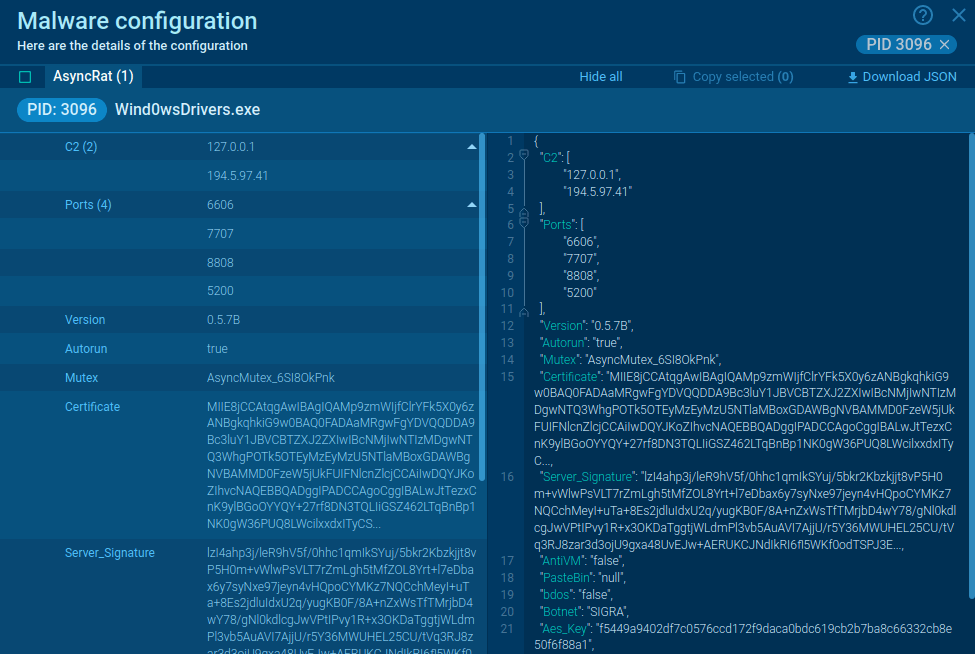
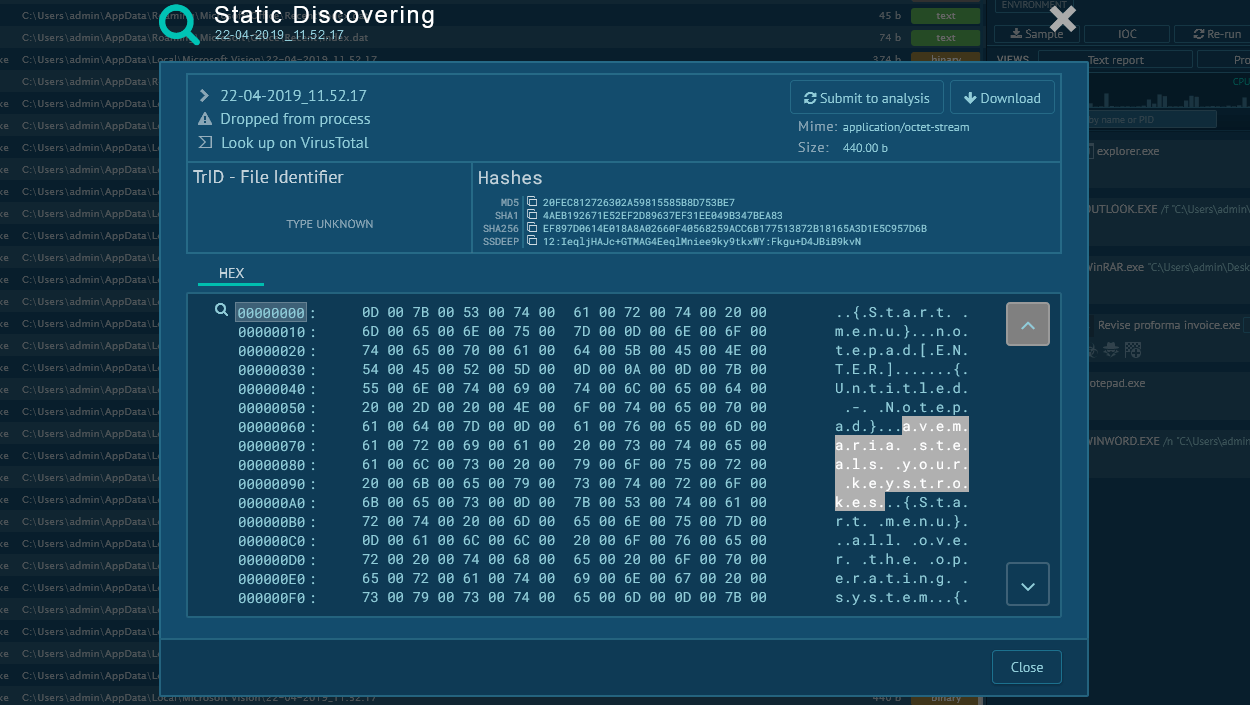
What is LokiBot malware?
LokiBot, also known as Loki-bot or Loki bot, is an information stealer malware that collects credentials from the most widely used web browsers, FTP, email clients, and over a hundred software tools installed on the infected system. It was developed in one of the ex-USSR countries.
The trojan was discovered for the first time on May 3rd, 2015, from a sale announcement made by the creator, and the malware is still active to this day.
General description of LokiBot
Initially created and sold by a hacker known as "lokistov" or "Carter," the first versions of LokiBot spyware used to cost up to $400. However, almost identical malware appeared on hacker forums soon after, available for as little as $80 from several sellers. As it is thought, "lokistov" himself was hacked, and the virus's source code was leaked, allowing others to use its techniques and sell remarkably similar malware.
Curiously, a researcher subsequently found out that the first version of the virus got patched by someone without accessing the source code, which gave the hacker community the ability to set a series of individual domains used to receive the retrieved data.
Even though several versions of the virus exist today, after the analysis, it was found that all of them are actually modifications of the original malware. Interestingly, the server to which LokiBot stealer sends data is unique for every particular malware sample.
In the latest versions of LokiBot, a third stage is added to the process of compromising systems, besides more encryption, a technique to escape detection. Each layer of the trojan is encrypted to attempt to hide the eventual source of code.
The malware uses the known technique of blurring images in documents to force users to enable macros. This trick infects machines quite successfully.
LokiBot malware analysis
A video displaying the simulation of the contamination process created by the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service provides the perfect opportunity for malware analysis to see how the contamination process unfolds on an infected machine. As shown in the simulation, LokiBot trojan needs email attachments, such as a Microsoft Office file or an archive file to be opened to enter an active phase.
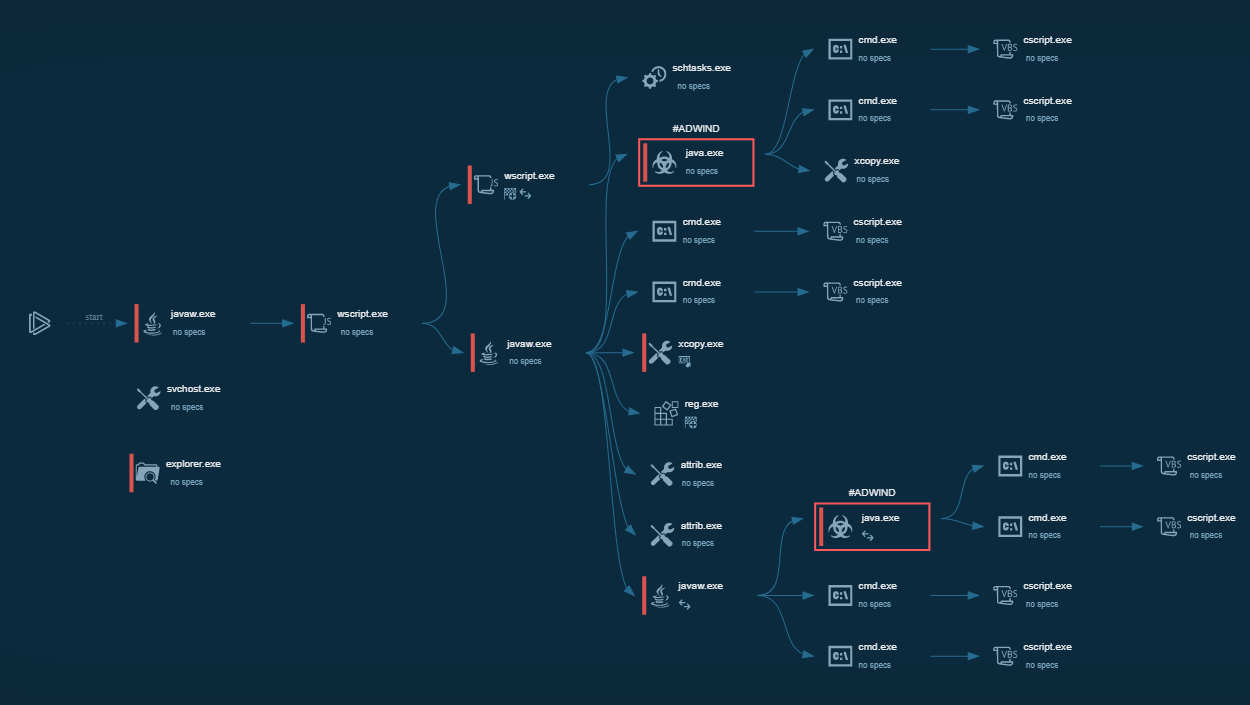
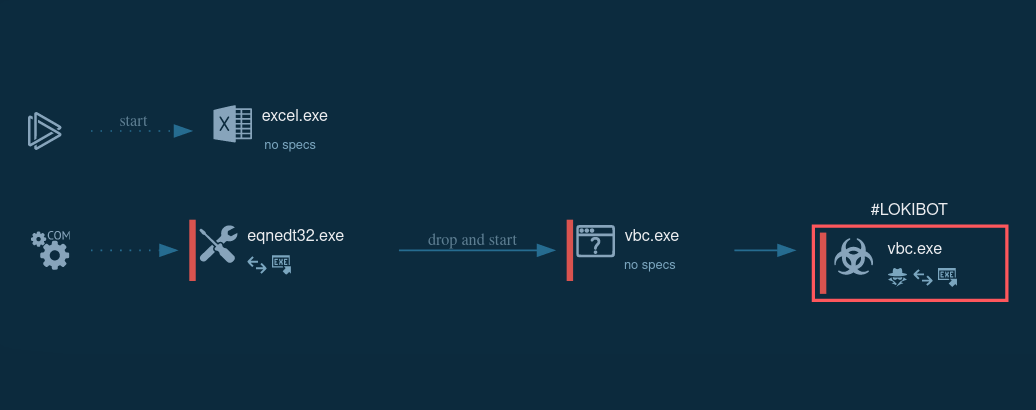 Figure 1: Process graph generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service
Figure 1: Process graph generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service
During the analysis, we found out that the malware life cycle can be broken down into the following stages:
- Contamination. The victim downloads a malicious archive or a Microsoft Office file which eventually downloads the malware;
- Being packed initially, the keylogger unpacks itself and begins the execution of the main payload;
- The virus creates unique loop-functions for each application that it is targeting and saves retrieved data into a buffer;
- Then, a registry key is modified, and the trojan is explicitly copied into a folder with a specific name unique name under the %APPDATA% folder. This allows the virus to establish persistence. MachineGuid MD5 is used for the name generation, and the name can also be used as a Mutex as well as bot-id. As the last action of this step, the virus generates a registry key that points to the file it copied before to the specific folder inside the %APPDATA% folder;
- Then, depending on if the current user is privileged or not, the virus sets persistence either under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE or KEY_CURRENT_USER;
- Next, general system information is sent to the C&C server;
- For persistence, the keylogger then applies the triple-DES encryption technique to the URL and the registry key;
- After this, the virus starts waiting for commands from C&C, creating a new thread to detect the C&C response.
How to avoid infection by LokiBot virus?
Since LokiBot spyware requires macros to be activated to infect the system, attackers will do everything in their power to make the victim enable them. Thus keeping macros turned off is the best bet to stay protected from the trojan. Notably, extra caution should be exhibited when a document downloaded from a suspicious source or an unknown email address prompts to enable macros.
Also, having antivirus software from trusted developers and keeping it updated is an excellent way to decrease the probability of becoming the malware's victim and protecting credentials. Another good common practice is to be highly mindful when opening attachments or clicking links in emails from unidentified sources as it's a popular method of malware spreading, including FormBook and Dridex.
Distribution of LokiBot
LokiBot stealer is distributed mostly via mail-spam campaigns, prompting the user to download a malicious file that is attached. Remarkably, the three most commonly used types of files are Microsoft Office documents configured to begin the download and installation processes of the malware, archive files containing a Loki-Bot executable or ISO files, and a Loki-Bot executable.
LokiBot execution process
Interactive sandbox simulation conducted on the ANY.RUN malware hunting service allows us to take a closer look at how the execution process of LokiBot unfolds in a case when a contaminated Microsoft Office file is the infection source.
- The simulation starts with opening a Microsoft Office file. Immediately, WINWORD.EXE is executed with enable macros.
- Then, through the exploitation of the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability, Microsoft Office Equation Editor proceeds to download a malicious executable file;
- Finally, a malicious executable file runs itself and then proceeds to steal the personal data and connect to the C&C server.
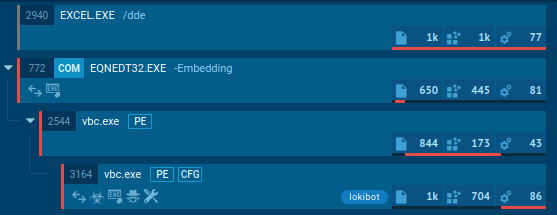 Figure 2: Illustrates the execution processes of LokiBot as shown by ANY.RUN simulation
Figure 2: Illustrates the execution processes of LokiBot as shown by ANY.RUN simulation
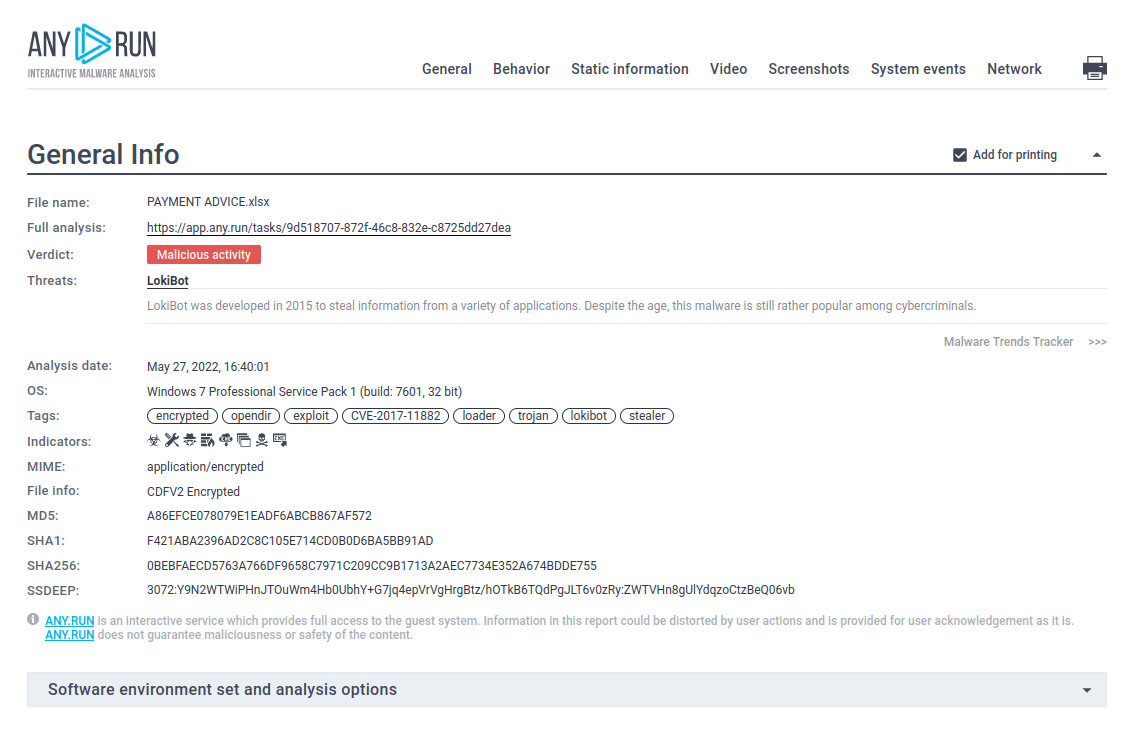 Figure 3: A text report created by ANY.RUN
Figure 3: A text report created by ANY.RUN
The virus generates multiple artifacts during its execution process. Particularly, four types of files can be simultaneously stored in the secret %APPDATA% directory at any point in time. Those files can have ".exe," ".lck," ".hdb" or ".kdb." extensions, and each file type is used for a specific purpose:
- .exe files contain an executable copy of the trojan that triggers when a user logs into an account,
- .lck files are generated to prevent resource conflicts when either Windows Credentials or Keylogging are decrypted,
- .hdb files are used to store the hashes of all data samples already transmitted to the C&C server
- .kdb files are in turn used to hold information about the data that is yet to be sent to the server
Based on the analysis, the keylogger uses the following algorithm to name the files:
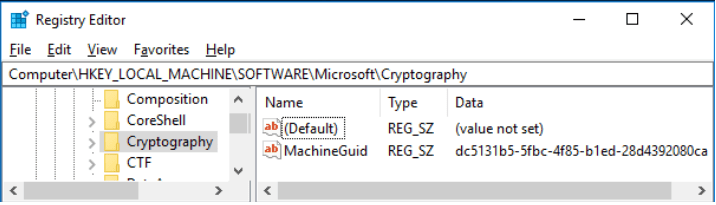
- First, LokiBot takes the value of MachineGuid from the registry branch HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SOFTWARE \ Microsoft \ Cryptography . In the case of our simulation, it was set to dc5131b5-5fbc-4f85-b1ed-28d4392080ca.
- Then, the virus uses the MD5 algorithm to calculate the hash sum of the MachineGuid, which in our case ended up being c83ba0aa282a966263dda560052b3caf.

- Finally, characters from the 8th to the 13th of the resulting hash amount are used as the subdirectory's name, and the characters from the 13th to the 18th are used as the name of the files.

LokiBot communication with C&C
To communicate with the C&C server, the patched version of the virus, which is also the most widely spread strain, sends a "ckav.ru" string. Interestingly, the sent data is also is a substring of "fuckav.ru."
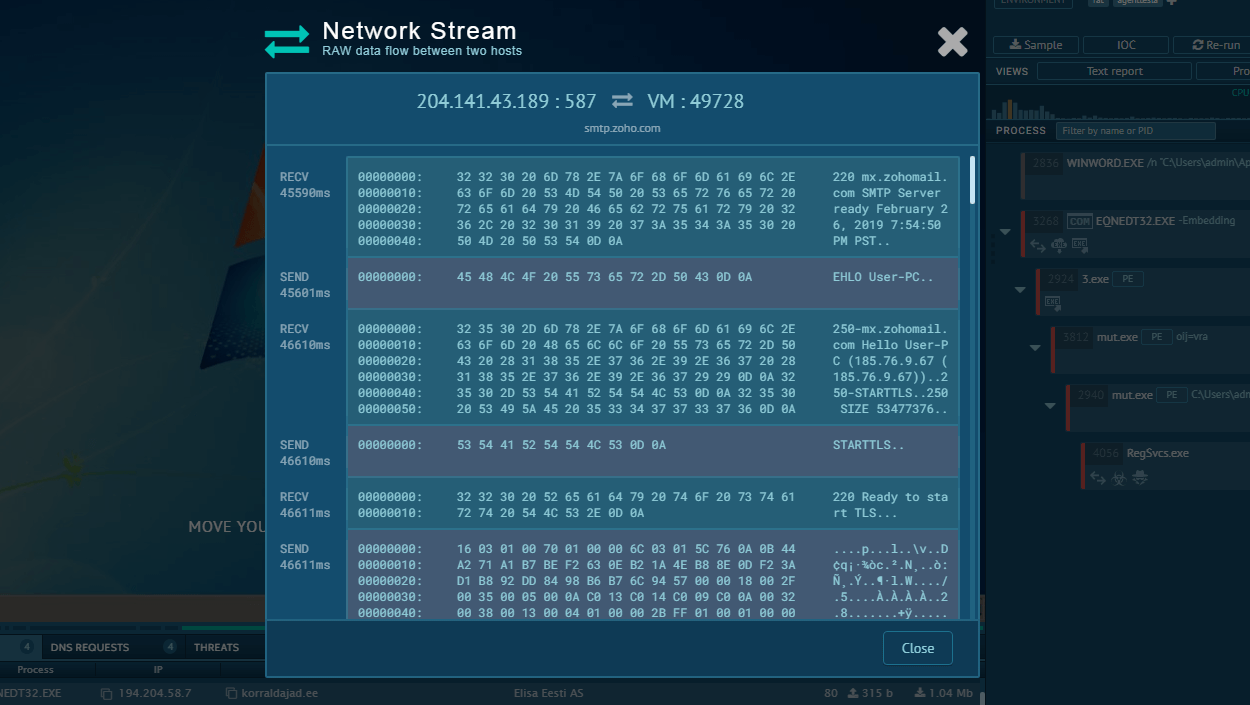
How to detect LokiBot malware using ANY.RUN?
Among other things, you can detect whether it is LokiBot in front of you or not by looking inside sending packets - there's always text "ckav.ru" inside them. Just click on the sent packet in the "HTTP REQUESTS" tab and take a look inside a packet.
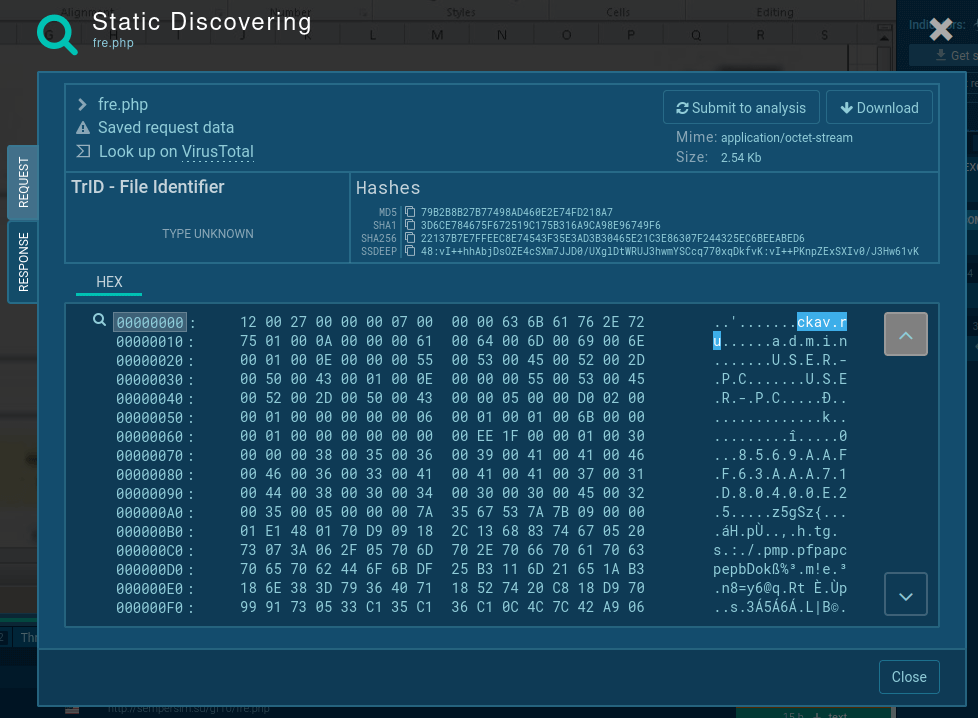 Figure 4: Lokibot network stream
Figure 4: Lokibot network stream
Conclusion
Lastly, since the first version of the malware was leaked and cloned, eventually becoming available for a significantly lower price than the original, LokiBot spyware became a widely spread malware that continues to appear in several mail-spam campaigns. In fact, the virus has become so popular that its set-up explanation videos on stealing credentials are publically available on YouTube.
Fortunately, modern malware hunting tools like ANY.RUN provides the ability to examine the malware behavior in detail and establish solid protection against the hazard.



 0
0