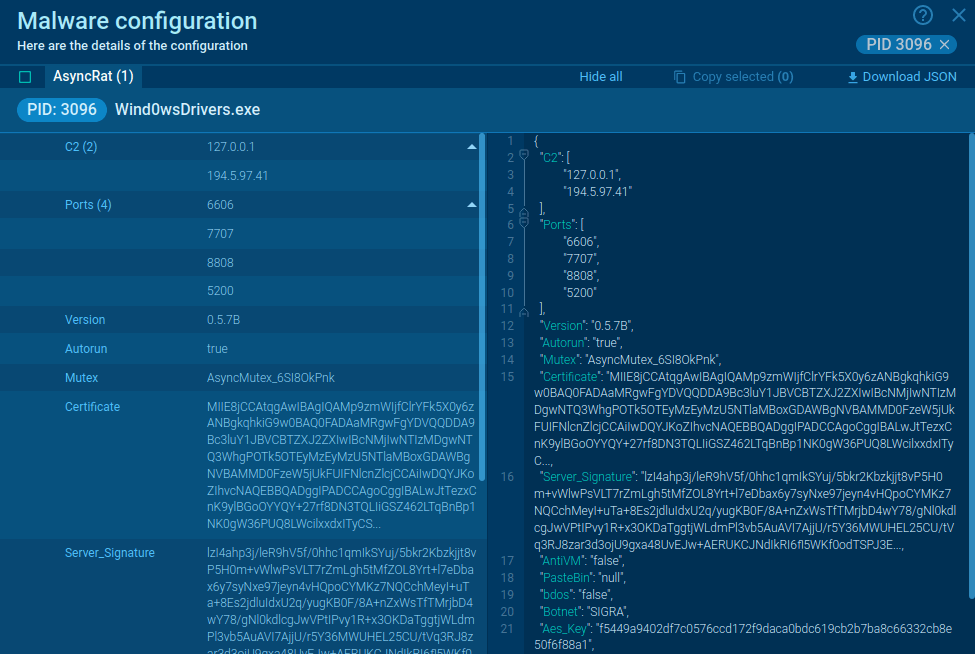
What is LimeRAT malware and cryptocurrency stealer?
Lime Remote Administration Tool (LimeRAT) is a versatile Remote Access Trojan, which also may function as ransomware, cryptominer, cryptocurrency stealer, worm, keylogger, and bot. This versatility is one of the traits that set it apart from other RATs, such as njRAT.
Similarly to Quasar RAT, LimeRAT’s code is written in C#, but is dependent on .NET 4.0, and is a part of an open-source malware library that includes Lime_Miner, Lime_Crypter, and Lime_USB. While it claims to be an educational tool for .NET malware, its robust and well-documented features make it an attractive choice for malicious activities.
Lime RAT uses multiple ports for communication, allowing for redundancy in communication channels. The initial setup only requires port numbers and an AES 128-bit encryption key for secure communication between the client and server. The payloads can be created with a simple interface of checkboxes and text input fields, allowing even inexperienced operators to produce potent, malicious binaries. Customizations include different features and icons, and settings for Command and Control infrastructure and the location for persistent drop files on targeted machines.
Once a payload has been sent to and executed on a target machine, it connects to the control panel, sending details about the system it's on, including OS, CPU, user, and more.
The panel can also automatically assign tasks, such as downloading and executing specific files. The operator can issue commands to the infected machine, initiating various attacks, including encryption for ransomware, mining Monero, enabling Remote Desktop Protocol, or stealing information.
The malware can spread like a worm through USB or pinned task bar applications. Its ransomware feature encrypts the targeted host, changing file extensions to '.Lime'. It also includes a rudimentary keylogging feature, logging only keyboard inputs, not auto-filled or clipboard data.
The screengrab feature within the control panel captures screenshots of the infected machine, while its logging feature records timestamps and IPs of connections and disconnections. Despite being an open-source, well-documented malware, Lime RAT poses a serious threat, capable of stealing a range of valuable information, encrypting data for ransom, and converting the target host into a bot.
LimeRAT malware technical details
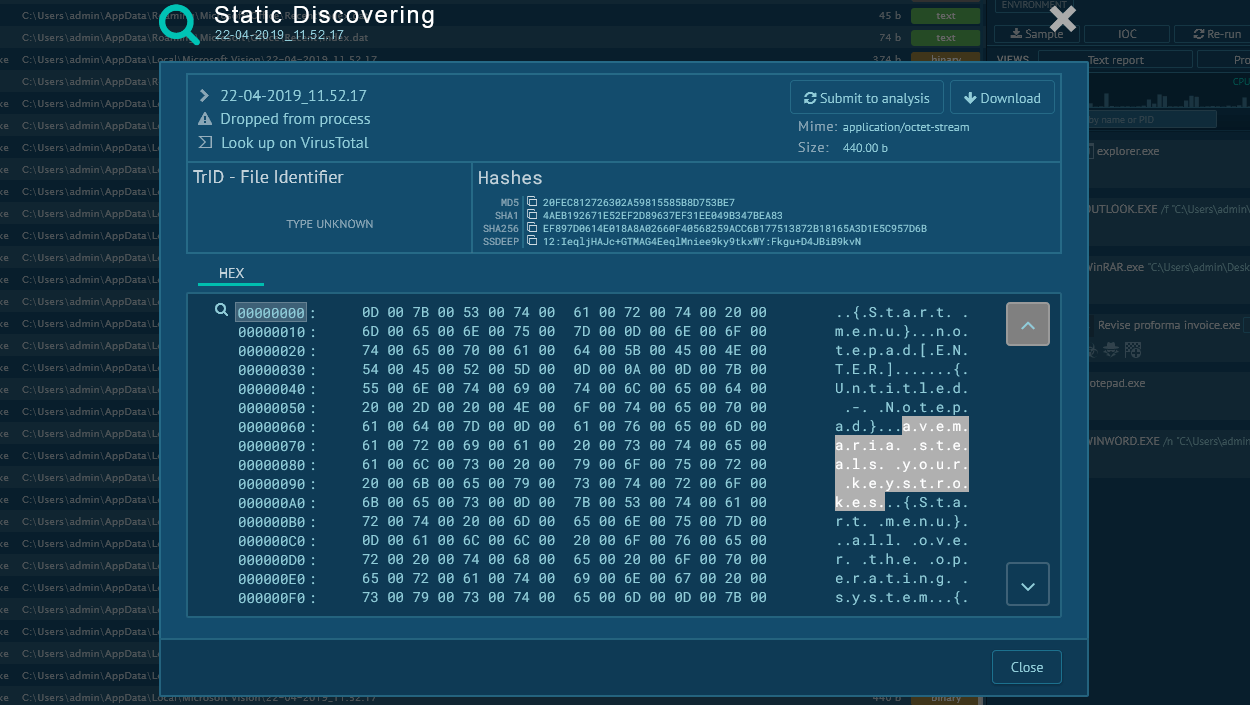
LimeRAT employs advanced obfuscation techniques (MITRE T1027), rendering the classes, methods, and variables in its code into a series of random glyphs. This complex obfuscation aids in evasion of static analysis.
Embedded within LimeRAT's configuration class is a Base64 encoded string. This string isn't just encoded but also encrypted, demonstrating the malware's sophisticated design. Deciphering the string involves a comprehensive understanding of LimeRAT's decryption algorithm.
The decryption mechanism is built upon the RijndaelManaged class — an implementation of the AES encryption algorithm — and the MD5CryptoServiceProvider class. To generate the AES key for decryption, LimeRAT uses the MD5 hash of a particular string from the configuration class. This MD5 hash undergoes a sequence of specific byte manipulations. Post-decryption, the original string is revealed, decoded using the Base64 algorithm, and then decrypted with the AES256-ECB algorithm.
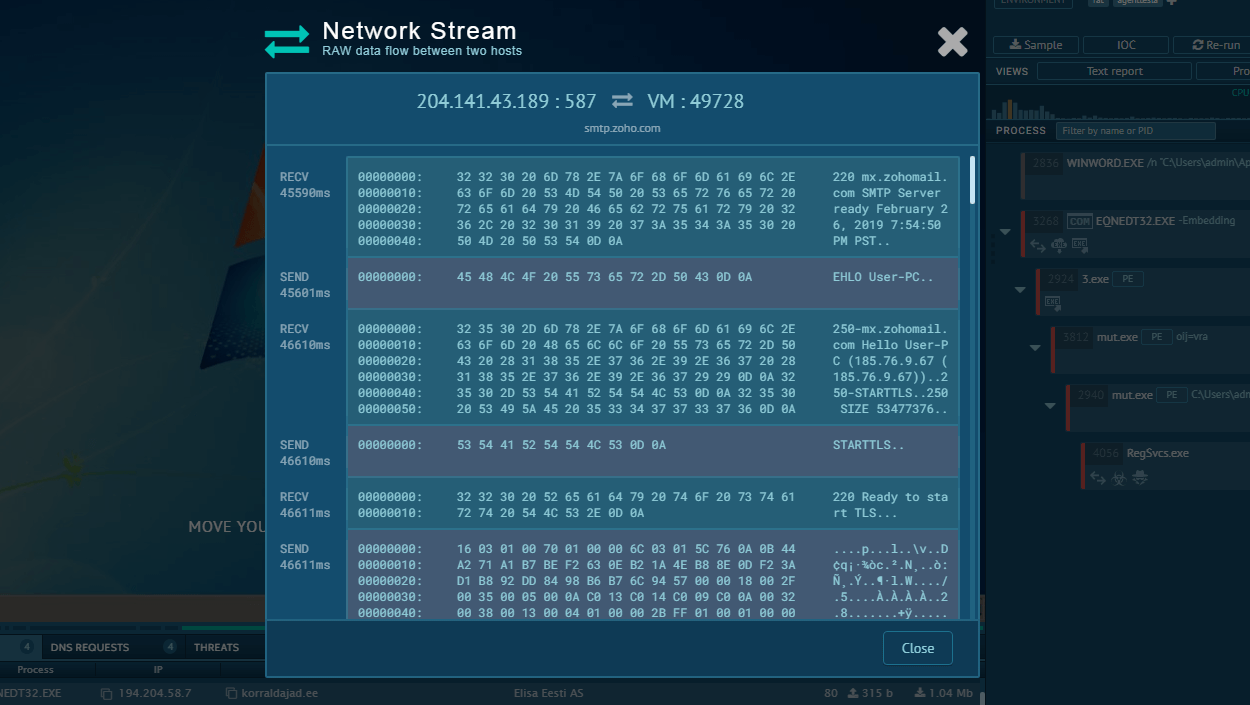
The decrypted string exposes a critical piece of information: a link to a PasteBin note. This link is essentially the C2 address for LimeRAT, serving as a communication channel for the malware to receive commands and exfiltrate data. It's a clear example of the malware's robust concealment tactics, specifically its effective use of encrypted strings to veil C2 communications.
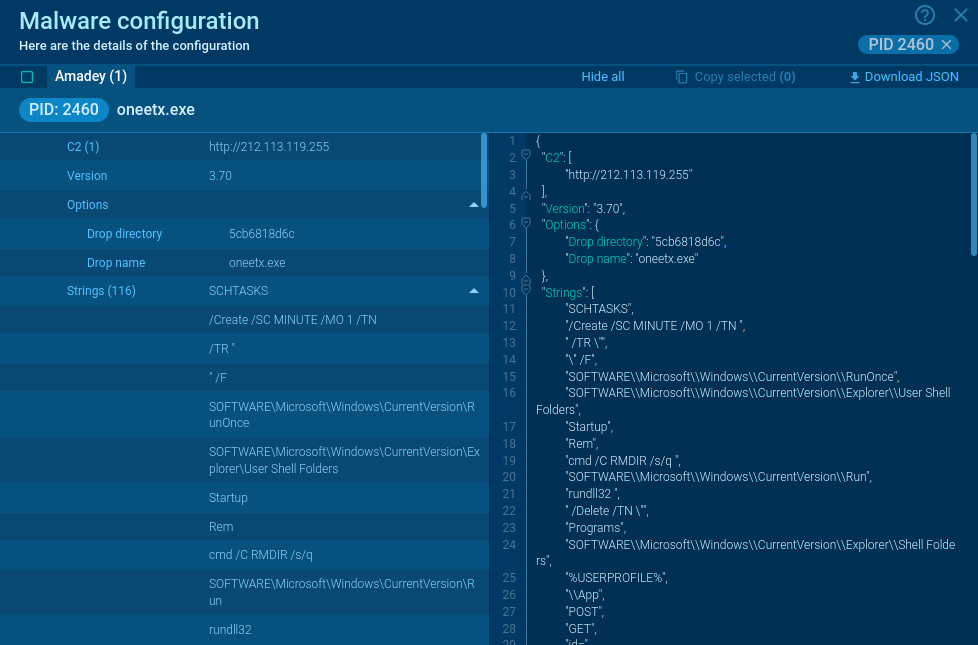
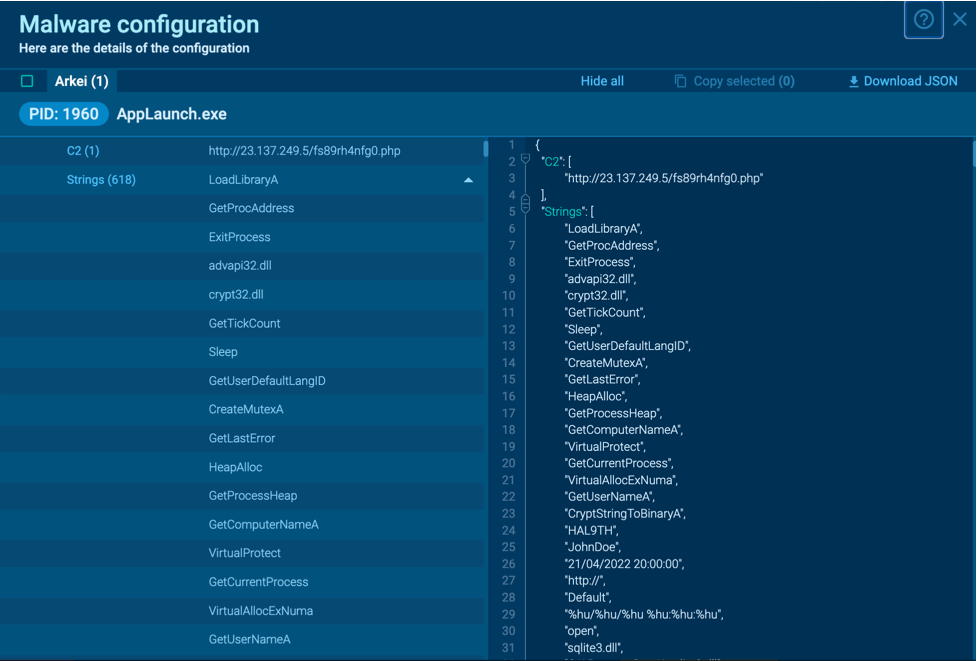
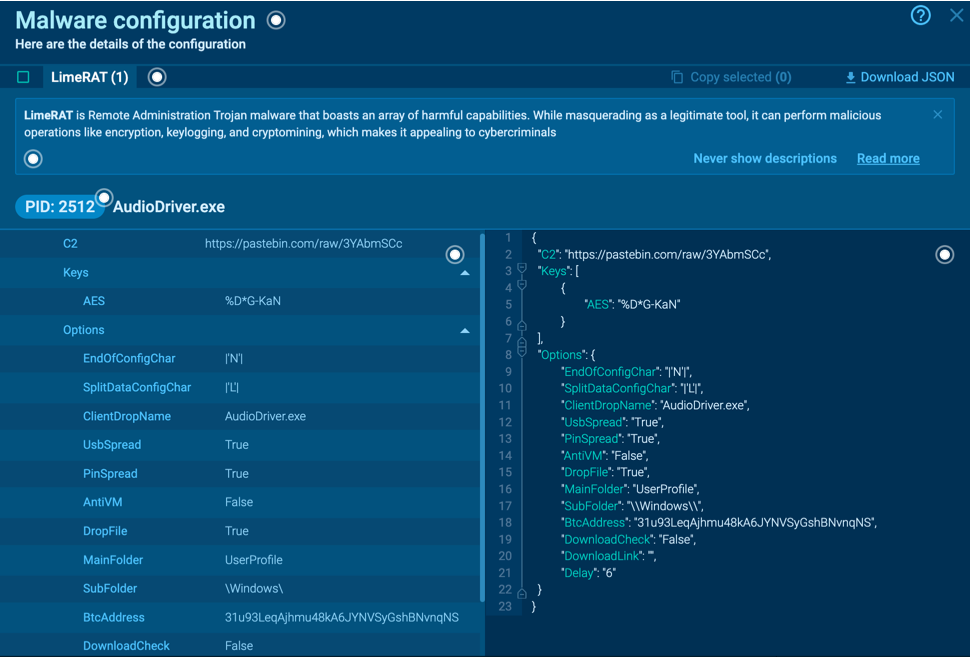 LimeRAT’s malware configurations
LimeRAT’s malware configurations
LimeRAT malware execution process explained
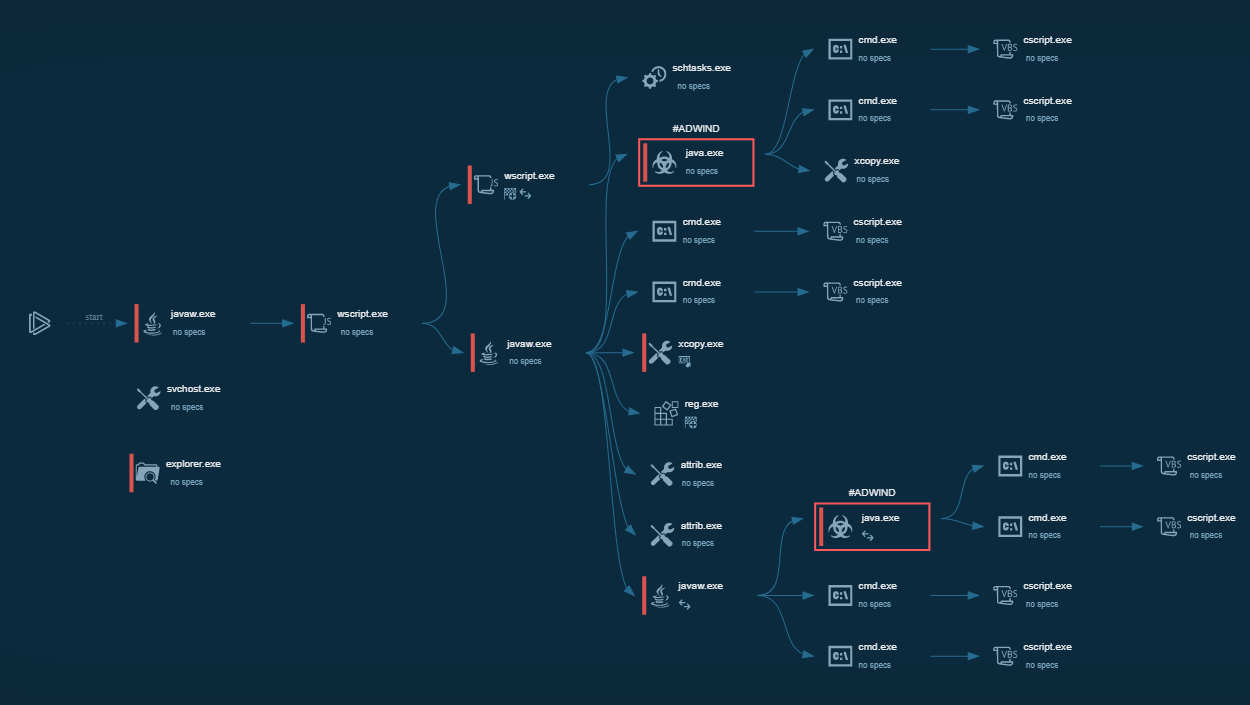
Typical execution flow of the LimeRAT is straight. After the initial access is made, the trojan starts its execution. Firstly, it copies itself into a user directory such as %appdata% or, in our sample, into the directory inside the admin folder. Then it runs with different filenames and starts malicious activity. Further execution flow may vary. In our sample, the C2 server is already dead and doesn't send anything back to malware. When C2 is alive, LimeRAT may download some additional modules based on the commands from C2.
Read a detailed analysis of LimeRAT in our blog.
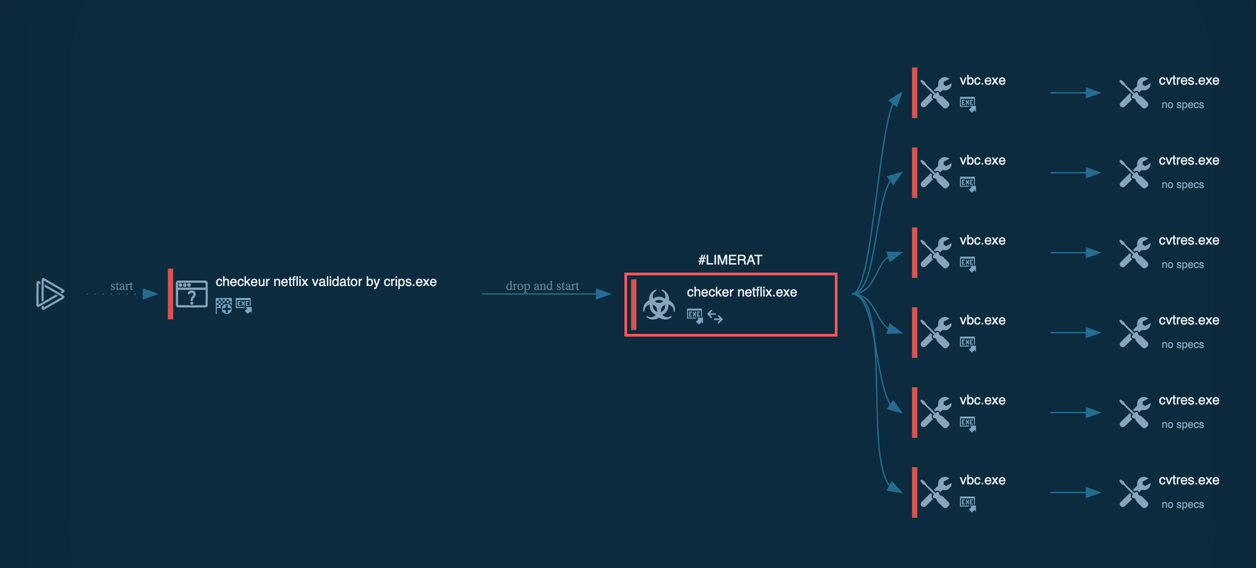 LimeRAT’s process graph
LimeRAT’s process graph
LimeRAT malware distribution methods
LimeRAT primarily propagates through phishing campaigns. It leverages malicious email attachments, often employing embedded macros within Office documents. Upon the execution of these macros, the payload of LimeRAT is released, initiating the infection process. Cracked software, P2P distribution channels and malvertising has also been observed.
Additionally, LimeRAT exploits drive-by downloads. It's designed to take advantage of software vulnerabilities, in both web browsers and installed applications. This can lead to the unintended downloading and installation of LimeRAT merely by visiting a compromised website.
The developers of LimeRAT are persistent in updating its exploits, which maintains its effectiveness against even the latest software patches and updates.
Notably, LimeRAT also employs worm-like behavior for spreading via removable drives. The malware is programmed to replicate itself onto any connected removable drives from an already compromised system. This ability allows LimeRAT to further propagate when these infected drives are connected to other systems.
LimeRAT malware conclusion
LimeRAT's wide range of capabilities, coupled with its lightweight footprint, advanced obfuscation and AES encryption, make it a powerful adversary. While its ability to hide its C2 communication behind encrypted strings shows off the sophisticated tactics adopted by modern malware.
The most effective way to mitigate malware threats like LimeRAT, which are typically spread through phishing, is by educating your team about the potential dangers of malicious emails. For a detailed understanding of how LimeRAT operates, it's recommended to examine its samples using a robust tool like ANY.RUN.
ANY.RUN doesn't just detect and identify this malware family, but it also simplifies the analysis of its execution process. This is particularly useful given that LimeRAT is known for its heavy use of obfuscation, which can make static analysis difficult. With ANY.RUN, the dynamic analysis of this malware becomes a more approachable task.




 0
0