Less than a month after its launch, DeepSeek has already shaken up the industry, caused NVidia’s stock to shed $600 billion, and sparked political controversy.
Now, the AI company is dealing with the consequences of major cyber attacks. As of February 5, DeepSeek is still having trouble letting new users join.
Let’s review the entire timeline of the attacks and take a closer look at the two botnets, HailBot and RapperBot, responsible for the latest disruptions, using ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox.
What is DeepSeek
DeepSeek is an Artificial Intelligence company based in China and founded in late 2023. On January 20, 2025, it launched its first DeepSeek-R1 model, which instantly gained millions of app downloads worldwide.
The success of the release came down to several factors:
- DeepSeek achieved AI model performance comparable to OpenAI’s (the company behind ChatGPT) for under $6 million.
- DeepSeek uses less-advanced chips, making its AI operations up to 50 times cheaper than competitors.
- DeepSeek’s AI is open source.
Cyber Attacks on DeepSeek: Timeline
January 27
DeepSeek paused new user registrations, citing “large-scale malicious attacks” on its infrastructure.
January 28
Wiz.io reported discovering a leaked ClickHouse database linked to DeepSeek, which contained users’ chat histories and API keys. This leak was likely unrelated to the cyber attacks mentioned by DeepSeek.
January 29
Global Times revealed that DeepSeek had been facing regular distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks since early January, involving reflection amplification techniques.
Starting January 22, HTTP proxy attacks began, gradually increasing in frequency and peaking on January 28. These were further accompanied by brute-force attack attempts, which allegedly originated from IP addresses in the United States.
January 30
Based on a report by XLab, Global Times disclosed that the latest wave of attacks on DeepSeek involved two botnets, HailBot and RapperBot, both variants of the infamous Mirai botnet.
The attacks launched early on January 30 used 16 command-and-control (C2) servers and over 100 C2 ports.
Why Businesses Must Pay Attention
The cyber attacks on DeepSeek highlight that businesses of all sizes and industries, especially those dependent on extensive digital infrastructure, can be vulnerable to such threats. With botnets like HailBot and RapperBot available as a service, attackers can launch cyber assaults without needing advanced technical skills.
For companies that rely on AI services, the consequences can be even more severe, including service disruptions, data breaches, and loss of customer trust. As AI becomes more integral to business operations, it is crucial for companies to invest in robust cybersecurity measures.
How HailBot and RapperBot Botnets Work
HailBot
HailBot, named after the string “hail china mainland,” is known for its DDoS attack capabilities. This variant of Mirai exploits vulnerabilities such as CVE-2017-17215, which affects certain Huawei devices.
HailBot can compromise a wide range of devices and use them to launch distributed denial-of-service attacks.
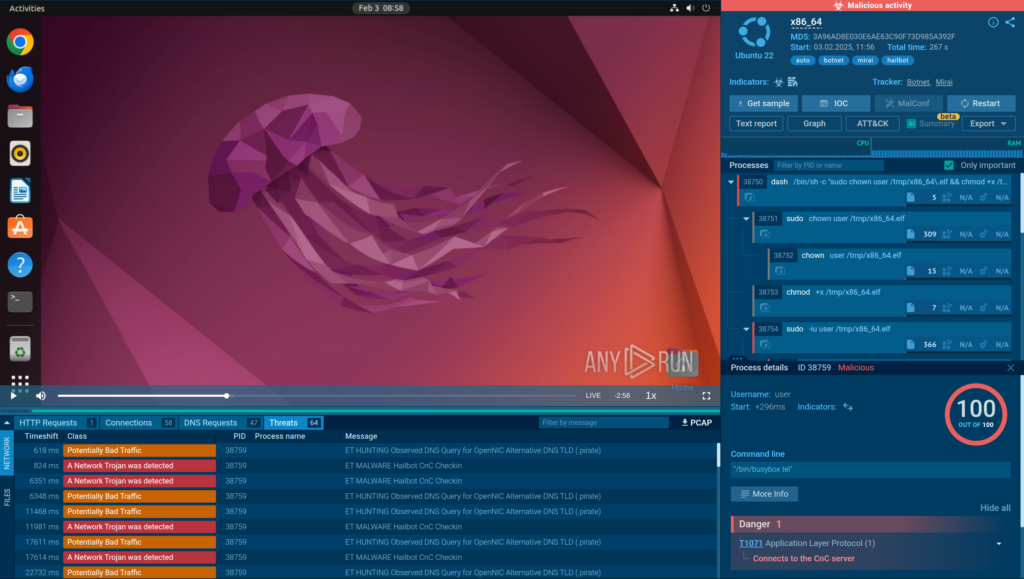
By uploading a sample of HailBot to ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, we can get a detailed view of how it operates.
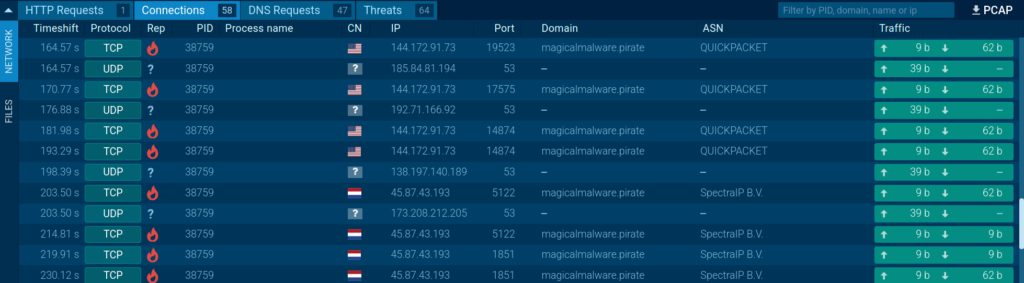
The network traffic shows how the malware connects to its C2 server.
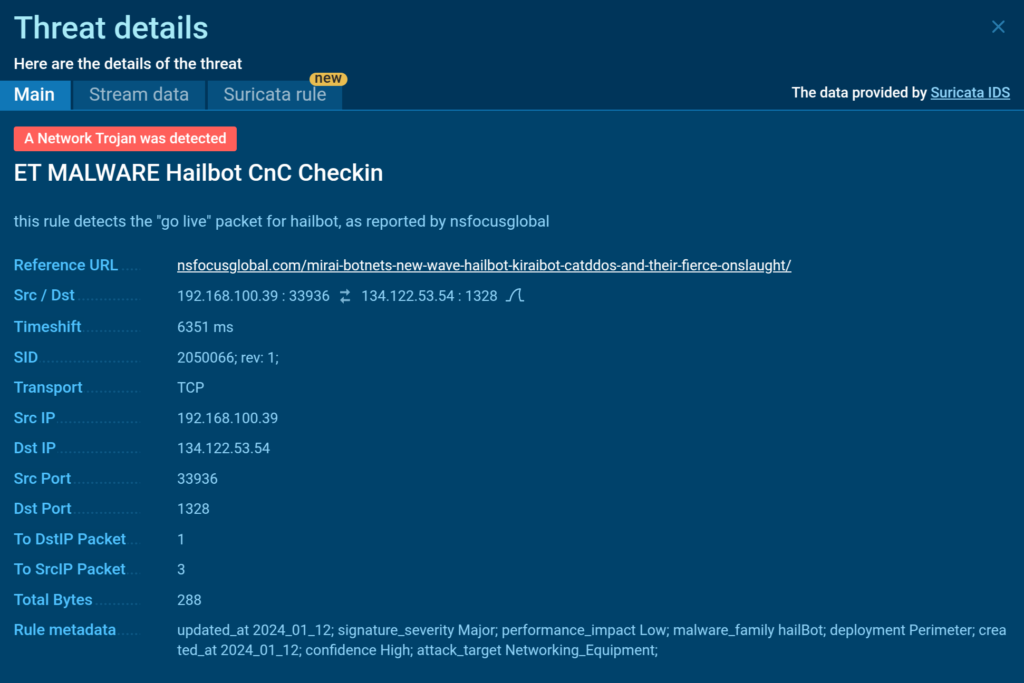
Suricata IDS instantly identifies HailBot’s connection and notifies the user about its activities.
RapperBot
RapperBot primarily spreads through SSH brute-force attacks. It is identified by the string “SSH-2.0-HELLOWORLD” and reports valid credentials back to its command and control (C2) server. Once RapperBot compromises a device, it performs several malicious actions:
- Replaces the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file with its own public key, ensuring persistent access to the compromised device.
- Creates a superuser account called “suhelper” by editing the /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow files.
- Continually scans for more targets using updated credential lists provided by its C2 server.
RapperBot also includes cryptojacking capabilities through the XMRig Monero miner, allowing it to mine cryptocurrency on compromised devices.
After we upload RapperBot’s sample to the sandbox, we can see how it generates significant network traffic.
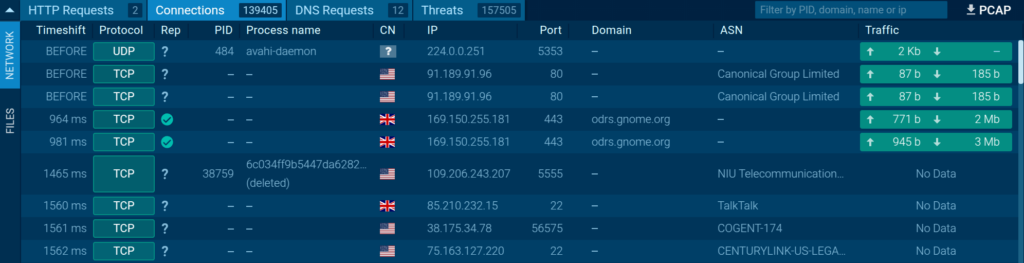
In less than three minutes, nearly 140,000 attempts to establish network connections were recorded.
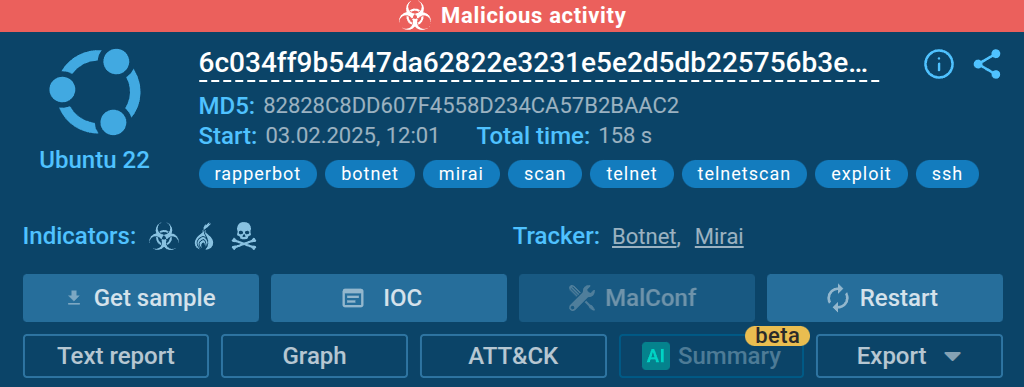
This high volume of traffic makes these botnets easily detectable in ANY.RUN’s sandbox environment.

Learn to analyze cyber threats
See a detailed guide to using ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox for malware and phishing analysis
Conclusion
The cyberattack on DeepSeek underscores the ongoing threat posed by sophisticated botnets like HailBot and RapperBot. As cybersecurity experts continue to analyze the incident, it is crucial for organizations to remain vigilant and proactive in their defense strategies.
ANY.RUN’s detection capabilities have proven effective in identifying these threats, and we will continue to monitor and report on such incidents.
About ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN helps more than 500,000 cybersecurity professionals worldwide. Our interactive sandbox simplifies malware analysis of threats that target both Windows and Linux systems. Our threat intelligence products, TI Lookup, YARA Search, and Feeds, help you find IOCs or files to learn more about the threats and respond to incidents faster.







0 comments