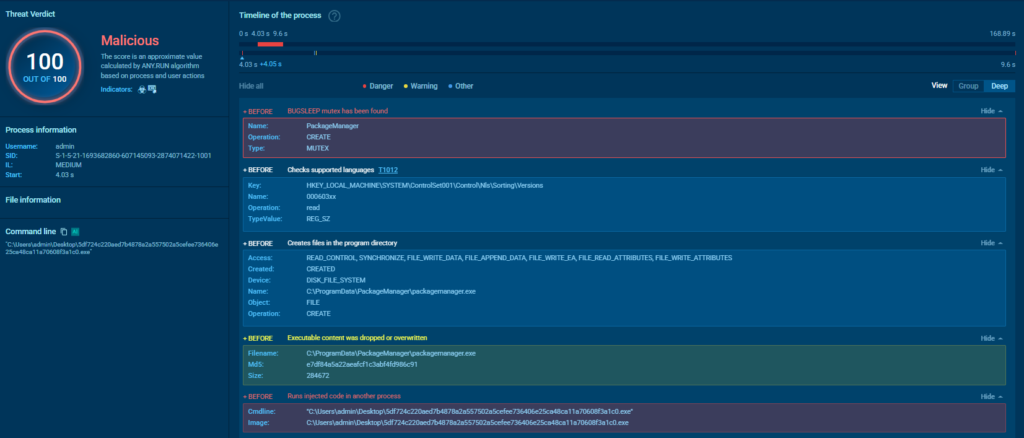
We can navigate to the sandbox sessions where these mutexes were used to explore the threat and its behavior in greater detail.

Learn to Track Emerging Cyber Threats
Check out expert guide to collecting intelligence on emerging threats with TI Lookup
Lazarus Group: Following North Korea’s Biggest APT
Lazarus is one of the most active threats coming from North Korea. The group has been involved in many cyber attacks on both businesses and individuals. One of the recent examples involved conducting fake interviews with tech professionals to install malicious programs on their devices.
With TI Lookup, we can not only explore the most recent samples and collect indicators related to Lazarus but also subscribe to receive updates on specific queries.
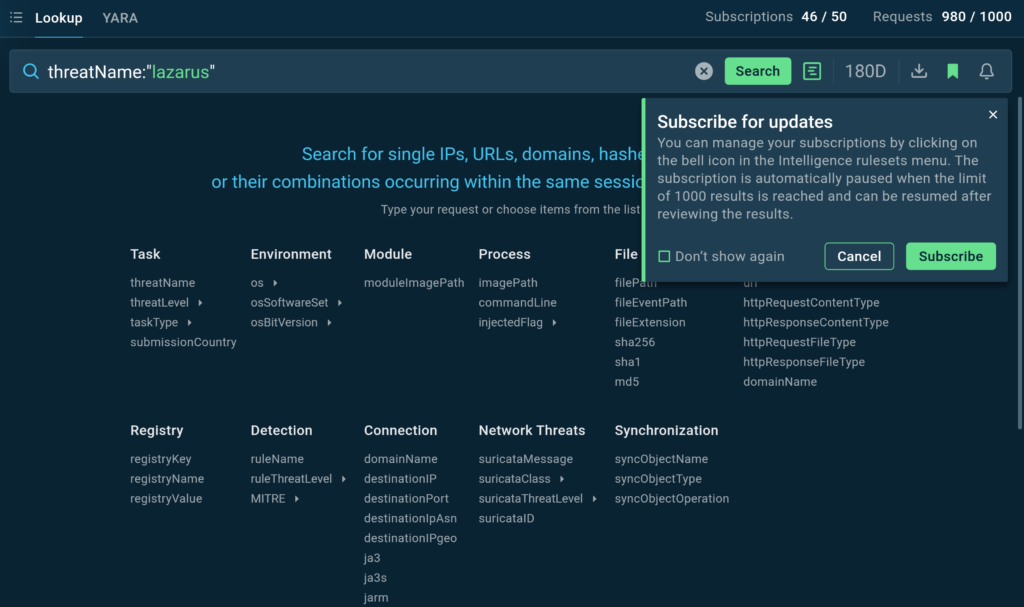
Let’s use the simple query like threatName:”lazarus” and click the bell icon to subscribe to updates.
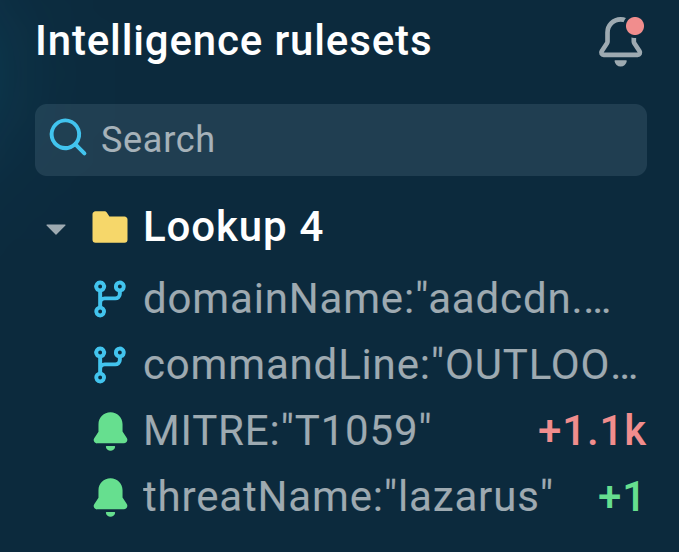
As soon as new indicators or sandbox sessions relevant to the query appear in TI Lookup’s database, we will be notified about them.
Learn more about notifications in TI Lookup
Conclusion
APTs represent a high level of cyber threat due to their strategic nature, the resources behind them, and their capability to adapt and evolve over time. Organizations, especially those in critical sectors or handling sensitive information, need robust cybersecurity strategies to defend against such threats. Threat intelligence is a cornerstone of such a strategy, and TI Lookup from ANY.RUN has proven itself as a comprehensive tool for fueling intelligence with fresh contextual data.
About ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN helps more than 500,000 cybersecurity professionals worldwide. Our interactive sandbox simplifies malware analysis of threats that target both Windows and Linux systems. Our threat intelligence products, TI Lookup, YARA Search, and Feeds, help you find IOCs or files to learn more about the threats and respond to incidents faster.






0 comments