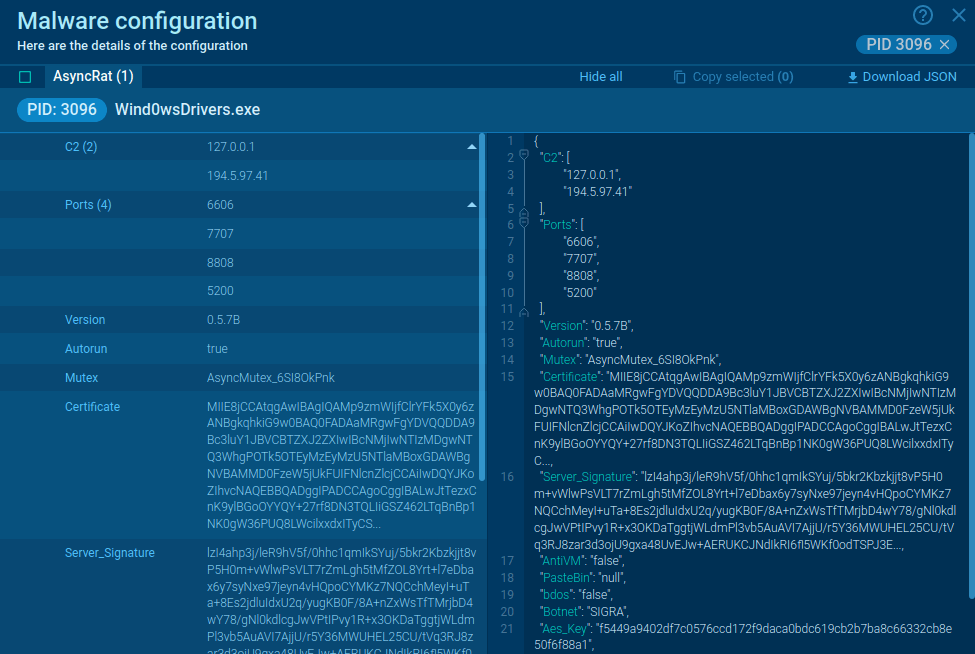
What is IcedID?
IcedID is a banking trojan-type malware that allows attackers to utilize it to steal the banking credentials of the victims. IcedID aka BokBot mainly targets businesses and steals payment information, it also acts as a loader and can deliver other viruses or download additional modules.
Researchers identified IcedID for the first time in Autumn 2017 when the first victims suffered from attacks by this malware. Upon further investigation, researchers revealed that IcedID is a modular virus that carries very advanced functions. In addition, it was initially reported that IcedID does not seem to feature any borrowed or stolen code from other trojans which is atypical for more developed malware samples like the one we are dealing with today.
General description of IcedID malware
It is thought that IcedID is being operated by a group of threat actors with connections to Eastern European cyber-bands. In addition, criminals behind IcedID are known to collaborate with creators or distributors of Emotet and TrickBot.
IcedID attacks are targeted mostly at banks in North America and a few select banking organizations in the United Kingdom. This malware targets mostly corporate bank accounts, payment card providers, mobile services providers, payroll, webmail, and e-commerce sites. We were not able to find any information about attacks directed at private users at this point.
However, this very well might change at some point in the future as evidence suggests that the criminals behind IcedID are preparing new and, possibly, bigger campaigns. There have appeared several removal tools, so it's no wonder hackers try to level the game up. As a matter of fact, network propagation functionality was added to this malware, giving it the ability to move across various endpoints.
Speaking of additions, IcedID is being actively maintained and upgraded by its authors despite several removal tools. For example, the second version of the virus significantly reworked the code and made the IcedID modular, giving it the ability to fetch plugins on-demand after the execution of the base file. This made the virus much harder to detect and defend against. While it is generally believed that this virus relies 100% on code created from scratch, some researchers suggest that the malware does, in fact, reuse code from version 2.0 of Pony malware. Apparently, the borrowed function is in charge of stealing data from email accounts although Pony code may have been used for other applications within the virus.
Unfortunately, constant upgrades are most likely one of the leading factors that contributed to the rising popularity of this trojan. This is bad news especially considering that this trojan is already using extremely advanced techniques as complex web injects.
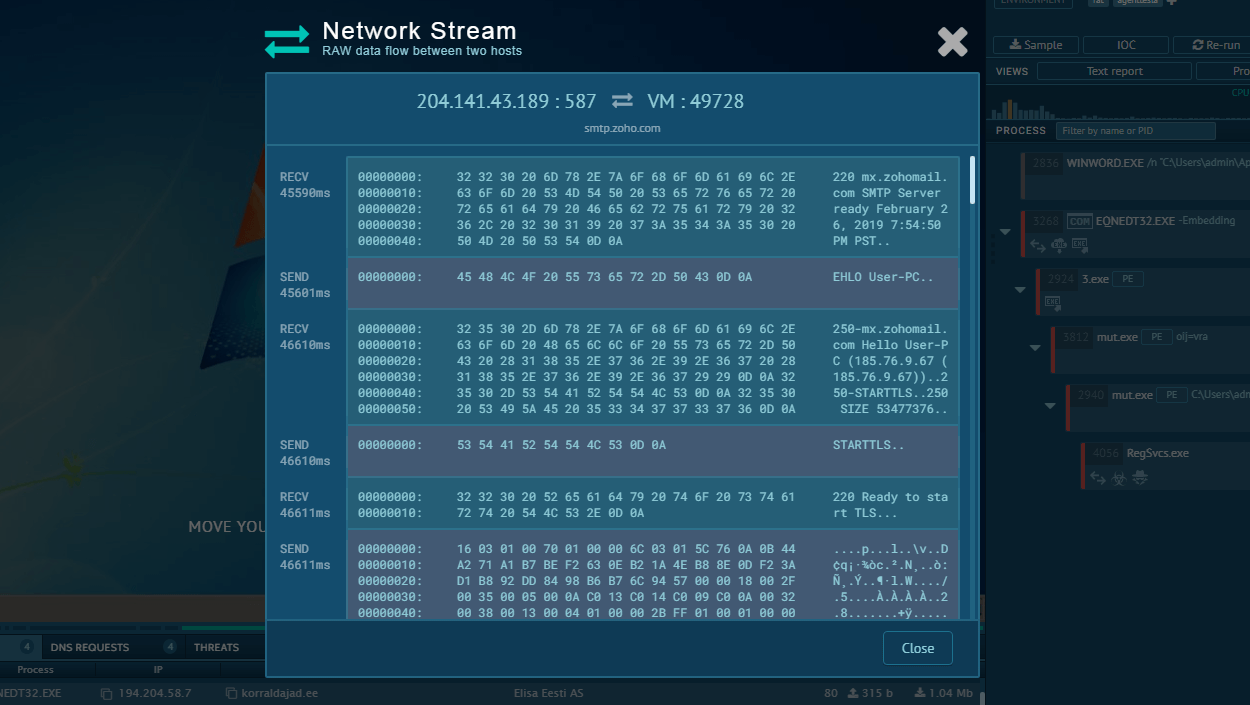
Once the execution process is complete, IcedID creates a local proxy to intercept and control all web traffic of the infected user.
When the malware detects that a victim is navigating to the bank's website, IcedID can redirect the user to a replica of the webpage located on the server that is controlled by the attackers. Threat actors carefully reconstruct the webpage and make the experience as seamless as possible for the victim by maintaining an active connection with the real website all the time. This allows IcedID to use the correct URL in the address bar and even display a legit SSL certificate.
Of course, from this point on every action of the user is being recorded and social engineering is used to retrieve as many credentials and administrative information as possible.
IcedID malware analysis
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service shows the execution process of IcedID. Users can utilize this information to take a deep dive into how this malware functions under the hood.
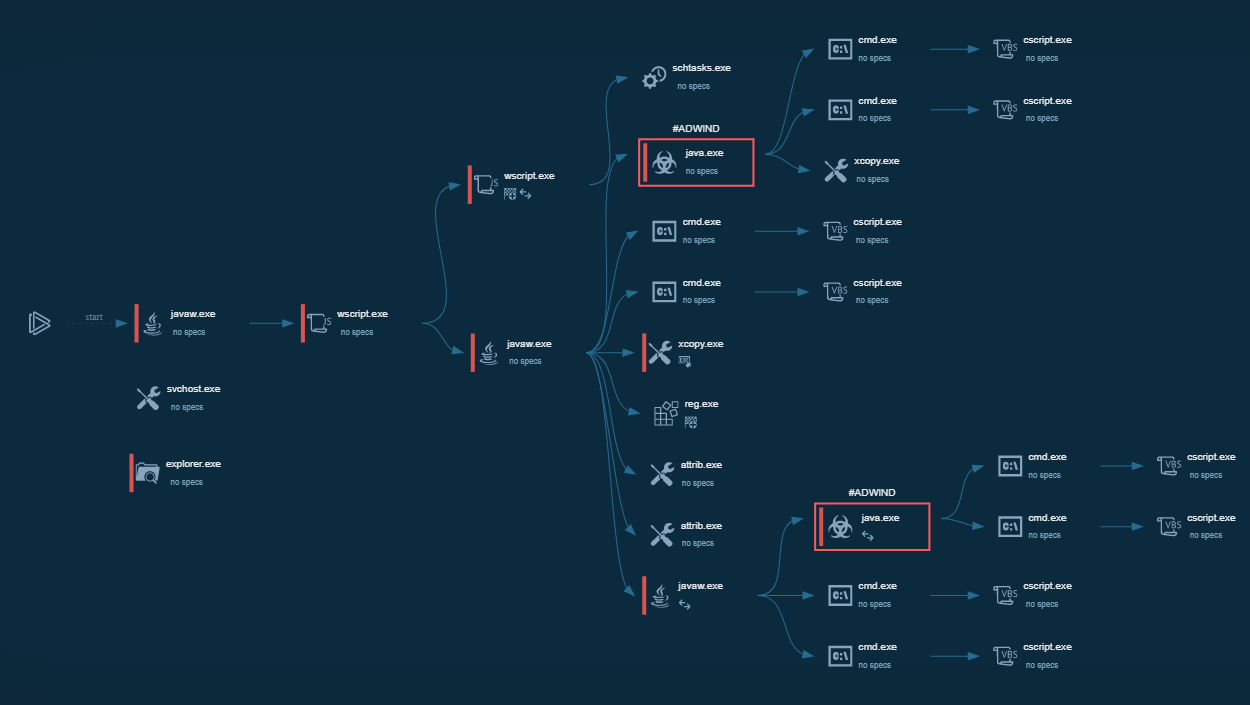
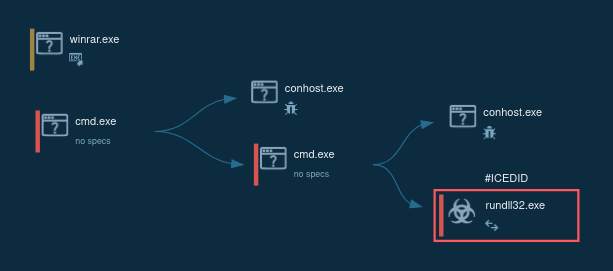 Figure 1: Shows the graph of processes generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service.
Figure 1: Shows the graph of processes generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service.
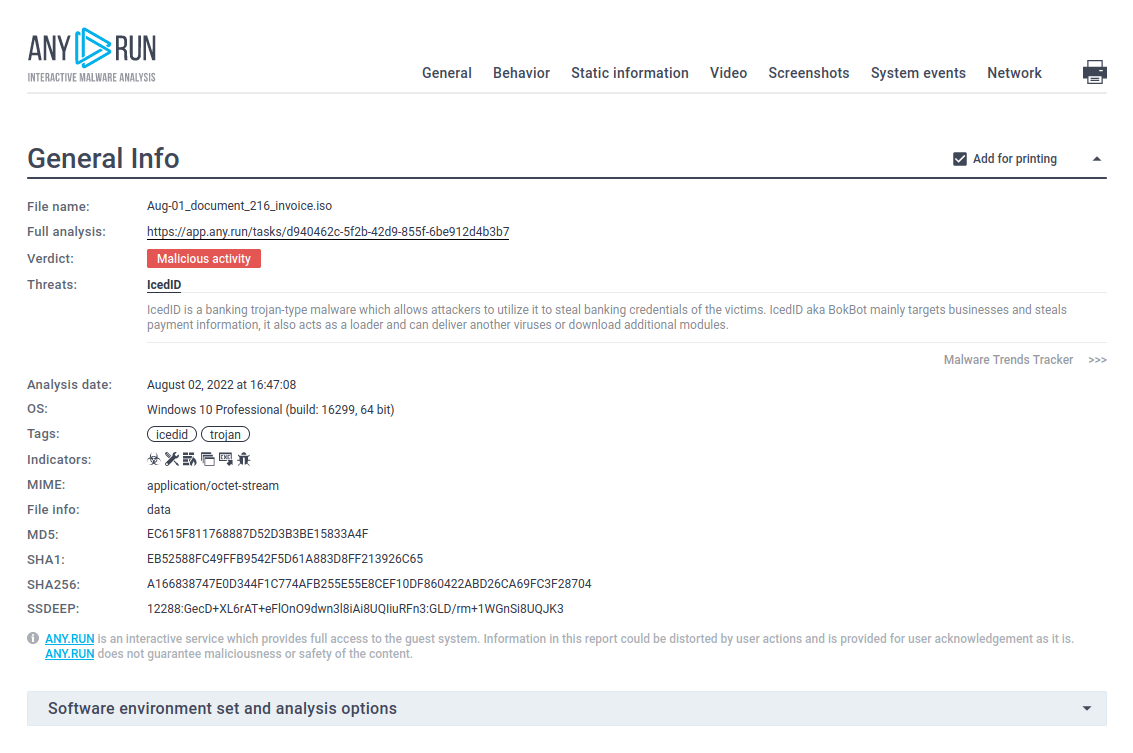 Figure 2: ANY.RUN allows creating customizable text reports that contain detailed and nicely structured information. This function is perfect for making presentations.
Figure 2: ANY.RUN allows creating customizable text reports that contain detailed and nicely structured information. This function is perfect for making presentations.
IcedID execution process
IcedID authors constantly make changes to the malware, so its execution process can dramatically vary from one version to another.
Our example was distributed in the form of a malicious Microsoft Office document with macro. Maldocs macro dropped an obfuscated command-line file and started its execution. Wscript.exe was started through the command-line execution process to download the payload which was, in turn, executed by cmd.exe. After the payload started its execution, it injected into the svchost.exe process which, then, activated malicious activities such as stealing personal data, establishing a connection with the C2 server, creating scheduled tasks, and more.
Distribution of IcedID malware
IcedID uses a typical delivery method for banking trojans — attackers distribute it in malicious Microsoft Office documents that prompt the users to enable macros and, once it is done, activate the download of the executable to the victim's machine.
The unique aspect of IcedID distribution campaigns lies in the meticulous approach to email crafting that threat actors employ. While most malware types that use email campaigns as the mains distribution channel tend to target the broadest audience they can, IcedID authors choose to work with much narrower focus groups and craft every email with greater detail than the usual standard in the industry.
While any email with a malicious attachment is designed to lower your guard and make you download and open the file, usually attackers pick very general topics with little to no personalization.
IcedID authors use spear-phishing techniques, meaning that they learn details about their victims and use them to increase the effectiveness of their emails. If a latter carrying IcedID is directed at a car dealer from Arizona, it is likely to contain information about a car dealership in Arizona, references to local companies or even colleagues of the victim.
The creation of such targeted campaigns requires hackers to devote time to investigative work in preparation for each bunch of emails, but it is guaranteed to make messages look less like a scam and more like legit business communication.
It should be noted that in some cases IcedID may infect the system in tandem with other malware samples. It can download and can be downloaded by malware such as Emotet or TrickBot trojans.
How to detect IcedID?
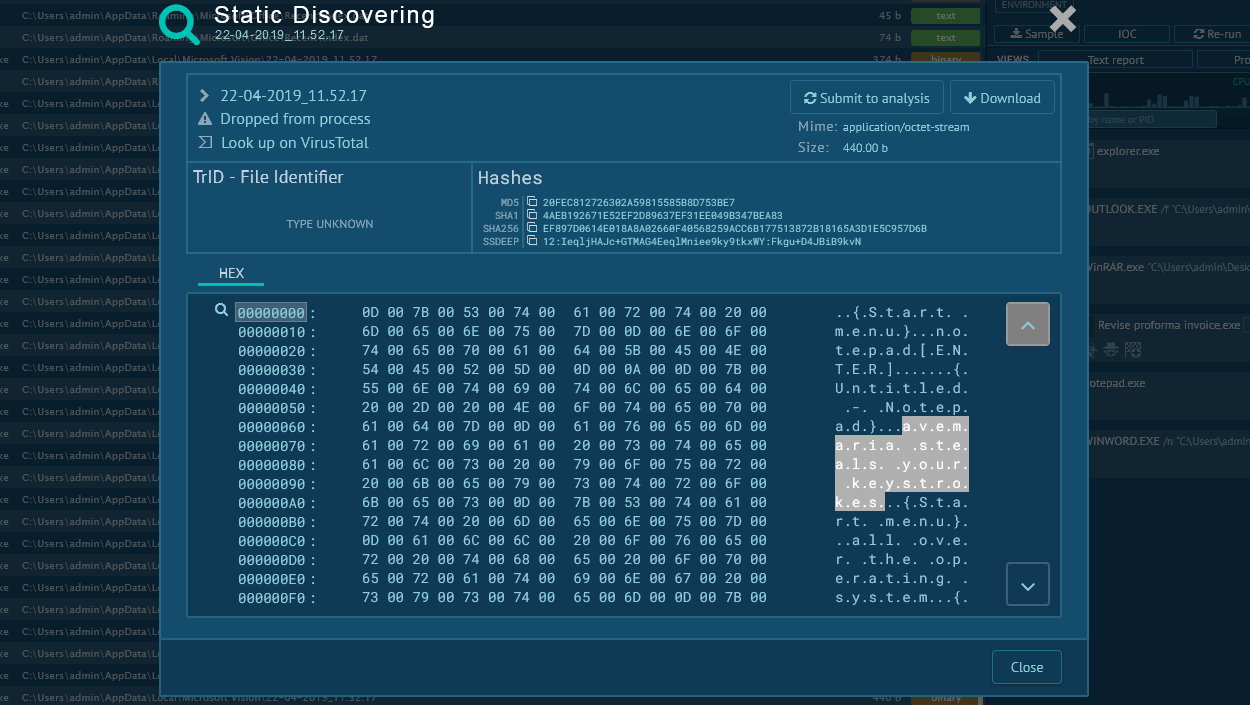
This malware creates files that allow analysts to detect it with a high degree of certainty. To detect IcedID, Open the "Files" tab in the lower part of the task's window and take a look at the created files. If you see folders with names such as "lchej" and "ydmfipkzqfsb" within C:\Users\admin\AppData\Local\ directory and files with names "pczapabclgpba", "mtkdonmlmxelaa", "ozwzefgpkzmzba", and "zcnejolyretaa", as shown on the figure below, be sure that it is IcedID in front of you.
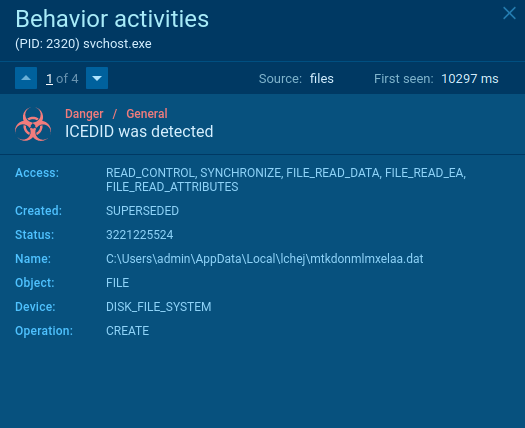 Figure 3: File created by IcedID malware
Figure 3: File created by IcedID malware
Summary
IcedID trojan is one of the examples of the new generation of malware. Although it was built from the ground up by its creators, it uses a lot of unique code and has functions not much inferior to those found in the most advanced older viruses such as Trickbot.
However, what makes IcedID potentially even more dangerous is the evolved mentality of its authors, who use spear-phishing to increase the effectiveness of their distribution campaigns.
Before, we could secure ourselves from a lot of threats by removal tools and raising awareness about the dangers of suspicious emails and infected documents. With IcedID we need to rely more on technological lines of defense since some email templates that authors have used and will use again are indistinguishable from real professional communication.
Here, at ANY.RUN it is our job to provide cybersecurity researchers with all the necessary tools to study and neutralize threats like IcedID and we hope that you will find these tools extremely useful in your line of work!



 0
0