Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


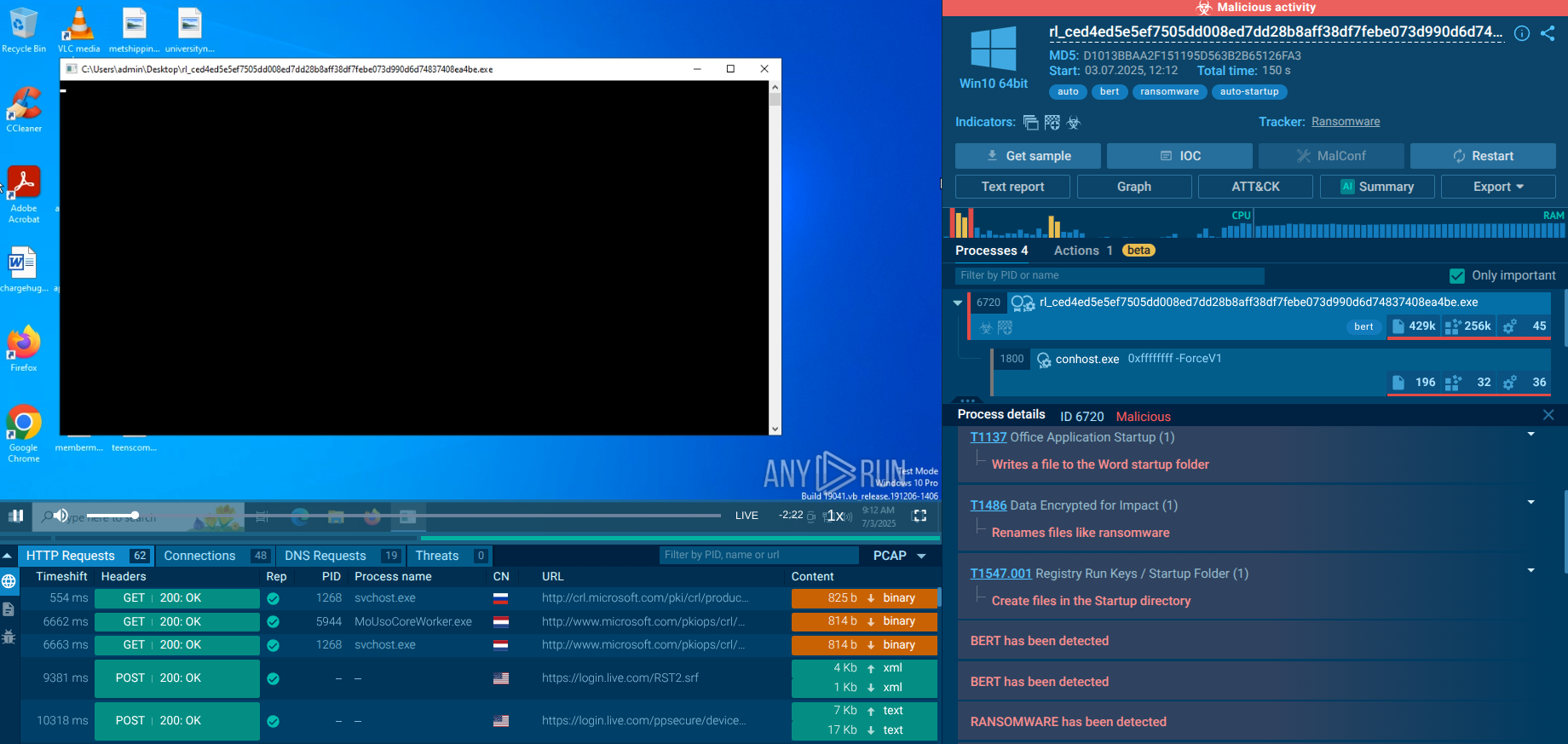
Glupteba is a loader with information-stealing and traffic routing functionality. It is designed primarily to install other viruses on infected PCs but can do much more than that. In addition, it is being constantly updated, making this virus one to watch out for.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2011
First seen
:
|
5 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2011
First seen
:
|
5 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 446
446
 0
0

 2339
2339
 0
0

 4522
4522
 0
0
Glupteba is a dropper — it is commonly used to install other malware samples on infected machines. Although it was initially thought that Glupteba was developed to be a part of a malicious campaign codenamed Operation Windigo, researchers now believe that it is independent malware.
Although Glupteba trojan classifies as a dropper it has some additional dangerous functions. For example, it has the ability to steal information from infected systems. In addition, it can download a component that is able to control routers and relay traffic.
Furthermore, it seems that this malware is under active development and creators employ dangerous and rarely used techniques to keep their creation active despite various malware removal programs. The reason is probably behind their presumable move to a pay-per-install distribution scheme which means that they must keep the malware relevant to profit from it.
Glupteba malware was first spotted in the wild in 2011 when it was distributed by TDL-4 bootkit among a series of other malware types. The virus went quite for a long time thanks to the malware removal tools until it surfaced again three years later. This time Glupteba was seen in Operation Windigo.
In addition, researchers discovered that command and control domains of Glupteba dropper were hosted on the same machines that powered parts of the Operation Windigo infrastructure. However, the exact connection between Glupteba and Windigo is unclear.
Until recently we didn’t hear much about Glupteba trojan anymore before it surfaced again carrying new, dangerous functionally.
Today, apart from the main dropper functionality Glupteba malware comes with two components: the browsers stealer component and the router exploiter.
The browser stealer comes in two versions that target Chrome, Opera, and the Yandex browser. The malware is capable of stealing cookies and browser history as well as private login credentials.
Then there is the router exploiter component. It exploits the CVE-2018-14847 vulnerability to take control of the routers. This allows attackers to turn compromised routers into SOCKS proxies, which redirect traffic from compromised machines. Thus, infected routers can become relay points for spam distribution and more.
For instance, there is a theory that some of the relayed traffic is part of an attack on Instagram, though it is impossible to tell for sure due to the HTTP encryption.
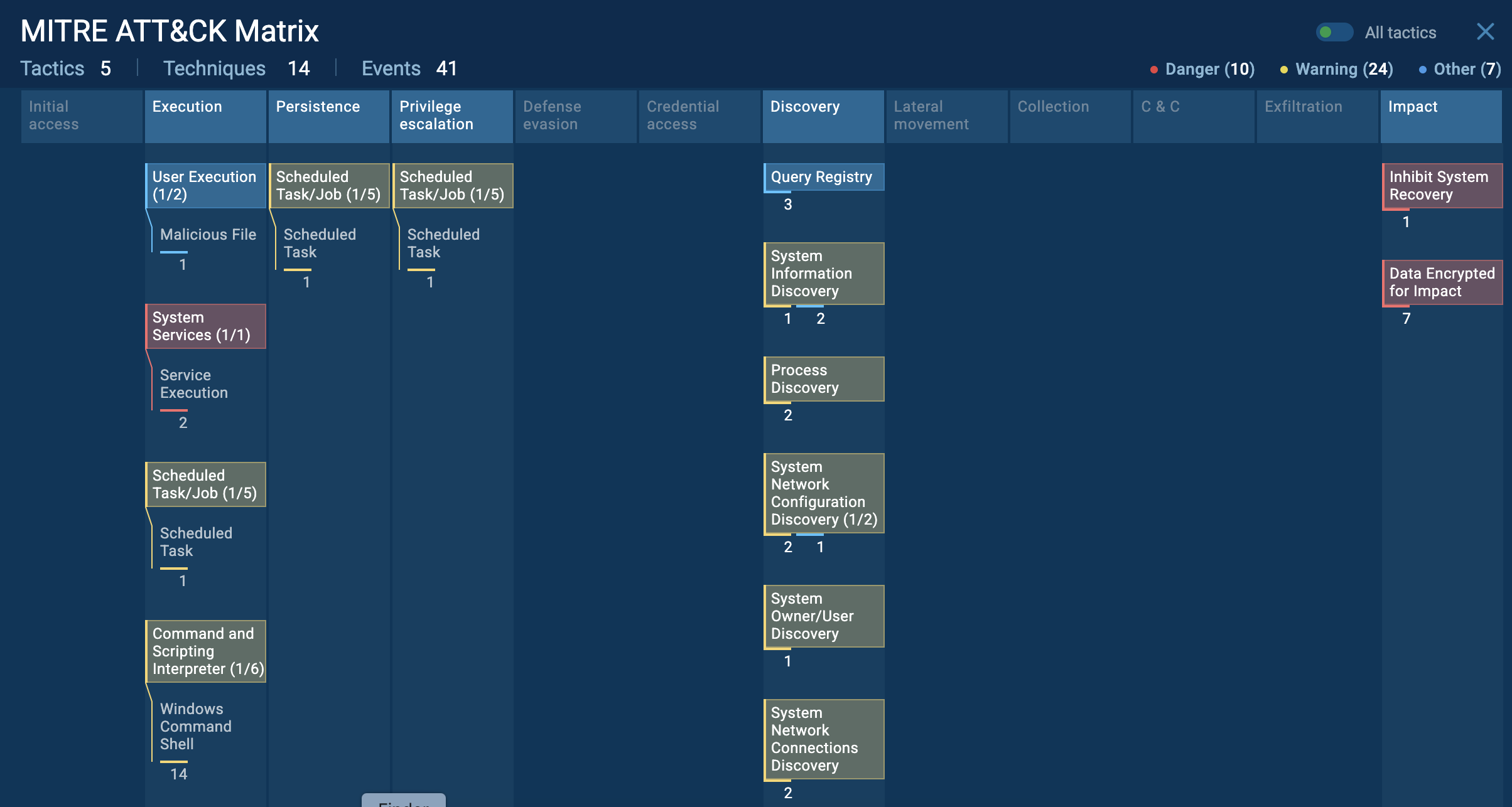
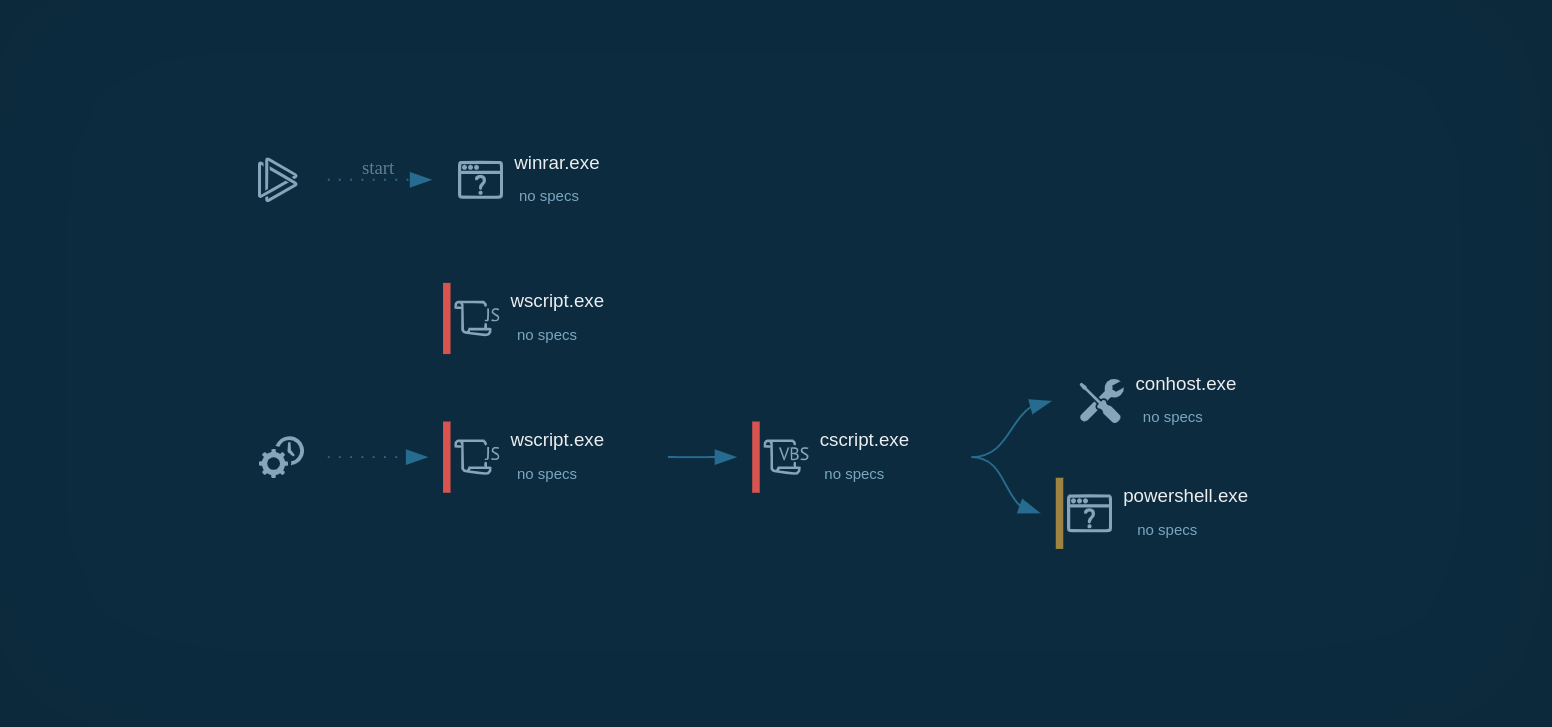
The video generated by the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service shows the execution process of Glupteba. You can also analyze other malicious objects like Ave Maria and Smoke Loader.
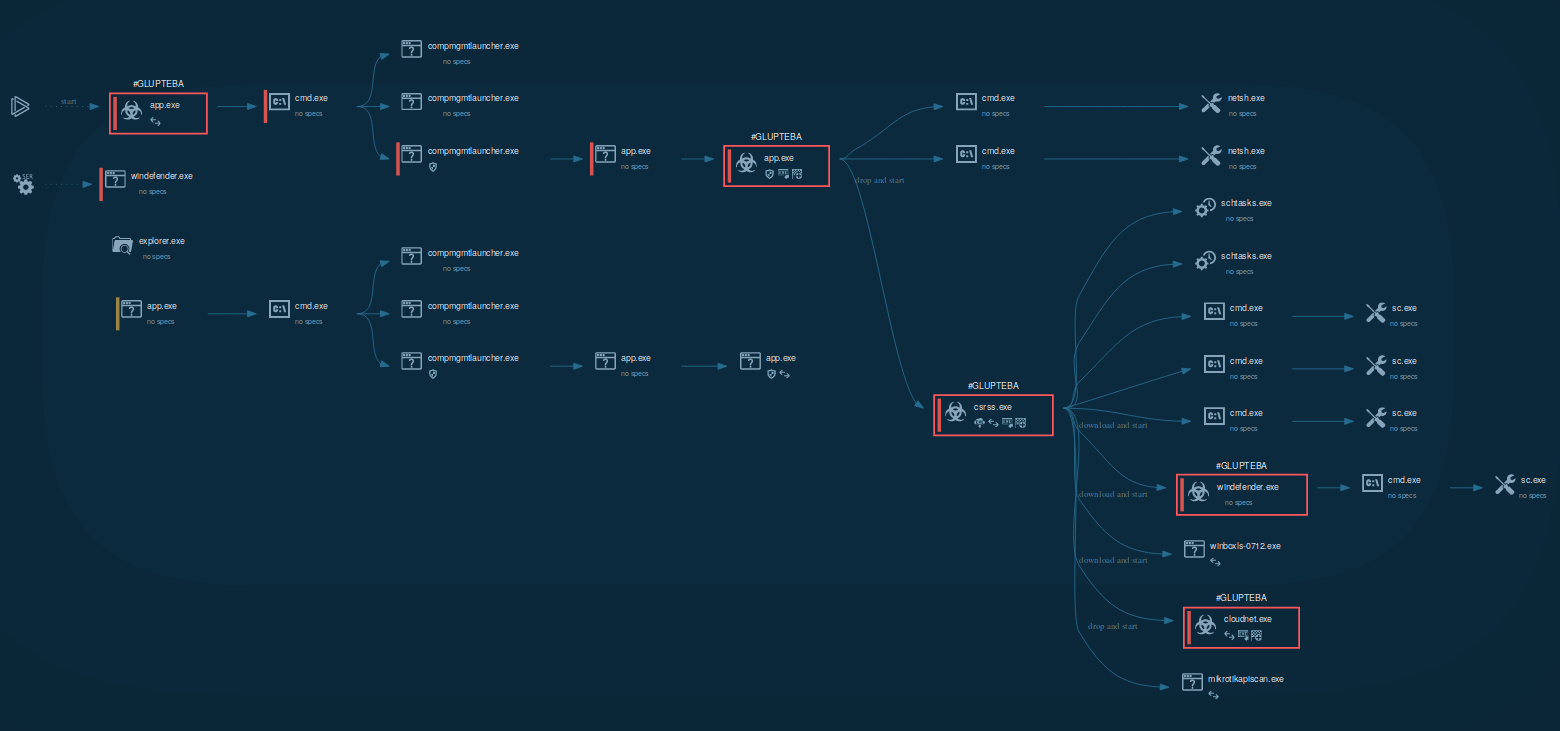 Figure 1: This graph generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service shows processes started by Glupteba Trojan
Figure 1: This graph generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service shows processes started by Glupteba Trojan
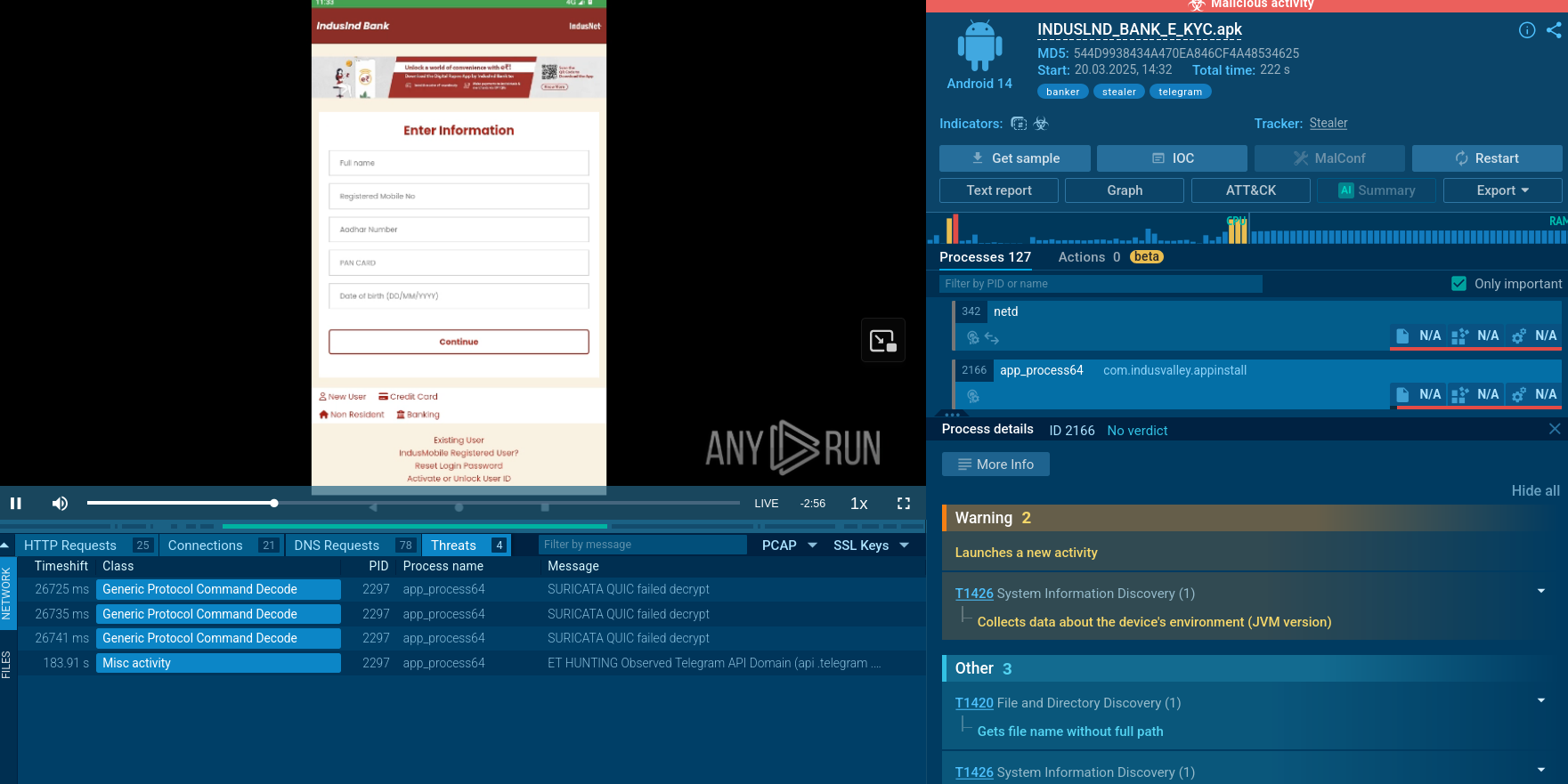
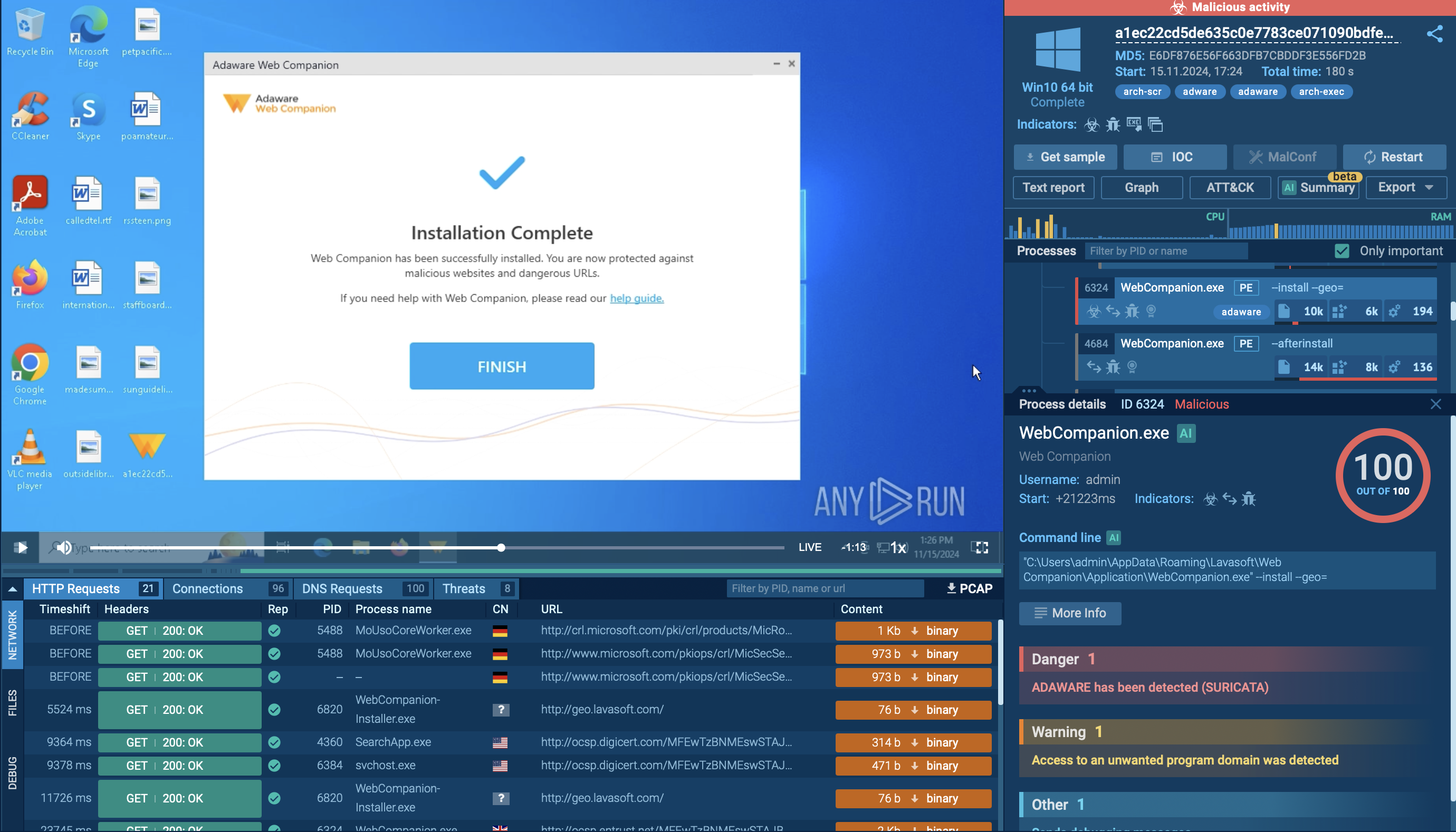
 Figure 2: A customizable text report created by ANY.RUN
Figure 2: A customizable text report created by ANY.RUN
After Glupteba makes its way into the system it's starts CMD.exe process to run CompMgmtLauncher.exe ("Computer Management Snapin Launcher"). The malware uses CompMgmtLauncher.exe to bypass UAC and run itself with administrative privileges. After that, it typically adds itself to autorun in the registry, renames an executable file and copies it to Windows subdirectories. Glupteba also checks the system for anti-malware solutions, adds firewall rules and defender exclusions. In addition to the above, this malware also adds itself to Schedule Tasks to persistence in the infected system. Throughout its lifecycle, Glupteba exchanges packets with the C2 server and has the ability to download other malware.
Glupteba has a rather unique trick up its sleeve that involves no other than the Bitcoin blockchain. It can use transactions in the Bitcoin network to receive C&C domains. This function is triggered on schedule or by demand if there is a need.
It enables the attackers to pass new C&C domains to the malware, allowing it to restore operation by reconnecting to a new domain if something happens to the old one.
It should be noted that Glupteba has a very wide distribution range. Since 2017 it has been spotted in 180 countries, though almost one-third of the attacks were concentrated in Ukraine, Russia, and Turkey.
In the past, the malware was distributed using the infrastructure provided by Windigo’s, however, currently, it is using its own botnet and employes CsdiMonetize adware. The latter downloads another dropper which, in turn, installs the trojan itself.
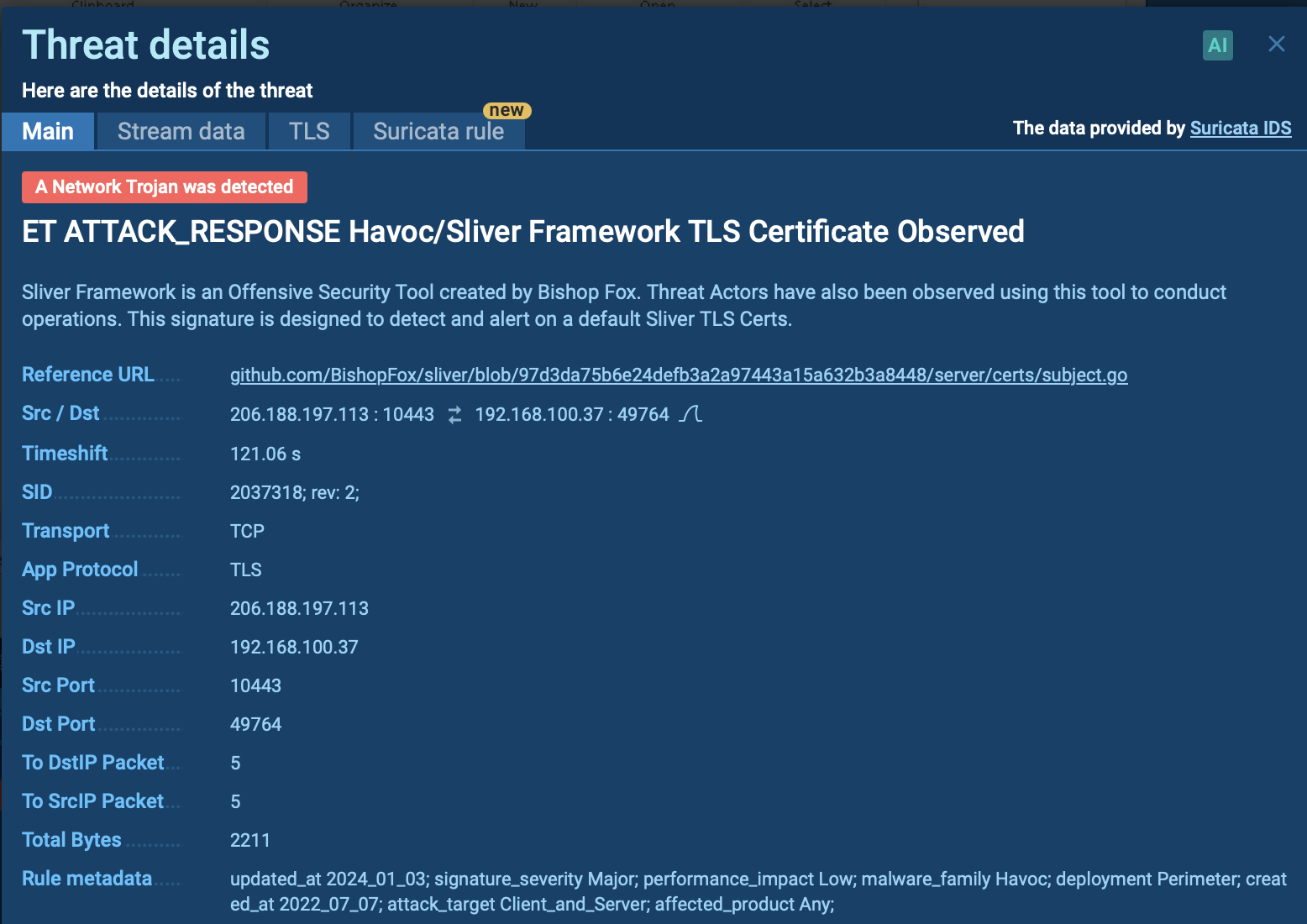
Since Glupteba adds records into the registry, analysts can detect it by looking at registry keys. To do so, choose the process by clicking on it in the process tree of the task then click on the "More info" button. In "Advanced details of process" window switch to the "Registry changes" tab and take a closer look. If the analyzed sample writes a key with the name "UUID" into the key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\TestApp, you are dealing with Glupteba and it's time to get the malware removal program ready.
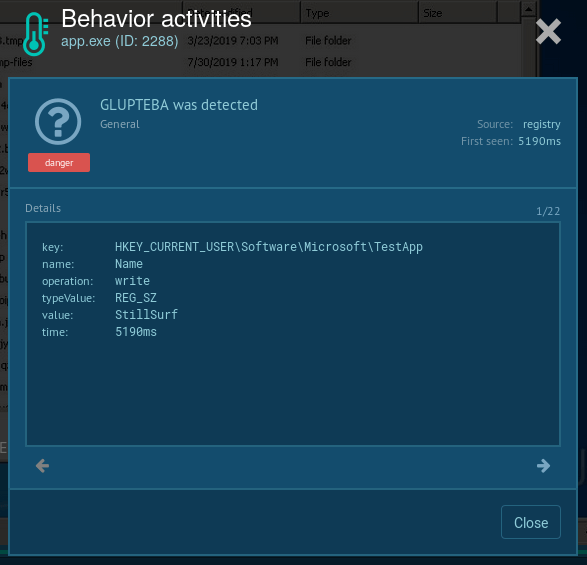 Figure 3: Changes Glupteba made in the registry
Figure 3: Changes Glupteba made in the registry
Glupteba is proving to be a rather dangerous malware that researchers and cybersecurity specialists should not take lightly. Besides its ability to install other malware samples on infected machines, the malware is capable of stealing information from web browser applications. It can also download a component that reroutes traffic by taking control of web-routers.
We also know that this malware uses unique techniques when it comes to C&C communication. And if that was not enough, evidence suggests that it is in active development and attackers seem to be adding more potentially destructive features.
ANY.RUN has prepared a selection of advanced tools that allow to dissect and study a sample of Glupteba in an interactive sandbox environment which gives the researcher an ability to pause the simulation and make corrections at any time. Hopefully, by studying this threat along with many others we will be able to medicate the consensus of future malicious attacks.