We’re excited to launch a new monthly update format that gives you a closer look into the work we’ve done in the last 30 days.
In addition to releasing several new features, this past month, here at ANY.RUN, we focused on improving threat detection, adding new rules and contributing to the ET Labs community.
Let’s jump right in — there’s a lot of ground to cover.
Product updates
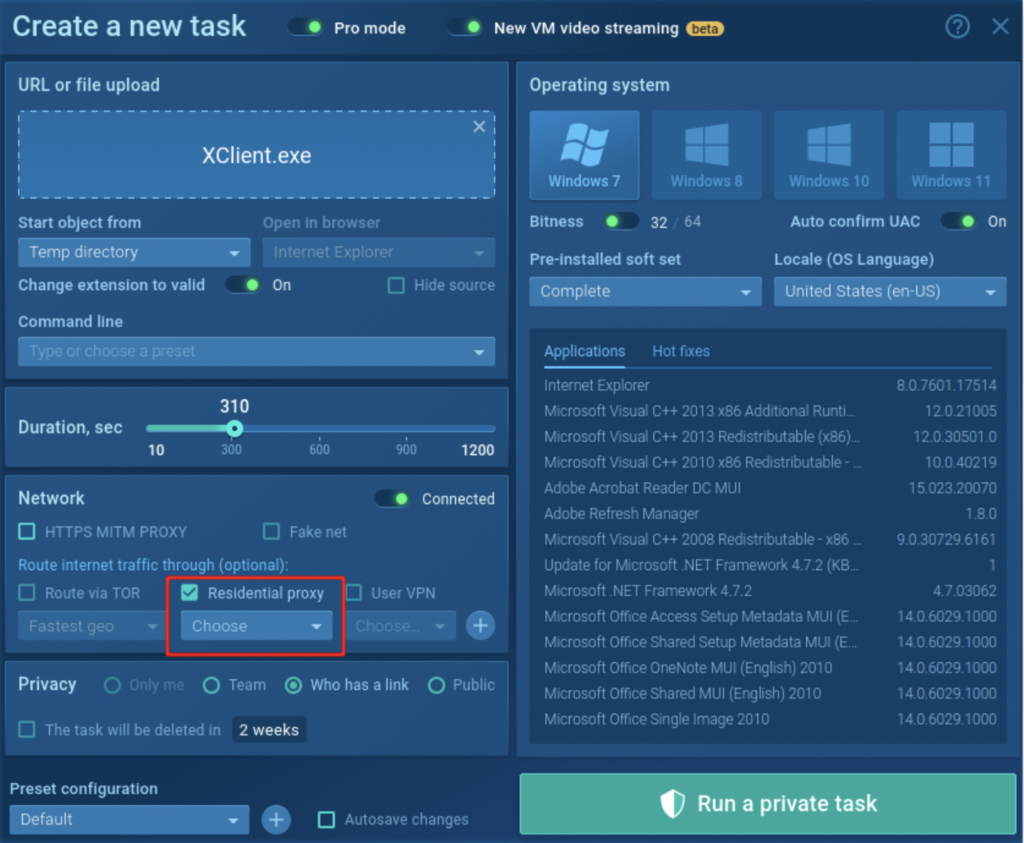
- Residential Proxy You can now assign a home user’s IP to virtual machines and change the location, making it easier to work with geo-targeted samples and evade detection.
- Updated default browsers. On Windows 10 and 11 machines, we’ve changed the default web browser to Edge, instead of the previously used Internet Explorer.
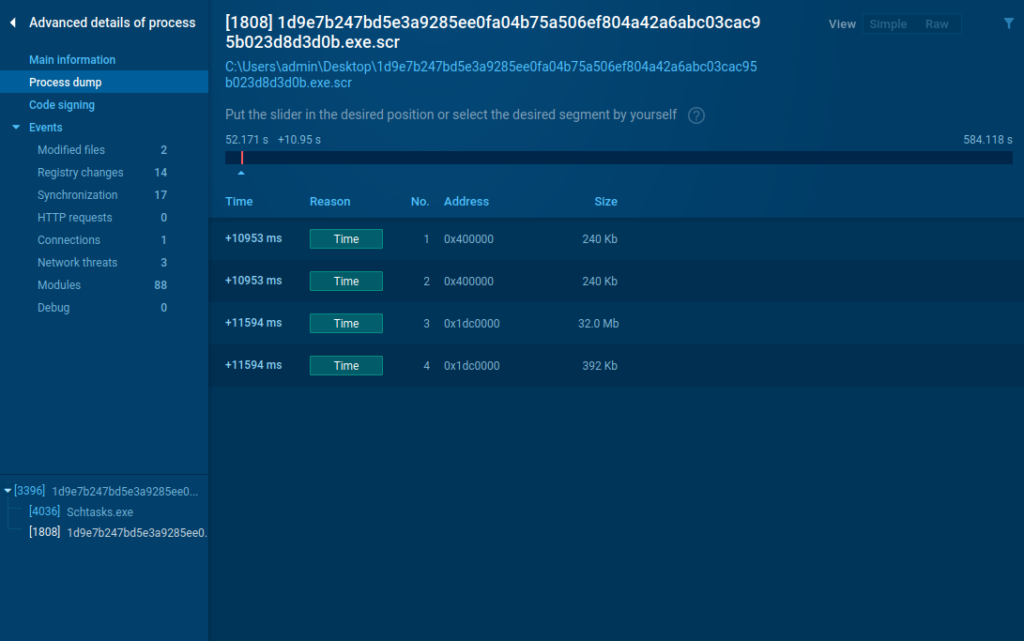
- Downloadable memory dumps. You can now download memory dumps and analyze them locally. This option is available under the “Advanced details” section of the process window.
Malware config extractors
We’ve added 4 new extractors to the sandbox:
PrivateLoader
Privateloader is a loader that distributes a wide variety of malware types. Some samples are covered by VMprotect. All of PrivateLoader’s important strings are encrypted with an XOR key. We’ve implemented a fix which now allows you to extract C2 and payload.
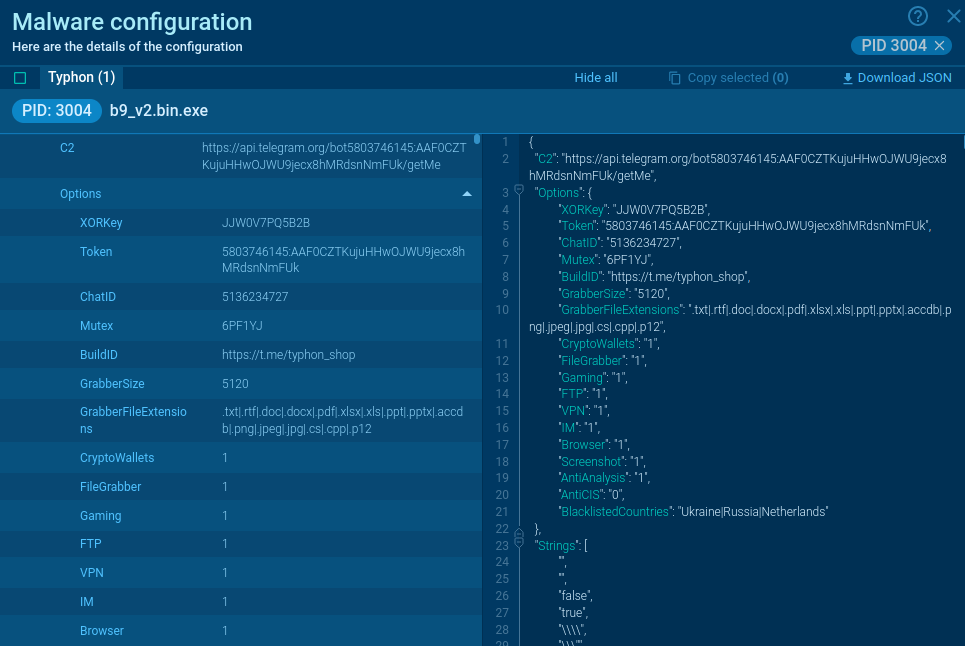
Typhon
Typhon is an info stealer. A year ago, the revamped second version of V2 Reborn was launched. This iteration involved a complete overhaul of the code, and now it boasts an expanded set of anti-analysis features such as process detection, emulation, and virtual machine capabilities, among others. Moreover, it presents a broad array of methods for data theft.
LaplasClipper
LaplasClipper is designed to monitor cryptocurrency wallet addresses on a victim’s clipboard. When it identifies an address, it communicates this information to the C2. The server then generates a similar wallet address and replaces the original one on the victim’s clipboard.
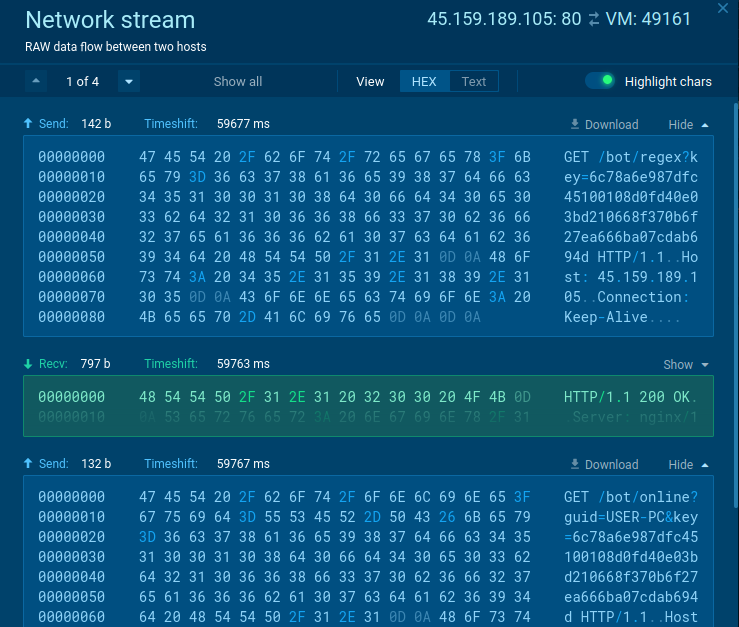
LummaStealer
We’ve introduced the capability to detect and extract configurations of LummaStealer, an information-stealing malware that targets data from browsers, wallets, and more.
It communicates with its command and control (C2) server via a POST request along the /c2sock route, carrying data in multipart/form-data format, and sends information such as HWID, LummaID, PKZIP with stolen data, and an obscure PID.
In recent times, we’ve come across variants of Lumma Stealer written in C++, likely wrapped with Pascal/Delphi in a manner similar to Inno Setup. We’ve noticed a surge in the number of samples in .pif format. Inside the original .exe file (which is sometimes Inno Setup), there lies an encrypted and obfuscated script (akin to AutoIt) that is extracted to the %temp% directory. This script then produces a .pif file (which is in actuality a PE file), which subsequently executes.
A new variant has emerged as well. In the past, the configuration was stored internally within the malware. However, it is now delivered from the C2 server. The malware accesses its C2 server via the /c2conf route and receives a base64 response, which contains a 32-byte XOR key and an encrypted JSON.
Here are some useful links if you want to dive deeper into this malware:
AgentTesla‘s updates
AgentTesla is a prominent spyware strain that has been making rounds in the cyber threat landscape for several years. It is essentially a keylogger and information stealer, often used by cybercriminals to extract sensitive data, such as login credentials, system information, and credit card details. We completely updated the malware’s config extractor.
YARA rules
We released YARA rules that detect gh0stbins and zgrat
New Malware and Threat Detection Rules
- 367 new detection rules added. We’ve significantly increased threat coverage of our sandbox.
- QuasarRAT connection detection. We now detect QuasarRAT connections in GCM_SHA384, CBC_SHA384, and RAW TCP encryption modes.
- Added 9 rules to detect suspicious PowerShell scripts. We’ve created 9 new rules to help identify potentially malicious PowerShell scripts.
- Gh0stCringe tool detection. We’ve written 9 rules to detect this tool, including a content-agnostic universal rule.
- Exfiltration to Discord and Telegram. Detection of data exfiltration attempts into these platforms is now available across all pricing plans without decrypting the traffic.
Increased threat coverage
- Bibleoteka backdoor discovery. We uncovered a new Bibleoteka backdoor while investigating zgRat activity and improved our threat coverage.
- PseudoManuscrypt access. We introduced a rule to detect attempts to access PseudoManuscrypt’s C2 server.
- Malware on file-sharing services. You can now detect malicious content stored on file-sharing services like OneDrive.
- Faster Xworm detection. You can now identify Xworm in the first client packet.
- Response to Medusa Stealer. To tackle this emerging threat, we’ve established comprehensive coverage.
Detecting even more threats
- GoGateway identification. Added the ability to detect GoGateway, a rare, previously untagged gateway written in Go.
- PE EXE files detection. We created a large pull of 255 rules, all generalized into one under the 8000467 number. They will help you to detect encrypted executable files of this format.
- SilverFox Group’s tool detected. Thanks to our community for their help detecting this tool.
- Better phishing HTML page detection. We enhanced our ability to detect phishing attempts from HTML pages containing stolen user credentials.
- We’ve introduced a new signature to detect UxCryptor
Sharing Threat Intelligence with the Community
- LummaStealer detection rule shared. We shared the rule that detects LummaStealer’s C2 server configuration request with the ET Labs community.
- New Phonk signature. We wrote a signature for Phonk a trojan frequently submitted to ANY.RUN.
- Graphican backdoor investigation. We probed into the Graphican backdoor, an evolution of the old Ketrican malware, now using Microsoft Graph API and OneDrive.
- Unauthenticated connection rules. We expanded our detection capabilities with rules for unauthenticated SOCKS5 and VNC connections.
We’ve also shared rules that detect the following threats with ET Labs:
Software Threat Identification
- Threat detected in TektonIT’s RMS program. Threats embedded in legal software are highly dangerous. In this case, adversaries seem to have exploited an encrypted Microsoft Cabinet to store malicious libraries. The new rule classifies under the STEALER category and is an extension of the existing ETPRO MALWARE Win32/RA-based.NLR Exfil rule.
- StatusRecorder stealer discovery. We found this previously unrecognized stealer, wrote a detection rule and shared it with the ET Labs community.
- BitRAT TLS traffic activity detection. We’ve improved detection of BitRAT TLS traffic and created associated rules.
Our team works hard to keep up with emerging threats, ensuring that ANY.RUN detection remains industry leading. This happens largely behind the scenes, and we haven’t written about it a lot. Did you find this sneak peek useful? Let us know in the comments below. We’ll keep regular updates coming.
To try these new rules in action in ANY.RUN. Request your 14 days free trial →







0 comments